Revolutionizing the Future of Transportation: A Comprehensive Analysis of AC vs DC Electric Car Batteries
Electric cars are the future of transportation, and their popularity is soaring with each passing year. One of the most critical components of electric cars is their batteries. Every electric car needs a battery to power its motor, and this battery determines the car’s range and performance.
While there are many types of electric car batteries available on the market, one of the most critical decisions car manufacturers face is whether to use AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current) batteries. In this blog, we’ll explore the pros and cons of each type and help you understand which battery may be the best fit for your electric car.
Understanding the Basics
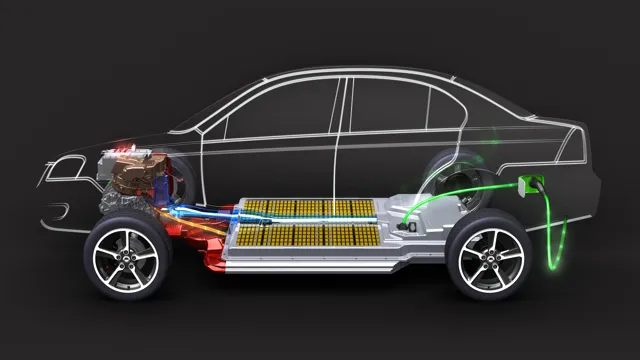
When it comes to electric car batteries, the power source for the motor, the question often arises – AC or DC? The truth is, it’s more complicated than a simple choice between the two. Most electric cars use DC (direct current) batteries as they are more efficient at storing and delivering power to the motor. However, the electricity sourced from the charging infrastructure is typically AC (alternating current).
Therefore, the battery management system within the car converts the incoming AC power into DC power, allowing the battery to be charged. The conversion process can vary, with some electric vehicles using an onboard charger to convert the power and others using external charging stations. Ultimately, it’s not about choosing between AC or DC, but more so about understanding how the battery management system works to ensure your electric car is performing at its best.
Difference between AC and DC
When it comes to electricity, there are two basic types – AC and DC. But what are the differences between these two kinds of electric currents? Let’s break it down: AC stands for “alternating current,” which means the flow of electricity is constantly changing direction. This is commonly used for powering appliances and devices in homes and businesses because it is easier to transmit over long distances.
DC, on the other hand, stands for “direct current,” which means the flow of electricity goes in one direction. This type of current is often used for smaller devices like batteries and circuitry, as it is more reliable and doesn’t have the same level of energy loss that AC does. So, in simple terms, the main difference between AC and DC is the way electricity flows – AC is constantly changing direction, while DC flows in one direction.
In the end, which one you use will depend on what you need to power and how far you need to transmit energy.

How Electric Cars Use Batteries
Electric cars run on rechargeable batteries, and understanding how these batteries work is key to understanding how electric cars operate. The batteries inside an electric car are similar to those found in a smartphone or laptop, but they are much bigger and more powerful. Most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, which store energy in a chemical reaction that takes place between the anode and cathode.
When the battery is charged, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, and when it is discharged, the process is reversed. This movement of ions generates a flow of electrons, which can be used to power the electric motors. The batteries are typically located under the floor of the car to help keep it balanced and stable.
Although electric cars have limited range compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles, advancements in battery technology are continually improving, and electric cars are becoming more practical for everyday use.
Pros and Cons of AC and DC Batteries
When it comes to electric car batteries, there are two main types: AC and DC. AC batteries are known for their efficiency and low cost, as they require fewer cells to produce the same amount of power as DC batteries. However, they do have some downsides.
For one, they are not as powerful, so they may not be suitable for larger vehicles. They also don’t have the same level of energy density as DC batteries, meaning they may not be able to store as much energy in the same amount of space. On the other hand, DC batteries are known for their high power and energy density, making them ideal for larger vehicles or those that require more power.
However, they are also more expensive and may not be as efficient as AC batteries. Ultimately, the choice between AC and DC batteries will depend on the specific needs of the vehicle and its intended use.
Advantages of AC Batteries
AC batteries have become increasingly popular and are considered to have several advantages over DC batteries. One of the main benefits of AC batteries is that they are more efficient and can store energy more effectively. This is because AC batteries are able to convert the energy from solar panels or wind turbines into usable electricity more efficiently than DC batteries.
Additionally, AC batteries are generally cheaper and easier to install than DC batteries. They also have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance. However, one drawback of AC batteries is that they require an inverter to convert the electricity from AC to DC, which can be an additional expense and require extra installation time.
Overall, AC batteries are a great choice for anyone looking to invest in energy storage and reduce their dependence on traditional grid power.
Disadvantages of AC Batteries
When it comes to choosing between AC and DC batteries, there are pros and cons for each. AC batteries, for instance, have the disadvantage of being less efficient than DC batteries. This is because the AC power needs to be converted into DC power to be stored in the battery, which results in energy loss.
AC batteries are also typically heavier and more expensive than DC batteries. However, one advantage of AC batteries is that they can handle a wider range of input voltages, which can be helpful in situations where the voltage of the power source fluctuates. Ultimately, it’s important to consider your specific needs and use case when deciding between AC and DC batteries.
Advantages of DC Batteries
DC batteries offer numerous advantages over their AC counterparts, making them a popular choice for those seeking a reliable power source. One key benefit of DC batteries is that they are less prone to power loss and voltage drop, ensuring more consistent and efficient performance over time. Additionally, DC batteries are typically more affordable and easier to install than AC batteries, making them a practical option for those on a budget or with limited DIY experience.
However, there are some drawbacks to consider as well, such as limited compatibility with certain devices and the need for a separate AC/DC converter for appliances that require AC power. Overall, while both AC and DC batteries have their pros and cons, the decision ultimately comes down to personal preferences and individual use cases.
Disadvantages of DC Batteries
DC batteries have several disadvantages when compared to their AC counterparts. The first issue is that DC voltage drops over distance, which can lead to decreased performance or complete failure of the battery. Additionally, DC batteries have a limited lifespan due to chemical reactions that break down the electrodes over time.
This can result in reduced capacity and reduced output power. The maintenance cost of DC batteries is also higher, as they require periodic replacement and disposal of their chemical components. On the other hand, AC batteries do not suffer from voltage drop and have a longer lifespan due to their unique design, which allows them to resist chemical breakdown.
While AC batteries are typically more expensive than DC batteries, their reduced maintenance and longer lifespan make them a more cost-effective option in the long run.
Which One is Right for Your Car?
When it comes to electric car batteries, there’s often confusion around whether alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) is the better option. The truth is, it depends on your car and charging system. AC charging is generally slower, but it’s more widely available and can be used with standard wall outlets and public charging stations.
DC charging, on the other hand, is much faster, but requires special equipment and is typically only available at select charging stations. So if you’re looking for convenience and accessibility, AC is likely the way to go. But if you’re in a hurry and don’t mind seeking out specific charging options, DC could save you valuable time.
Ultimately, it’s important to consider your particular car and needs to determine which type of charging is right for you.
Consider Your Driving Habits
When trying to determine whether to go for synthetic or conventional motor oil, consider your driving habits. For those who drive in extreme conditions, such as in cold weather or on dusty roads, synthetic oil might be the better option. Synthetic oil flows easier at low temperatures, providing better protection against wear and tear.
It is also engineered to resist breakdown in high temperatures. On the other hand, if you have a low-mileage car or only drive occasionally, conventional oil might fit your needs. It costs less and can still offer adequate protection for your engine.
Ultimately, your owner’s manual will offer the best guidance on oil requirements, but considering your driving habits can help you make an informed decision on which type of oil is right for your car.
Check Your Car’s Compatibility
Before purchasing any car accessory, it’s important to check its compatibility with your vehicle. Car accessories come in different sizes and shapes, and not all of them will fit perfectly in your car. Before making a purchase, research the specifications and dimensions of the accessory, and cross-check with your car’s make and model.
This will ensure that you don’t waste your money on an accessory that won’t fit or worse yet, might harm your car. Some car accessories also require additional hardware or modifications to your car’s existing setup. This is where checking compatibility becomes even more important.
For example, not all car stereos will fit perfectly in all cars, so it’s important to check if any additional hardware or modifications are needed before making a purchase. By doing your research and checking compatibility, you can save yourself a lot of time, money, and headaches in the long run. So, the next time you’re looking to purchase a car accessory, don’t forget to check your car’s compatibility first!
Conclusion: Choose the Right Battery for Your Electric Car
In conclusion, when it comes to electric car batteries, the debate of AC versus DC is not just about the type of current being used. It represents a larger discussion around innovation, sustainability, and the future of transportation. While both AC and DC have their advantages and disadvantages, it’s ultimately up to the auto industry and consumers to determine which technology will power the next generation of electric vehicles.
So let’s charge ahead and embrace the electrifying possibilities of the future!”
FAQs
What is the difference between AC and DC electric car batteries?
AC and DC batteries refer to the type of current flow in the battery. AC batteries can switch between alternating current and direct current, while DC batteries only provide direct current. In electric cars, DC batteries are generally used for their efficiency and simplicity.
How long do electric car batteries last before needing to be replaced?
This can vary depending on the brand and model of the car, as well as how often it is used. However, most electric car batteries are designed to last at least 8 years or 100,000 miles before needing to be replaced.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, electric car batteries can be recycled. In fact, recycling the lithium-ion batteries used in electric cars can help reduce the environmental impact of the production and disposal of these batteries.
How does the temperature affect the performance of electric car batteries?
Extreme temperatures, either hot or cold, can affect the performance of electric car batteries. Cold temperatures can reduce the battery’s range, and hot temperatures can reduce the battery’s lifespan. Harvesting the heat generated from batteries can improve temperature control and range.