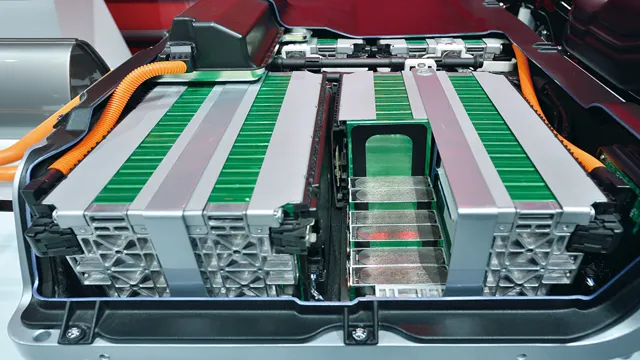
The Ultimate Guide to the Components of an Electric Car Battery: From Lithium-Ion Cells to Power Management Systems
Electric vehicles have been slowly making their way into the mainstream in recent years, and have certainly been gaining popularity among environmentally-conscious individuals. But what makes these vehicles tick? At the heart of an electric car is the battery, which was a major source of concern among consumers when the technology was first introduced. Today, however, electric cars have come a long way, and their batteries have vastly improved.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at what makes up an electric car battery, how it functions, and why it’s such a vital component of these innovative vehicles.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
If you’re wondering what electric car battery is made of, the answer is lithium-ion. Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular type of battery used in electric cars due to their high energy density, long lifespan and fast charging capabilities. Contrary to popular belief, a lithium-ion battery is not a single unit but rather a collection of smaller cells that are interconnected to form a larger battery pack.
Each cell contains three main components – a positive electrode, a negative electrode and an electrolyte – which produce charges that move from the positive side to the negative side, creating the electrical power necessary to power an electric car. Though lithium-ion batteries are incredible energy sources, they do have some downsides such as the potential for overheating and explosion, which is why proper care and maintenance is crucial in their usage.
Composition of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-Ion Batteries Lithium-Ion batteries are the powerhouses behind most of our modern-day gadgets like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. These rechargeable batteries consist of multiple cells that work together to store and release energy. Each cell comprises a cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator.
The cathode is the positive electrode that houses lithium ions, while the anode is the negative electrode that releases these ions during discharge. The electrolyte serves as a conductor, facilitating the movement of ions between the cathode and anode. Finally, the separator prevents the electrodes from touching and causing a short circuit.
The composition of these components and their arrangement determine the type and quality of the battery. For instance, most electric vehicles use large Lithium-Ion batteries that combine thousands of cells, whereas smartphones use smaller ones. Lithium-Ion batteries are not only powerful but also highly efficient, making them an ideal choice for many applications.

Function of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are rapidly becoming ubiquitous in our modern lives. These batteries offer the high energy density and low maintenance required for use in countless devices, including electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops, and more. The secret to these batteries’ success lies in their use of lithium ions to conduct electricity.
These ions travel between the two electrodes in the battery, creating a flow of electricity. Lithium-ion batteries can hold a charge for a long time while remaining lightweight, making them an ideal choice for devices that need to be portable. Additionally, these batteries are rechargeable, so they can be used repeatedly, reducing waste and saving money in the long term.
As a sustainable energy source, lithium-ion batteries are slowly but surely changing the way we power our devices and vehicles, making our lives cleaner, safer, and more efficient.
Nickle-Cadmium Batteries
If you’re curious about what an electric car battery is made of, you might be surprised to learn that it’s usually made up of a series of nickel-cadmium batteries. These batteries, also known as NiCad batteries, have been popular in various applications since the 1950s. NiCad batteries are known for their high energy density and long life cycles, which make them ideal for electric cars.
One of the primary benefits of using NiCad batteries in electric vehicles is that they can be recharged quickly, which means that drivers can spend less time waiting for their cars to charge and more time on the road. Additionally, NiCad batteries are relatively inexpensive, making them a more affordable option for electric car manufacturers. While there are other battery technologies available for electric vehicles, nickel-cadmium batteries remain a popular choice due to their performance and cost-effectiveness.
Composition of Nickle-Cadmium Batteries
When it comes to rechargeable batteries, nickle-cadmium, or Ni-Cd batteries, have been a popular choice for many years. The composition of these batteries includes a positive electrode made of nickel oxide hydroxide and a negative electrode made of cadmium. These electrodes are separated by an electrolyte, typically made of potassium hydroxide, which allows for the flow of electrons between the two electrodes.
The casing of the battery is made of nickel-plated steel. Ni-Cd batteries are known for their long life and ability to handle high discharge rates. However, they are also known for their relatively low energy density and the presence of toxic materials, which can pose a risk if the batteries are disposed of improperly.
Despite these downsides, Ni-Cd batteries remain a popular choice for applications such as cordless power tools, emergency lighting, and backup power systems.
Function of Nickle-Cadmium Batteries
Nickle-Cadmium (NiCad) batteries, also known as rechargeable batteries, are widely used in electronic devices due to their durability and long lifespan. These batteries are made up of a positive electrode made of nickel oxide hydroxide, a negative electrode made of cadmium metal, and an electrolyte solution made of potassium hydroxide. The function of a NiCad battery is based on the transfer of electrons between the positive and negative electrodes, allowing for the storage and release of energy.
As electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge, the battery’s voltage decreases, and the battery becomes less efficient. To recharge the battery, an external electrical source is used to reverse the flow of electrons, thereby restoring the battery’s voltage and energy capacity. NiCad batteries are widely used in portable electronics, power tools, and medical devices due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and handle high discharge rates.
With proper care and maintenance, NiCad batteries can provide years of reliable service.
Solid State Batteries
An electric car battery is made up of different components, but one crucial piece is the battery technology used to store and release energy. In recent years, researchers have been exploring the potential of solid-state batteries as a safer and more efficient alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. Unlike their liquid electrolyte counterparts, solid-state batteries use a solid material to transfer ions between electrodes, resulting in a higher energy density and better performance.
Solid-state batteries also have the potential to reduce the risk of overheating and fire hazards that come with traditional batteries. While still in the development stage, solid-state batteries could revolutionize the electric car industry by improving range, reducing charging times, and making electric vehicles safer for consumers. As advancements continue to be made in battery technology, it’s exciting to consider the future of electric cars and the role solid-state batteries could play in powering the vehicles of tomorrow.
Composition of Solid State Batteries
Solid state batteries are an exciting new technology that promises to revolutionize the way we power our devices. Unlike traditional batteries, which use liquid or gel electrolytes to carry charge, solid state batteries utilize a solid electrolyte. This not only makes them safer and more stable, but also allows for much higher energy densities, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller space.
The composition of solid state batteries varies depending on the specific type, but they generally consist of a solid lithium electrolyte, a positive electrode made of a lithium metal oxide, and a negative electrode made of a lithium metal or lithium alloy. These components are typically arranged in a layered structure, with the solid electrolyte sandwiched between the positive and negative electrodes. One of the most promising aspects of solid state batteries is their potential to replace the traditional lithium-ion batteries used in everything from smartphones to electric cars.
This is because solid state batteries are denser, meaning they can deliver more power and energy. Additionally, they are less prone to overheating or catching fire, which has been a major concern with lithium-ion batteries. Overall, the composition of solid state batteries is still being researched and developed, but it is clear that they offer significant advantages over traditional battery technologies.
With ongoing advancements, it is likely that we will see solid state batteries become even more common in the years to come, transforming the way we power our devices.
Function of Solid State Batteries
Solid state batteries are an exciting new development in the world of battery technology. These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, which can greatly increase their energy density and overall efficiency. The main advantage of solid state batteries is that they are safer than traditional batteries.
Because they do not have a flammable liquid electrolyte, they are much less likely to catch fire or explode. This makes them ideal for use in electric cars, where safety is a major concern. Solid state batteries can also be smaller and lighter than traditional batteries, making them a good choice for portable electronic devices.
Overall, solid state batteries represent an important step forward in battery technology, and they have the potential to revolutionize many industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an electric car battery is not just a simple power source. It is a complex combination of advanced materials, including lithium-ion cells, nickel, cobalt, and manganese. It is a concoction of chemical wizardry that allows electric cars to navigate the roads quietly and efficiently.
So next time you see an electric car on the road, remember that behind its sleek exterior lies a battery pack that is a product of modern science and technological innovation.”
FAQs
What materials are typically used to make electric car batteries?
Electric car batteries are typically made with lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, or lead-acid materials.
Are electric car batteries as durable as traditional car batteries?
Yes, electric car batteries are designed to be just as durable as traditional car batteries, if not more so.
How long do electric car batteries typically last before needing to be replaced?
Electric car batteries can last anywhere from five to 15 years, depending on various factors such as use, maintenance, and climate.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, electric car batteries are recyclable and often have valuable materials such as lithium that can be reused. Many car manufacturers have their own recycling programs in place.