Revolutionizing Transportation: Unveiling the Incredible 1886 Electric Car Battery
In the world of electric vehicles, the battery remains the heart of the machine. Without it, there would be no power to drive the wheels and make the car move. But did you know that over a century ago, a revolutionary electric car battery was developed that could have changed the course of automotive history? Enter the 1886 Electric car battery, a remarkable invention that could have made electric cars the norm instead of gasoline-powered ones.
Powered by a lead-acid battery, the 1886 Electric car boasted a range of up to 50 miles on a single charge – an impressive feat for its time. Back then, however, gasoline cars were fast becoming the norm, and the electric car was seen as a novelty. Despite its potential, the 1886 Electric car simply could not compete with the power and convenience of gasoline cars.
Today, however, electric cars are making a comeback, and the 1886 Electric car battery has become the stuff of legend. It serves as a reminder of the potential that electric cars had even before cars became a ubiquitous presence on our roads. Today, modern electric car batteries are even more advanced, boasting ranges that far exceed those of the 1886 Electric car.
As we look towards a future where electric cars become the norm, it’s worth looking back at the humble beginnings of this remarkable technology. Who knows? Perhaps one day, we may see a revival of the 1886 Electric car battery – a battery that could power our cars without requiring a single drop of gasoline.
History
In 1886, an electric car battery was invented by Gaston Planté. This was a significant milestone in the history of electric vehicles, as it allowed them to become more practical and efficient. Planté’s battery was a rechargeable lead-acid battery that could power electric vehicles for long distances.
His innovation paved the way for further development of the electric car battery and helped to establish the electric vehicle industry we know today. However, it was not until the 20th century that electric vehicles really began to gain widespread popularity, largely due to advancements in battery technology. Today, electric cars are becoming more common as people turn towards environmentally friendly options for transportation.
Technologies such as lithium-ion batteries have improved the efficiency and range of electric vehicles, making them more practical for everyday use. The 1886 electric car battery was the beginning of an era of innovation and sustainability in the transportation industry, and we continue to see progress towards a more sustainable future.
The backstory of the first electric car battery in 1886
The first electric car battery was invented in 1886 by Carl Benz, the founder of Mercedes-Benz. It was a significant development that paved the way for the modern electric vehicles we see on our streets today. The battery itself was made of lead and acid, which could be recharged multiple times, making it an efficient and practical solution for powering a car.
Interestingly, Benz initially created the battery for his wife’s sewing machine, but after recognizing its potential, he adapted it for use in his cars. This invention revolutionized the transportation industry and set the stage for the electrification of vehicles in the years to come. The legacy of the first electric car battery lives on today, as the world continues to push towards a more sustainable future.

Details on the inventor and patent
The history behind the inventor of a patent can often be fascinating and the story of how an invention came to be is always worth exploring. One example of this is the story of Thomas Edison, who is known as one of the most prolific inventors in American history. Edison held over a thousand patents during his lifetime, and his most famous invention is the light bulb.
However, what many people don’t know is that his invention was not the first electric light bulb. Several other inventors had already created incandescent bulbs before Edison, but their designs were flawed. Edison’s bulb was different because he used a carbon filament that glowed for over 40 hours, making it practical for everyday use.
He patented his design in 1880 and quickly began marketing and selling his light bulbs. This invention not only revolutionized the way we light our homes but also paved the way for advancements in electricity and technology.
Functionality
The 1886 electric car battery was a groundbreaking invention that paved the way for modern electric vehicles. This battery, which was invented by Karl Benz, used a lead-acid cell and had a capacity of 5 kilowatt-hours.
While this may not seem impressive by today’s standards, it was a significant improvement over the batteries used in earlier electric vehicles. The 1886 electric car battery also had a number of other important features, including a compact design, low cost, and a long lifespan. All of these factors helped to make the electric car more practical and affordable for consumers.
Thanks to the innovations of pioneers like Benz, electric vehicles are now a viable alternative to gas-powered cars and are helping to reduce the world’s reliance on fossil fuels. The 1886 electric car battery may have been a small step, but it was a crucial one that helped to launch a new era in transportation.
How the battery worked and powered the first electric car
The battery of the first electric car was a crucial component in the functionality of the vehicle. It was responsible for powering the electric motor and keeping it running. Essentially, the battery acted as the car’s fuel tank.
This early battery was made up of several cells, that generated electricity through a chemical reaction between zinc and copper. By connecting these cells, the battery could produce enough electricity to power the electric motor and move the car. It was a simple yet innovative design that paved the way for more advanced batteries and electric cars today.
Without the battery, the first electric car would not have been possible. It was the battery’s ability to store and release energy that allowed the car to move for extended periods. Unlike gasoline-powered cars, which require continuous refueling, electric cars only require charging of the battery.
This made the idea of an electric car more appealing, as it was a more sustainable and cost-efficient way of transportation. To better understand the functionality of the battery of the first electric car, think of it as a water tank. Just as a water tank holds and distributes water to a home’s plumbing system, the battery stores and releases power to the car’s electric motor.
The more cells the battery has, the more energy it can produce and the further the car can travel on a single charge. In summary, the battery was a key component in the functionality of the first electric car. It allowed for sustainable and cost-efficient transportation, by powering the car’s electric motor and storing energy for extended use.
Today, batteries have come a long way and are more efficient and powerful than ever before, making electric cars a viable option for the future of transportation.
Charging and range of the 1886 electric car
The 1886 electric car, invented by Karl Benz, had a charging and range functionality that was quite different from today’s electric vehicles. The car’s batteries needed to be charged every 50 miles, which was a significant limitation for long journeys. However, this was a major improvement from previous electric vehicles that could only go a few miles before needing a charge.
This was due to the car’s lead-acid batteries, which were much more efficient and allowed for longer distances to be traveled. While charging the car’s batteries, the process was slow and required 6-8 hours to fully charge. However, the car’s battery life was impressive at the time, and it was considered a significant leap forward for electric vehicles.
Nowadays, modern electric vehicles have an average range of around 250 miles and can charge much faster, but it’s important to remember that the 1886 electric car was a pioneering innovation that paved the way for modern electric vehicles.
Impact
The 1886 electric car battery is often credited as the precursor to the modern electric car battery. Invented by French physicist Gaston Plante, the lead-acid battery had a significant impact on the automotive industry and paved the way for a greener mode of transportation. Despite its limitations, including bulkiness and lack of range, the electric car battery had the potential to revolutionize transportation and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
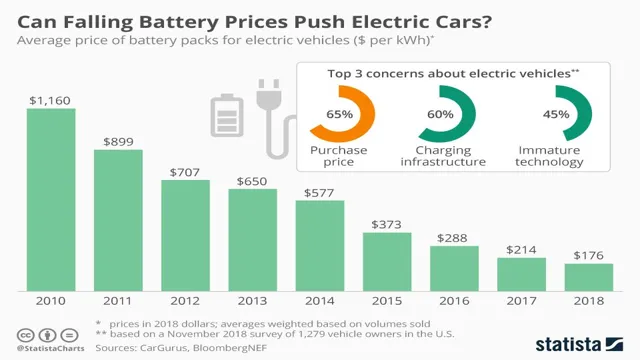
Today, advancements in battery technology have allowed electric cars to achieve longer ranges and become a more viable option for consumers. The 1886 electric car battery may have been the first step in the development of sustainable transportation, but it is the ongoing innovation and evolution of battery technology that will ultimately create a world powered by clean energy.
The impact of the 1886 electric car battery on the automobile industry
The invention of the electric car battery in 1886 marked a significant turning point in the automobile industry. This technology paved the way for the development of electric vehicles, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels that emit harmful gases into the environment. The impact of this breakthrough was felt almost immediately, as electric cars began to replace horse-drawn carriages in cities, and motorists began to see the potential of this new mode of transportation.
Although initial adoption was slow due to limitations in battery life and charging infrastructure, the electric car battery laid the groundwork for a more sustainable future. Today, we continue to see advancements in electric vehicle technology, with some estimates predicting that electric cars could make up almost half of all new vehicle sales by 2040. The electric car battery truly changed the game for the automobile industry, setting it on a path towards a greener future.
The potential future impact and advancements
Impact The potential future impact of advancements in technology is vast and varied, with numerous possibilities for both positive and negative outcomes. For instance, breakthroughs in artificial intelligence and automation may revolutionize industries, allowing for greater efficiency and productivity. However, this could lead to job losses and income inequality if not managed properly.
Similarly, advancements in medicine could drastically improve healthcare outcomes, but could also lead to ethical dilemmas and increased healthcare costs. It is clear that the future impact of technology will depend on how it is developed and integrated into society. It is our responsibility to ensure that we make the most of the benefits while mitigating the risks.
Conclusion
In 1886, the electric car battery was a novel invention that sparked excitement and curiosity. But little did anyone know that it would pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future. Fast forward to the present day, and electric cars are no longer a novelty, but a viable option for eco-conscious individuals.
The 1886 electric car battery may have been the first spark, but the flame of electric transportation is burning brighter than ever.”
FAQs
What type of battery was used in the 1886 electric car?
Lead-acid batteries were used in the 1886 electric car.
Who invented the 1886 electric car battery?
The lead-acid battery used in the 1886 electric car was invented by Gaston Planté.
What was the range of the 1886 electric car on a single charge?
The 1886 electric car had a range of 50 miles on a single charge.
How long did it take to recharge the battery of the 1886 electric car?
It took approximately eight hours to recharge the battery of the 1886 electric car.