Revving up Sustainability: Exploring the Potential of Reusing Electric Car Batteries
Have you ever wondered what happens to electric car batteries when they run out of juice? The truth is, these batteries can still be useful even after they can no longer power an electric vehicle. Reusing electric car batteries has become a popular topic of conversation among manufacturers and environmentalists alike. But what are the possibilities and challenges of repurposing these batteries? One possibility is to use them for energy storage.
As renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power become more widespread, there is a growing need for efficient and cost-effective ways to store energy. Used electric car batteries can be repurposed for this purpose, providing a valuable resource for off-grid and backup power systems. However, there are also challenges to reusing electric car batteries.
One issue is that these batteries degrade over time and cannot maintain the level of performance required for electric vehicles. This means that they may not be suitable for all types of energy storage applications. In addition, there are concerns about the environmental impact of reusing batteries, including the disposal of any hazardous materials.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of reusing electric car batteries are clear. By giving these batteries a second life, we can reduce waste, conserve resources, and contribute to a sustainable energy future. As we continue to develop new technologies and explore new applications for these batteries, the possibilities are virtually endless.
Introduction
When it comes to electric vehicles, one of the biggest concerns for potential buyers is the cost and lifespan of the batteries. However, the good news is that electric car batteries can actually be reused, even after they have reached the end of their lifespan in a car. This is because while the batteries may no longer have enough power to run a vehicle, they can still hold a significant charge.
This means that they can be repurposed for use in energy storage systems, such as those used for renewable energy sources like solar panels. In this way, the batteries can still be useful long after they have been removed from the car, reducing the environmental impact of electric vehicles even further. This also has the potential to reduce the cost of energy storage, making renewable energy more accessible to everyone.
So while the lifespan of electric car batteries may be a concern for some, it’s important to remember that there are many ways in which they can be reused, making them a sustainable and cost-effective choice for the future.
Why Reuse Electric Car Batteries?
Electric car batteries are not only expensive but also an essential component of electric cars. These batteries often have a lifespan of about 8-10 years, and after that, they need to be replaced. However, instead of discarding these batteries, it is possible to reuse them, and there are several reasons why this is necessary.
Firstly, reusing electric car batteries is beneficial for the environment. By extending the life of these batteries, we can reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. Additionally, reusing these batteries can help reduce the cost of producing new batteries, which can make electric cars more affordable for consumers.
Furthermore, since electric car batteries still have a significant amount of energy left in them when they are replaced, repurposing them is a smart idea. These batteries can be used to power other devices like homes, businesses, or even be used as backup power sources. Overall, reusing electric car batteries is essential and should be done to reduce waste, save money, and help power the world.
Lifespan of Electric Car Batteries
Electric car batteries are a crucial component in the world of EVs, and understanding their lifespan is essential for potential buyers. The lifespan of electric car batteries is a frequently discussed topic, with many factors impacting their longevity. The battery lifespan of an EV refers to the amount of time the car’s battery will last before it needs to be replaced.
The lifespan of an electric car battery can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of battery, the temperature it operates in, and how it’s been used. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of battery in electric vehicles and have a typical lifespan of around 8-10 years. However, several advancements have been made in the technology of EV batteries, and manufacturers are working to enhance the lifespan of electric car batteries continually.
This means that the lifespan of these batteries will only improve in the future, making electric vehicles even more convenient and cost-effective for consumers.
Types of Electric Car Batteries
When it comes to electric cars, the battery is one of the most critical components, determining not only the car’s range but also its performance and cost. There are several types of electric car batteries available in the market, each with its unique features, advantages, and limitations. Choosing the right type of battery goes a long way in ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and durability of your electric car.
From lead-acid to nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) to lithium-ion, electric car batteries have progressed significantly, providing a much longer range, faster charging times, and increased safety features. As technology continues to evolve, we can only expect to see more cost-effective, energy-dense, and sustainable battery options in the future.
Challenges of Reusing Electric Car Batteries
Can you reuse electric car batteries? Although it may seem like a good idea to give these batteries a second life after powering a vehicle, there are several challenges that make the process difficult. One of the biggest hurdles is the degradation of the battery over time and use. This degradation can lead to reduced capacity and overall performance, making the battery less efficient for other applications.
Moreover, electric car batteries are often specialized and built to fit specific vehicles. This means that repurposing them for other purposes may require significant modifications or even complete redesigns. Additionally, there are concerns about the safety and environmental impact of reusing these batteries, which may contain hazardous materials such as lithium and cobalt.
Despite these challenges, researchers and companies are working to find ways to safely and effectively reuse electric car batteries, which could help reduce waste and extend the life cycle of valuable resources.
Battery Degradation
Battery degradation is a common issue faced by electric car owners. It refers to the gradual loss of a battery cell’s ability to hold a charge, which affects the overall performance and range of the vehicle. However, even after a battery is deemed unsuitable for use in a car, it can still hold a significant amount of energy.
This has led to attempts to reuse electric car batteries in other applications, such as energy storage for homes and businesses. While this seems like an innovative solution, there are challenges to reusing electric car batteries. One major concern is the variability of battery degradation.
Battery cells degrade at different rates depending on various factors like temperature and usage patterns, which means it is difficult to predict how long a reused battery will last. Another challenge is the cost of repurposing batteries. It can be expensive to test and refurbish them to ensure they are safe and reliable.
Despite these challenges, the potential for more sustainable battery use and reduced waste make it a promising avenue for future development.
Standardization and Compatibility
When it comes to reusing electric car batteries, one of the biggest challenges is standardization and compatibility. Different car manufacturers use different battery chemistries, sizes, and designs, which can make it difficult to interchange them or use them in different applications. However, some companies, such as Nissan and BMW, are working on developing standardization and compatibility protocols to make it easier to reuse and repurpose electric car batteries.
By doing so, we can not only extend the lifespan of these batteries but also reduce waste and improve sustainability. It’s like having a bunch of puzzle pieces that don’t fit together, but with some effort, we can create a standard puzzle that can be used in various ways, creating a more efficient and harmonious system.
Safety Concerns
Electric car batteries present safety concerns when they are reused due to the risks associated with their degradation over time. The batteries used in electric vehicles have a limited lifespan, and as such, they lose their ability to hold a charge, which can cause safety risks in their reuse. Battery degradation causes increased internal resistance, heating, and potential chemical reactions that can lead to thermal runaway, which can cause fires and explosions.
It is important to note that when these batteries reach their end of life, they need to be safely disposed of, and their components recycled. Reusing electric vehicle batteries can have benefits in terms of sustainability, but it is essential to use caution and proper safeguards to minimize the potential for safety risks. Battery management systems must be in place that can monitor and control the batteries’ performance to reduce the possibility of overheating and other dangerous scenarios.
In summary, although reusing electric car batteries is an excellent way to reduce waste and maximize the use of available resources, it is essential to implement proper safety protocols to ensure that they are used safely.
Uses for Reused Electric Car Batteries
Can you reuse electric car batteries? The answer is yes! In fact, there are numerous uses for them even after they’ve lost their charge capacity for powering a vehicle. One popular option is to repurpose them into energy storage solutions for renewable energy sources such as solar panels. These used batteries can store the excess energy produced during the day and then release it at night or during times of high demand.
Another application is to use them as backup power for homes or businesses in the case of an outage. This not only provides a reliable power source but also reduces the need for fossil fuels. Some companies are even exploring using repurposed electric car batteries for large-scale community energy storage.
Overall, reusing electric car batteries is not only environmentally friendly but also has the potential to revolutionize the way we store and use energy.
Grid Storage
“reused electric car batteries” As electric cars become more commonplace on our roads, the question arises- what happens to their batteries once they’re no longer fit for use in the vehicles? The answer: many of them can be repurposed for grid storage. While they may no longer hold enough charge to power a car, these batteries still have significant energy storage capacity. By grouping them together, they can be used to store energy from renewable sources such as wind and solar power, helping to offset fluctuations in supply due to natural variations in weather conditions.
This can help to provide a more reliable source of renewable energy, reducing the need for fossil fuel backup generation, and ultimately leading to a greener future. It’s a win-win situation for the environment and the consumer- repurposing these batteries not only helps to reduce waste, but also provides a cost-effective energy storage solution.
Home Energy Storage
Home energy storage can bring a lot of benefits, and reusing electric car batteries is one way to achieve that. These batteries may no longer be suitable for powering a car, but they still have a lot of capacity left to store renewable energy. Reusing these batteries helps reduce waste and cut costs as compared to buying new ones.
Moreover, it helps solve the issue of intermittency that renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power have. By storing energy from these sources, we can use it when the sun isn’t shining or when there’s no wind. It’s like having a battery backup for your home.
Reused EV batteries can also find uses in other applications such as home backup power, mobile power, and even grid-scale storage. With more and more electric cars hitting the roads every year, reusing their batteries will become increasingly important to meet the growing demand for energy storage.
Conclusion: The Future of Reusing Electric Car Batteries
In conclusion, while it may seem appealing to repurpose old electric car batteries, it’s important to remember that these batteries have a limited lifespan and eventually need to be properly disposed of. So, before you start planning that DIY project, consider exploring alternative options, such as recycling or donating them to organizations that specialize in battery disposal. Because in the end, it’s our responsibility to ensure that these powerful batteries don’t end up in landfills, and instead find new life as valuable resources for our environment.
“
FAQs
How long do electric car batteries last?
Electric car batteries typically last between 8-10 years before they need to be replaced. However, with proper care and maintenance, the lifespan can be extended.
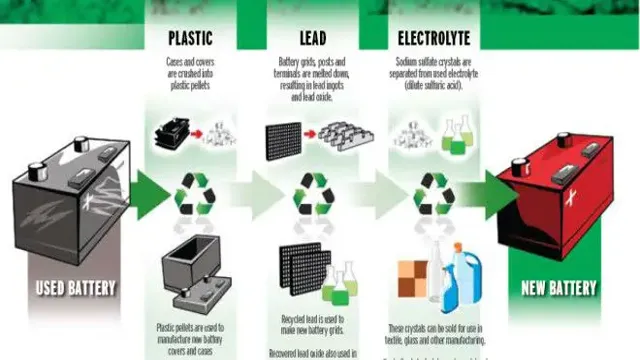
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, electric car batteries can be recycled to recover valuable materials such as lithium and cobalt. Recycling also reduces environmental impact by preventing toxic materials from ending up in landfills.
How much does it cost to replace an electric car battery?
The cost of replacing an electric car battery can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle. On average, battery replacement costs can range from $5,500 to $10,000.
Can electric car batteries be re-purposed for other uses?
Yes, electric car batteries that are no longer suitable for use in vehicles can be re-purposed for other applications such as home energy storage systems or solar power systems. This allows for a more sustainable use of the batteries and reduces waste.







