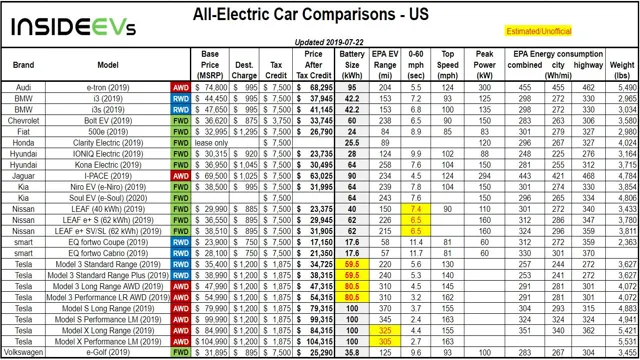
Revolutionizing the Future: Why Electric Car Batteries are Powered by High-Performing Lithium Cells
Electric vehicles are taking the world by storm, and for seemingly good reason. With a low carbon footprint, reduced emissions, and silent operation, it’s no wonder that more and more people are turning to EVs for their transportation needs. One of the critical components of an EV is the battery, and specifically, the type of cells used within that battery.
Lithium cells, in particular, have been gaining widespread popularity in recent years, thanks to their high energy density, long life span, and overall efficiency. But what role do they play in the bigger picture of electric vehicle technology, and why are they so crucial to the success of these eco-friendly cars? Let’s take a closer look and find out.
What are Lithium Cells?
Electric car batteries have become well-known for their use of lithium cells. Lithium cells are rechargeable batteries that use lithium ions to store and release energy. They’re known for their high energy density, which allows them to store more energy in a smaller space than other types of batteries.
This is why they’re so popular for use in electric vehicles. Lithium cells come in different chemistries, such as lithium-cobalt, lithium-iron phosphate, and lithium-manganese oxide, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. Lithium cells are also widely used in consumer electronics, medical devices, and other applications.
However, they do require special care and handling, as they can be sensitive to heat, cold, and overcharging, which can cause them to degrade faster or even fail. Overall, lithium cells have played a vital role in the development of electric cars and will be a key technology moving forward as the world shifts towards sustainable transportation.
Explaining the Technology Behind Lithium Cells
Lithium cells are compact and lightweight devices that store electrical energy using lithium ions. These cells are commonly used in electronic devices, including laptops and smartphones. The technology behind lithium cells is fascinating yet straightforward.
Essentially, lithium cells consist of two electrodes, an anode, and a cathode, separated by an electrolyte. When the cell is charged, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte. This movement of ions creates a flow of electricity, allowing the cell to store electrical energy.
When the cell is discharged, the process is reversed, and the lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode. Lithium cells offer several advantages over other types of batteries, including a longer life, high energy density, and a low self-discharge rate. Overall, the technology behind lithium cells has revolutionized the electronics industry, allowing for the development of more advanced and portable devices that consumers use every day.
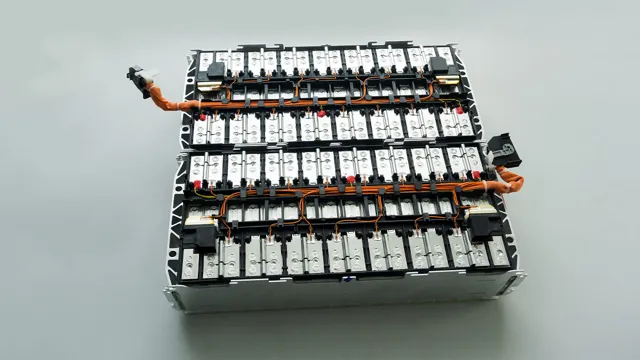
Why are Lithium Cells Used in Electric Car Batteries?
Lithium cells are small batteries made from lithium-ion, which are used to power many electronic devices, including electric cars. They’re known for their high energy density, which means they can hold a lot of power in a relatively small size. This makes them an ideal choice for electric car batteries, where space is limited and the battery needs to be as lightweight as possible.
Lithium cells are also highly efficient, meaning they can convert the stored energy into electricity with very little waste or heat generated. This results in longer battery life and faster charging times. Despite their benefits, lithium cells can be costly and require complex manufacturing processes.
Nonetheless, they remain the choice for most electric car manufacturers because of their power and efficiency.
How Many Lithium Cells are in an Electric Car Battery?
Electric car batteries have a significant number of lithium cells, usually ranging from hundreds to thousands depending on the size and capacity of the battery. These lithium cells are what power the electric motor of the car and determine the range the car can travel on a single charge. The most common type of lithium cells used are lithium-ion cells, which offer high energy density and long cycle life.
These cells are arranged into battery packs and are connected in series and parallel configurations to provide the necessary voltage and capacity. A larger battery pack with more lithium cells will generally provide a higher range, which is a crucial factor for many electric car drivers. As the demand for electric cars increases, advancements in lithium cell technology will continue to drive innovation in the industry and improve the performance of electric vehicles.
The Average Number of Lithium Cells per Electric Car Battery
If you’re wondering how many lithium cells are in an electric car battery, the answer depends on the specific car model. However, the average number of lithium cells per electric car battery is around 4,000. These cells are grouped together into modules, and it takes multiple modules to create a complete battery pack.
The number of modules needed also varies depending on the car model. For example, a Tesla Model S has 16 modules, while a Nissan Leaf only has 48 cells grouped into 24 modules. Lithium cells are the preferred choice for electric car batteries because they are lightweight, have a high energy density, and provide long-lasting power.
They also charge quickly and do not suffer from the memory effect, which means they maintain their full capacity even after repeated charging and discharging cycles. Overall, the number of lithium cells in an electric car battery may seem high, but it’s necessary to provide the power and range needed for these vehicles.
How Does the Number of Lithium Cells Affect the Battery Life?
Lithium cells play a significant role in the battery life of an electric car. Generally, the higher the number of lithium cells in a battery, the longer the battery life. So, how many lithium cells are in an electric car battery? The answer can vary depending on the make and model of the car.
For example, a Tesla Model S has an 85 kWh battery pack that is made up of 7,104 individual cells, whereas a Nissan Leaf has a 40 kWh battery pack made up of 192 cells. The more cells a battery has, the more energy it can store and the longer it can last. However, adding more cells also means more weight, which can affect the overall efficiency of the car.
Ultimately, the number of lithium cells in an electric car battery is a balancing act between battery life and overall performance.
The Impact of Lithium Cells on Electric Car Performance
When it comes to electric cars, the battery is a critical component that directly impacts performance. So, just how many lithium cells are in an electric car battery? The answer can vary depending on the specific make and model of the vehicle. However, most modern electric car batteries are made up of several thousand individual lithium-ion cells.
These cells work together to provide power to the electric motor and other systems in the car. Generally, the more cells a battery has, the greater its capacity and the longer it will last before needing to be recharged. This is why many electric car manufacturers continue to work on developing more powerful and efficient battery systems.
With advances in technology, we could soon see even more impressive range and performance from these eco-friendly vehicles.
Are All Electric Car Batteries Powered by Lithium Cells?
Electric car batteries have become more popular over the years, and one question that commonly arises is whether all electric car batteries use lithium cells. The answer is no. While lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used type of battery in electric cars, other types of batteries are also used, such as nickel-metal hydride and solid-state batteries.
However, lithium cells are preferred for their high energy density and long lifespan, making them a popular choice for electric cars. They also provide quicker charging times and a longer overall driving range when compared to other battery types. Additionally, as technology advances, more efficient and sustainable battery options are continually being developed and explored for use in electric cars.
Nonetheless, it’s important to note that while not all electric car batteries use lithium cells, they remain the most widely used and favored option for their reliability and performance.
Alternative Battery Technologies Used in Electric Cars
Despite the popularity of lithium-ion batteries, there are actually several alternative battery technologies used in electric cars. One example is nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which were commonly used in earlier models. Although NiMH batteries are less efficient than lithium-ion, they tend to be more affordable and offer greater longevity.
Another alternative is solid-state batteries, which use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one. This technology is still in development but could potentially offer greater energy density and faster charging times. There are also experimental technologies like sodium-ion and zinc-air batteries, which hold promise for their low cost and abundance of raw materials.
So, while lithium-ion batteries may currently be the most common, there are plenty of options for electric car manufacturers to choose from when it comes to powering their vehicles.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium Cells in Electric Cars
Lithium cells are commonly used as the primary battery source in electric cars. While other battery types, such as nickel-metal hydride and lead-acid, have been used in the past, the benefits of lithium cells make them the go-to choice for electric vehicle manufacturers. One major advantage of lithium cells is their high energy density, which means they can store more energy in a smaller space.
This allows for smaller, lighter batteries that can still provide a longer driving range. Additionally, lithium cells have a longer lifespan compared to other battery types, which means they can be charged and discharged more times before needing to be replaced. However, there are also some disadvantages to using lithium cells in electric cars.
They can be expensive to produce, which can add to the cost of the vehicle. Also, the raw materials used to make lithium cells are limited, which can create supply chain issues and potentially increase the price of these materials. Despite these drawbacks, it is likely that lithium cells will continue to be the dominant battery type for electric cars in the near future.
Conclusion
Electric car batteries have more lithium cells than a teenager’s phone plan – powering clean transportation with style and sustainability.”
FAQs
How many lithium cells are used in electric car batteries?
Electric car batteries have multiple lithium cells, typically ranging from a few dozen to a few hundred, depending on the size of the battery and its capacity.
What advantages do lithium cells offer for electric car batteries?
Lithium cells are ideal for electric car batteries because they are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can be recharged quickly, making them more efficient and reliable than traditional lead-acid batteries.
What is the average lifespan of lithium cells in electric car batteries?
The lifespan of lithium cells in electric car batteries varies depending on usage patterns, but most lithium batteries have a lifespan of 8-10 years or up to 1000 charge cycles before needing to be replaced.
How do electric car manufacturers ensure the quality and safety of lithium cells in their batteries?
Electric car manufacturers have strict quality control measures in place, such as testing each individual cell for consistency and performance, to ensure that their batteries meet safety standards and offer reliable performance. They also use advanced cooling and monitoring systems to prevent overheating and other safety risks.