Electric Car Battery: Unveiling the Cost Percentage Behind The Hype
Electric cars have become increasingly popular in recent years, and this is due to many reasons, including environmental concerns and the rising cost of traditional fuel. Although the initial cost of an electric car is a significant investment, it is the battery that usually causes the most concern in terms of its cost. The battery is the most crucial component of an electric car since it stores the energy that powers the vehicle.
Understanding the cost breakdown of electric car batteries can help you make an informed decision when considering buying an electric car. In this article, we will delve into the nitty-gritty of the electric car battery costs and help you understand why electric car batteries are as expensive as they are.
Battery Package Costs
When it comes to electric cars, the battery package is often the most expensive component. In fact, it can make up as much as 30-40% of the total cost of the car. This is because the battery module is the most complex and largest component of an electric vehicle, and requires advanced technology to manufacture.
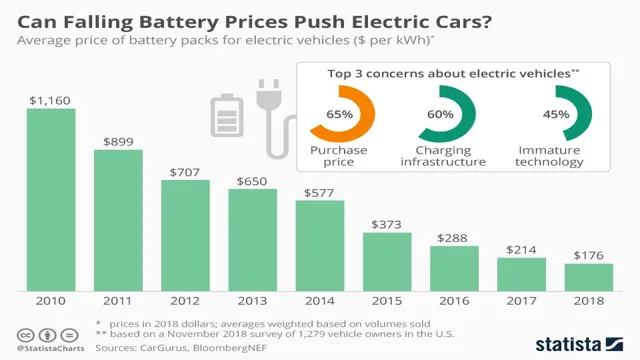
However, as more automakers invest in electric vehicle technology, the cost of batteries is expected to decrease in the coming years. Some experts estimate that battery costs could fall by as much as 50% by 2025, which would make electric cars more affordable for the average consumer. While the cost of batteries is currently a major barrier to widespread adoption of electric vehicles, advancements in battery technology and production processes could make them a more viable option in the near future.
Packaging and Delivery Charges
When it comes to batteries, packaging and delivery are essential costs that must be considered. Battery package costs can vary based on the type of battery being shipped. For smaller batteries, standard bubble wrap and cardboard boxes may suffice, but for larger or more delicate batteries, specialized packaging materials may be necessary.
Not only that, but the cost of shipping batteries can be higher due to regulations and restrictions around hazardous materials. It’s important to always factor in these packaging and delivery costs when considering the overall cost of purchasing and installing a battery. By doing so, you can ensure that you are budgeting appropriately and avoiding unexpected fees.

Battery Cell Materials Costs
Battery cell materials costs can be a significant factor in determining overall battery package costs. This is because each battery cell requires a complex combination of materials, including chemicals, metals, and polymers. The cost of these materials can vary depending on their availability and the manufacturing process involved.
For example, the cost of cobalt, a key material in many battery cells, can fluctuate based on global supply and demand. Additionally, advancements in materials science and engineering can lead to lower costs for certain components over time. Overall, battery manufacturers need to carefully consider the costs of each material used in their products in order to create competitive pricing for their battery packages.
Comparative Cost Analysis
Have you ever wondered how much an electric car battery contributes to the overall cost of an electric car? The answer may surprise you. While it varies by model and manufacturer, the electric car battery typically accounts for around 25% to 30% of the total cost of the vehicle. This may seem like a significant portion, but it’s important to consider the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance costs that come with owning an electric car.
In fact, over the lifetime of the vehicle, electric cars tend to be more cost-efficient than their gas-guzzling counterparts. It’s also worth noting that the cost of electric car batteries has been gradually decreasing in recent years, making electric cars more affordable and accessible than ever before. So, while the initial cost may be slightly higher, the financial and environmental benefits of owning an electric car make it a worthwhile investment.
Electric vs Combustion Engine Cars
When comparing the cost of electric vs combustion engine cars, there are a few factors that come into play. The initial cost of purchasing an electric car tends to be higher than that of a traditional gas-powered car. However, over time, the cost of ownership for an electric car tends to be lower due to the cost of fuel and maintenance.
Electric cars can be charged at home for a fraction of the cost of filling up a gas tank, and they require less maintenance since they don’t have as many moving parts as a traditional car. On the other hand, gas-powered cars have a lower upfront cost but require regular trips to the gas station and more maintenance. Additionally, the cost of gasoline fluctuates, which can make budgeting more difficult.
When considering the comparative cost over the lifespan of the vehicle, electric cars may end up being a more economical choice.
Electric vs Hybrid Cars
When considering the cost difference between electric and hybrid cars, it is important to look at both the upfront costs and the long-term savings. Electric cars tend to have a higher upfront cost than hybrid cars, due to the more advanced technology and larger battery systems required. However, when looking at long-term savings, electric cars have a significant advantage.
They require less maintenance and have lower fuel costs since they don’t require gasoline. In contrast, hybrid cars still run on gasoline and may require more maintenance as the internal combustion engine gets older. Additionally, the electric car’s battery system typically has a longer lifespan than a hybrid’s battery system.
Ultimately, while electric cars may have a higher initial cost, their long-term savings can make them a more economical choice in the long run.
Battery vs Fuel Costs Over Time
When it comes to weighing the costs of a battery versus fuel-powered device over time, there are several factors to consider. While battery-powered devices may have a higher initial investment cost, they typically save on fuel costs in the long run. However, this does not necessarily hold true for all devices.
For example, a battery-powered car may save on fuel costs over the lifetime of the car, but the cost of replacing the battery can be substantial. On the other hand, a fuel-powered lawn mower may have a lower initial investment cost but can rack up more frequent and expensive fuel costs in the long run. Ultimately, the comparative cost analysis will depend on the specific device and its usage, along with other factors such as the cost of electricity versus the cost of fuel.
Factors Affecting Electric Battery Costs
The cost of an electric car battery makes up a significant portion of the overall cost of an electric vehicle. In fact, it can account for up to one-third of the total cost of the car. There are many factors that affect the cost of an electric car battery, including the materials used, the size of the battery, and the production process.
The most expensive materials used in electric car batteries are lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Their prices can fluctuate based on supply and demand, which can impact the cost of the battery. The size of the battery also affects the cost.
The larger the battery, the more expensive it will be. The production process also has an impact on the cost of the battery. If the production process is inefficient, then the cost of the battery will be higher.
However, as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, the cost of electric car batteries is expected to decrease, making EVs more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Battery Production Volumes
Electric Battery Costs The volume of production is a critical factor that impacts the cost of producing electric vehicle batteries. It is important to produce batteries at scale to bring down the costs per unit. As production volumes increase, manufacturers can purchase raw materials in bulk, negotiate better prices, and streamline production processes.
Economies of scale can reduce costs significantly, as production teams can optimize processes to maximize output and reduce waste. However, high production volume is not enough to bring down costs. Automakers and battery manufacturers must also invest in research and development to improve battery technology.
As they work to extend battery life, increase power density, and reduce weight, advances in technology can improve the performance and affordability of EV batteries. Balancing production volumes with technological innovation is critical to bringing down the costs of EV batteries and making electric vehicles more accessible to drivers.
Difficulty and Cost of Accessing Raw Materials
Electric battery costs are affected by various factors, and one of the most critical factors is the difficulty and cost of accessing raw materials. There are several raw materials required to manufacture batteries, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These raw materials need to be mined, refined, and transported, which can be expensive and time-consuming, depending on the location and accessibility of the mines.
In addition, the demand for these raw materials is increasing globally, driving up the prices. Furthermore, the availability of these raw materials is uncertain due to geopolitical tensions and fluctuations in supply and demand. As a result, the battery’s production and its cost heavily depend on the access, availability, and affordability of raw materials.
The search for alternative raw materials and sustainable production practices can help to alleviate these issues and reduce reliance on specific materials.
Future Trends and Improvements
The cost of an electric car battery can vary greatly depending on the type of battery and the manufacturer. On average, an electric car battery can cost anywhere from 20-40% of the total cost of the vehicle. However, with the advancements in technology and production, we can expect to see a decrease in the cost of electric car batteries in the future.
One way this could be achieved is by increasing the scale of production, as the more batteries produced, the lower the cost per unit. Battery technology is also rapidly improving, with companies working on developing more efficient and higher capacity batteries. This will allow vehicles to travel longer distances per charge and decrease the need for frequent recharging.
The ultimate goal is to make electric vehicles more affordable and accessible to the general population, and we are moving closer to that every day. So, we can say that the electric car battery is around 20-40% of the total cost.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cost of an electric car battery can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle, but it typically accounts for a significant portion of the overall cost. Some estimates suggest that the battery can represent anywhere from 25% to 40% of the total cost. However, as technology continues to improve and economies of scale kick in, we can expect the cost of electric car batteries to continue to drop in the coming years.
So if you’re considering an electric car, rest assured that you’re not just buying a battery on wheels – you’re investing in a brighter, cleaner, and more sustainable future!”
FAQs
What is the average percentage of the electric car battery cost?
On average, the electric car battery cost accounts for around 30% to 40% of the total cost of the vehicle.
Is the electric car battery cost decreasing over time?
Yes, as the technology progresses, the cost of electric car batteries is decreasing. In fact, it is expected that the cost of batteries will continue to fall in the future.
How does the electric car battery cost compare to traditional car engines?
The cost of an electric car battery is significantly higher than that of traditional car engines. However, the cost of electric car batteries should be compared to the lifetime cost of owning a traditional car, which includes fuel, maintenance, and other expenses.
What factors influence the cost of electric car batteries?
The cost of electric car batteries is influenced by several factors, including the type of battery chemistry, manufacturing process, economies of scale, and research and development costs.