Unlocking the Power: Understanding Electric Car Battery Voltage Range for Optimal Performance
Electric cars are steadily becoming more popular as people seek out more sustainable and environmentally-friendly modes of transportation. A key component of these cars is their batteries, which power the vehicle and enable it to run without using gasoline. However, not all batteries are created equal, and the voltage range of electric car batteries can vary widely depending on the model and manufacturer.
This can leave many drivers wondering what voltage range is best for their needs, and how it affects the performance of their electric car. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at electric car batteries and explore the different voltage ranges available, so you can make an informed decision when it comes to choosing the right battery for your vehicle.
Electric vehicles (EVs) rely on battery packs as their primary energy source, which store and supply power to the electric motor. One key characteristic of an EV battery system is its voltage, which plays a critical role in determining the vehicle’s performance, efficiency, and charging speed.
Key Components of EV Battery Systems
- Battery Cells: The basic building blocks, typically lithium-ion cells, each with a nominal voltage of around 3.2 to 3.7 volts.
- Battery Modules: A group of cells connected in series or parallel to increase total voltage or capacity.
- Battery Pack: An arrangement of modules that forms the entire battery system. The pack’s total voltage depends on how many cells or modules are wired together.
Understanding Voltage in Electric Car Batteries
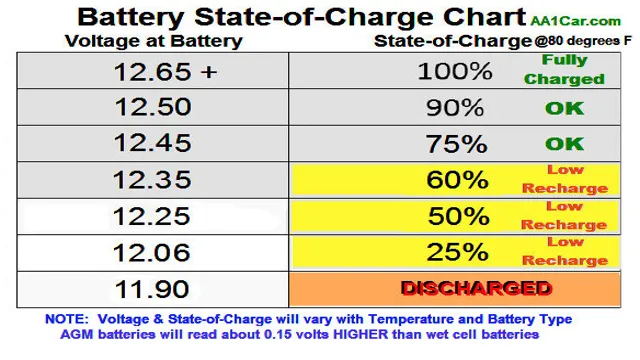
Electric car batteries are the lifeline of electric cars and understanding the voltage range is crucial in maintaining their performance and longevity. The voltage range for an electric car battery typically ranges from 200 to 400 volts, with each battery pack having a specific voltage range depending on its capacity. The voltage range plays a significant role in determining the car’s performance, including its acceleration, top speed, and overall range.
It’s essential to note that electric car batteries should never be charged above or below their recommended voltage range, as it can lead to damage and potentially dangerous situations. A battery management system (BMS) helps maintain the voltage range by regulating charging and discharging cycles and preventing overcharging and undercharging. Hence, as electric cars become more prevalent, educating drivers about the importance of maintaining the battery voltage range remains an essential aspect of the EV ownership experience.
What is voltage and how does it relate to electric cars?
Voltage is a measure of electric potential energy in an electric circuit, frequently expressed in volts. In electric cars, voltage plays a crucial role in determining the range the car can travel on a single charge. The higher the voltage, the greater the potential energy in the car’s battery, which makes the electric motor more efficient and stronger.
Electric vehicles employ high voltages because they require high amounts of energy to move from one place to another. Moreover, the batteries produce higher voltages, which reduces the heat generated during the conversion of electrical energy to mechanical power. Electrical engineers consider the voltage as a key factor in designing electric cars, as it influences the battery’s construction and layout.
Understanding the importance of voltage in an electric car’s battery helps drivers to realize the significance of maintaining their car’s battery voltage for optimized performance.
Different types of electric car batteries and their voltage range
Electric car batteries can range in voltage depending on the type of battery used. The most common types of batteries are lead-acid, nickel-metal hydride, and lithium-ion. Lead-acid batteries are the oldest type of battery and have a voltage range of 2V to 12V.
They are cheaper than other types of batteries, but are heavy and have a shorter lifespan. Nickel-metal hydride batteries have a higher voltage range of 2V to
2V and are more efficient than lead-acid batteries, but are still heavier and have a shorter lifespan than lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries have the highest voltage range of 6V to
8V and are the most efficient and lightweight option. They also have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance than other types of batteries. Understanding the voltage range of electric car batteries is important when choosing the right battery for your car’s needs.
Battery voltage refers to the electrical potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of the battery. Higher voltage systems can provide more power to the motor and typically allow for higher efficiency in energy transmission.
Common Battery Voltages in Electric Vehicles
- 48V Systems:
- Used in: Mild-hybrid electric vehicles (MHEVs) and some low-power applications.
- Characteristics: Primarily used for boosting fuel efficiency in hybrids rather than full electric propulsion.
- 200-400V Systems:
- Used in: Most traditional electric vehicles like the Nissan Leaf and Chevy Bolt operate within this range.
- Advantages: Well-suited for average EV applications, balancing performance, range, and safety.
- Charging Speeds: Compatible with standard Level 2 chargers (240V) and typically support up to 50-150 kW fast charging.
- 400-800V Systems:
- Used in: High-performance electric cars such as the Porsche Taycan and Lucid Air.
- Advantages: Higher voltage allows for faster charging times and better performance. For example, an 800V system can support ultra-fast DC charging, reducing charging times to around 15-20 minutes for 80% charge.
- Charging Speeds: These vehicles are compatible with ultra-fast charging stations (e.g., 350 kW).
- 1000V+ Systems:
- Used in: Upcoming high-performance and commercial vehicles, such as heavy-duty trucks and buses.
- Advantages: Ultra-high voltage systems can carry more power with less heat generation and losses, making them ideal for industrial applications.
- Efficiency: Higher voltages improve overall system efficiency, especially in heavy-duty or long-range EVs where energy demand is substantial.
How Voltage Range Affects Electric Car Performance
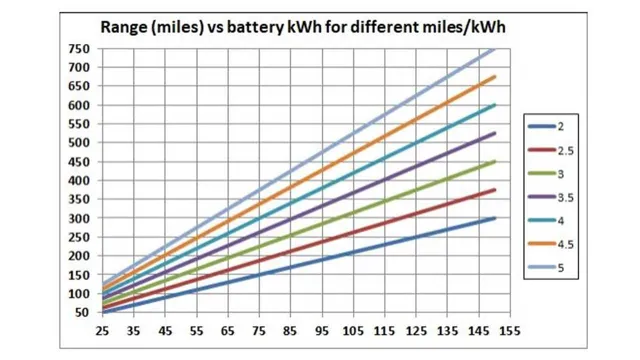
When it comes to electric cars, the voltage range of the battery can have a significant impact on its performance. A higher voltage range can provide more power and acceleration, while a lower voltage range could limit the car’s speed and acceleration capabilities. Additionally, the voltage range can affect the car’s range and charging time.
If the voltage range is too low, the car may not be able to go as far on a single charge, thus requiring more frequent charging. On the other hand, if the voltage range is too high, it could potentially shorten the battery’s lifespan and require more specialized charging procedures. It’s crucial that electric car manufacturers carefully consider the optimal voltage range for their vehicles to ensure maximum performance and longevity.
Power Output:
- Power (in watts) is the product of voltage and current. Higher voltage systems can deliver more power without increasing the current. This reduces heat and energy losses during transmission, which leads to better vehicle performance and efficiency.
Motor Efficiency:
- Electric motors tend to be more efficient when paired with higher voltage systems. Less heat generation translates to less energy wasted, which in turn increases the vehicle’s range on a single charge.
Charging Times:
- Higher voltage systems can handle higher charging currents, which leads to faster charging times. For instance, an 800V system can reduce the charging time by almost half compared to a 400V system if supported by a compatible fast charger.
Range Considerations:
- While voltage alone doesn’t determine the vehicle’s range (battery capacity in kilowatt-hours does), higher voltage systems can contribute to a more efficient energy transfer and reduced energy loss. This can marginally increase the range per charge, depending on other vehicle factors such as aerodynamics and weight.
Maximum voltage range for electric car batteries and its impact on driving range
Electric Car Batteries, Voltage Range, Driving Range, Performance When it comes to electric car batteries, the voltage range plays a significant role in determining the car’s performance and driving range. The higher the voltage range, the more energy the battery can store and provide to the car’s electric motors. This increased energy capacity translates into better performance, acceleration, and top speed.
However, a higher voltage range also means a higher cost for the battery, which can make the overall cost of the car more expensive. On the other hand, a lower voltage range can result in a shorter driving range, limited acceleration, and a slower top speed. Car manufacturers need to find a balance between developing a battery with the optimum voltage range that maximizes driving range while maintaining affordability.
In conclusion, the voltage range of electric car batteries is a significant factor that affects the performance, driving range, and cost of electric cars.
Minimum voltage range for electric car batteries and its impact on battery life
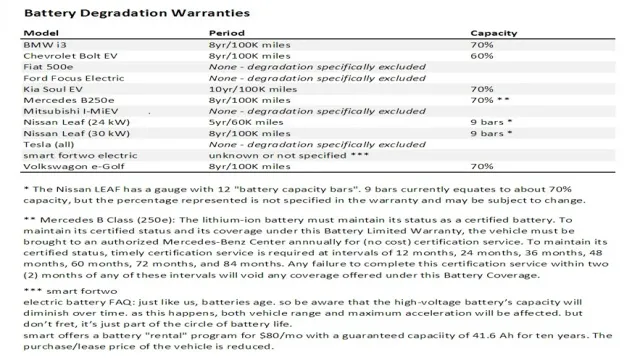
The minimum voltage range for electric car batteries is a crucial factor that significantly impacts battery life and overall electric vehicle performance. If an electric car battery falls below its minimum voltage range, it may result in a weaker battery performance and even a shorter lifespan. The voltage range is an important indicator of the battery’s state of charge and the amount of energy that the battery can deliver.
Keeping the battery charged within the recommended voltage range helps to optimize battery life and ensure consistent performance. For instance, driving an electric car on a low battery voltage range may cause the battery to run down quickly, leading to expensive replacements. Therefore, it is vital to pay attention to the voltage range and avoid driving the electric car on an empty battery or discharging it beyond its minimum voltage range.
Keeping your electric car battery within the recommended voltage range will help to protect it from damage and extend its lifespan.
Voltage and Charging Infrastructure
Electric vehicles use Level 1 (110V), Level 2 (240V), and DC Fast Chargers (typically 400-800V) to recharge their batteries. The higher the voltage of the vehicle’s battery system, the faster it can recharge using appropriate fast chargers:
- Level 1 Charging (110V):
- Uses household outlets.
- Slow charging, often adding only a few miles per hour of charge.
- Level 2 Charging (240V):
- Common for home and public chargers.
- Adds about 20-40 miles of range per hour of charging for most vehicles with 400V systems.
- DC Fast Charging (400V and 800V):
- Ultra-fast public charging stations.
- Capable of adding hundreds of miles in 20-30 minutes depending on battery voltage and charging station capacity.
How to optimize electric car battery voltage range for maximum performance
As electric cars become more common, it’s essential to understand how voltage range affects their performance. The voltage range determines the distance an electric car can travel, and it’s essential to optimize it for maximum efficiency. A higher voltage range will allow the car to travel farther, but it also puts more strain on the battery.
The key is to find the sweet spot that delivers the best balance between distance and battery life. Manufacturers are continually working to improve this balance, but drivers can take steps to optimize their electric car’s voltage range themselves. This may include maintaining the battery appropriately, avoiding high-speed driving, and choosing the optimal route.
By paying attention to the voltage range, drivers can ensure that their electric car performs to its maximum potential while also extending its lifespan.
Comparing Electric Car Models Based on Voltage Range
Looking for an electric car? One of the key features you’ll want to consider is the battery voltage range. This range determines how far the car can travel before needing to be recharged. Different car models come with different voltage ranges, so you’ll want to compare them to find the one that meets your needs.
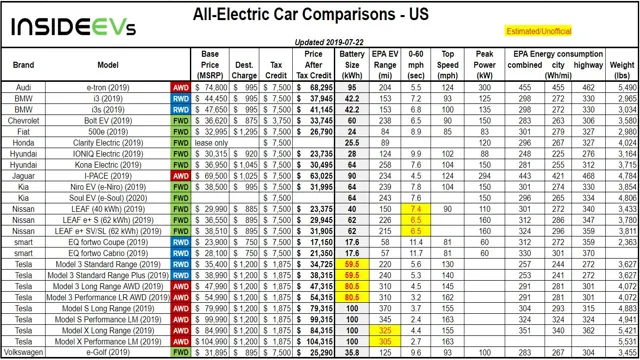
For example, the Nissan Leaf has a voltage range of around 150 miles, while the Tesla Model S can go up to 400 miles on a single charge. Keep in mind that driving habits and conditions can also affect the range, so be sure to factor in these variables when making comparisons. Ultimately, the voltage range will play a crucial role in determining the electric car that’s right for you.
Top electric car models and their voltage range specifications
When it comes to electric cars, one of the most important factors to consider is how far you can go before needing to recharge. This can vary widely depending on the specific model of electric car. For example, the Nissan Leaf has a voltage range of 110-220 volts and can go up to 150 miles on a single charge.
Meanwhile, the Tesla Model S has a much larger voltage range of 375-480 volts and can travel up to 402 miles on a single charge. Other popular electric car models like the Chevy Bolt and the Volkswagen ID.4 fall somewhere in between, with voltage ranges of 200-240 volts and 250-320 volts respectively.
Ultimately, the choice of electric car will depend on your specific needs and preferences, but it’s important to pay attention to voltage range and other key specifications when making your decision.
How to choose an electric car based on your driving habits and voltage range needs
When it comes to choosing an electric car, it’s important to consider your driving habits and the voltage range you’ll need. Comparing electric car models based on voltage range can help you find a car that meets your needs. Some models may have a higher voltage range than others, meaning they can travel farther on a single charge.
If you have a longer commute or frequently take road trips, it may be worth investing in a model with a higher voltage range. On the other hand, if you primarily use your car for shorter trips around town, a lower voltage range may be sufficient. Ultimately, the key is to find a car that fits your lifestyle and driving needs.
Future Trends in EV Battery Voltage
- Adoption of 800V Systems:
- As EV technology evolves, more manufacturers are expected to adopt 800V architectures, not just for performance models but for mainstream vehicles. This shift is motivated by the desire for faster charging and improved efficiency.
- High-Voltage Commercial Vehicles:
- The push toward electrifying heavy-duty trucks and buses will drive the development of systems with voltages exceeding 1000V. These vehicles need high power to carry heavy loads, and higher voltage systems reduce energy losses over long distances.
- Battery Technology Advancements:
- Innovations like solid-state batteries promise higher energy densities, which could enable further increases in voltage while maintaining or improving safety and longevity.
Conclusion: Importance of Voltage Range in Electric Cars
In conclusion, the voltage range of an electric car battery is like Goldilocks’ search for the perfect porridge – it can’t be too high or too low, but just right. Too high of a voltage can damage the battery and be dangerous, while too low of a voltage means the car won’t run. Just like finding the perfect balance in life, finding the perfect voltage range is key for a successful electric car journey.
So, remember, not too hot, not too cold, but just right!”
FAQs
What is the average voltage range for an electric car battery?
The average voltage range for an electric car battery is between 350 and 400 volts.
Can an electric car battery’s voltage range be increased?
Yes, electric car batteries can be designed with a higher voltage range, which can improve the vehicle’s overall performance.
What happens to an electric car battery if it goes beyond its voltage range?
If an electric car battery goes beyond its voltage range, it can cause damage to the battery and potentially become a safety hazard.
How can I determine the voltage range of my electric car battery?
You can determine the voltage range of your electric car battery by checking the specifications provided by the manufacturer or by consulting with a qualified electric car technician.