Driving towards the future: Everything you need to know about electric car battery voltages
Have you ever wondered about the voltage of an electric car battery? It’s an important aspect to consider when it comes to the performance and range of electric vehicles. With advancements in technology, electric cars have been able to travel further distances on a single charge, and this is largely due to the voltage of the battery. Electric car batteries typically have voltages ranging from 100-400 volts, with Tesla’s Model S having one of the highest voltages at 375 volts.
The voltage directly affects the power output of the electric motor, which in turn, affects the acceleration and top speed of the vehicle. It’s important to note that voltage is not the only factor in determining the range of an electric car. The weight of the vehicle, aerodynamics, and driving habits also play a significant role.
However, higher voltage batteries have been able to improve the efficiency of electric vehicles, reducing the amount of energy lost during charging and discharging cycles. In conclusion, understanding the voltage of electric car batteries is crucial when it comes to the performance and efficiency of the vehicle. Higher voltages can lead to greater power output and improved range, making electric cars a more viable option for daily use.
What Are Battery Voltages?
Electric car battery voltages vary depending on the type of battery used. Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in electric cars, have a nominal voltage of around 6-
7 volts per cell. A fully charged lithium-ion battery can have a voltage of around 2 volts per cell, while a completely discharged battery can have a voltage of around
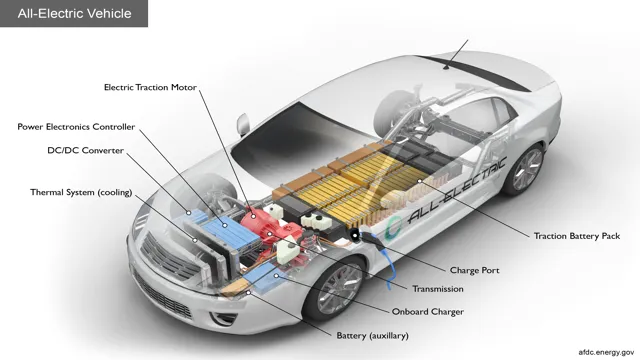
5 volts per cell. The total voltage of an electric car battery pack is determined by how many cells are connected in series. For example, a Tesla Model S uses 16 modules, each containing 74 cells in series, for a total of 1184 cells, resulting in a nominal voltage of around 355 volts.
Maintaining proper battery voltage is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of an electric car’s battery pack.
Explaining Different Levels of Voltages
Battery voltages refer to the amount of electric potential energy stored in a battery. Voltages can vary greatly depending on the type of battery, the number of cells it contains, and its chemistry. For example, a standard alkaline AA battery typically has a voltage of
5 volts, while a car battery can have a voltage of 12 volts. When multiple batteries are connected together in series, their voltages add up, creating a higher overall voltage. It’s important to note that voltage alone doesn’t determine the overall power or capacity of a battery, as other factors like current and resistance come into play.
Understanding different levels of voltages is important when choosing a battery for a specific device or application, as some devices require a specific voltage range to function properly.

Importance of Voltage for Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular all around the world. However, one thing that many people don’t know is how important voltage is for these vehicles. Voltage refers to the amount of electrical energy that a battery can generate and maintain.
It is crucial for electric vehicles, as it determines how much power the car can generate, and the distance that it can travel on a single charge. The battery voltage of a typical electric car is around 400 to 800 volts, which gives it plenty of power to function effectively. It is essential to have a high enough voltage to provide the necessary power to the electric motors, which power the wheels of the vehicle.
If the voltage is too low, the car will not be able to function properly, resulting in reduced performance, shorter driving distance, and even potentially damaging the vehicle’s battery. In summary, battery voltage is an essential factor to consider when it comes to electric cars. It determines the power and performance of the vehicle, as well as the distance it can travel on a single charge.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see newer, higher voltage batteries becoming available, further increasing the efficiency and reliability of electric vehicles across the globe.
Types of Electric Car Battery Voltages
When it comes to electric cars, one of the most important components is the battery voltage. Generally, there are two types of electric car batteries: high voltage and low voltage. High voltage batteries are typically used in electric vehicles with powerful electric motors.
These batteries usually range from 200 to 800 volts and are designed to provide a lot of power for a short amount of time. Low voltage batteries, on the other hand, are typically used in hybrid or mild hybrid electric vehicles. These batteries usually range from 36 to 144 volts and are designed to provide auxiliary power to the car’s systems like its lights, air conditioning, and infotainment systems.
It’s important to note that there are some electric vehicles that use both high and low voltage batteries. Regardless of the type of battery used, electric cars are expected to continue gaining in popularity as people seek more fuel-efficient and eco-friendly modes of transportation.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the primary type of battery used in electric cars today. But did you know that there are different types of voltages that these batteries can have? The most common voltage for electric car batteries is around 400 volts, with some models having a range of 300-500 volts. However, there are also higher voltage options, such as the Porsche Taycan which has a voltage of around 800 volts.
Higher voltage batteries can lead to better performance and faster charging times, but they can also be more expensive and require specialized equipment for maintenance. It’s important to consider the voltage of an electric car battery when purchasing a vehicle or looking to upgrade your current one, as it can affect the overall performance and cost of ownership.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the most commonly used batteries in electric cars, and they come in different voltages. The most common types of electric car battery voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V. The 12V lead-acid battery is mainly used to power the lights, stereo, and other accessories of the car.
It is the smallest and lightest among the three types of batteries, making it the most affordable and widely available. The 24V lead-acid battery is usually found in heavier vehicles and provides more power and longer-lasting charge than the 12V battery. The 48V lead-acid battery is the largest and most powerful of the three, providing high power efficiency and extended mileage to the vehicle.
The type of battery voltage used in an electric car depends on its size and power requirements, but lead-acid batteries are still an essential choice for many electric car manufacturers due to their affordability, reliability, and ease of maintenance. Nevertheless, newer types of batteries, such as lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride, have emerged as better alternatives due to their higher energy density, lighter weight, and longer lifespan.
Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel-metal hydride batteries have been widely used in electric vehicles due to their relatively low cost and high energy density. These batteries have a nominal voltage of 2 volts per cell, and the total battery voltage is determined by the number of cells connected in series.
Therefore, the voltage of nickel-metal hydride batteries used in electric vehicles varies from 100 volts to 400 volts depending on the specific vehicle design and the number of cells used. Higher voltages typically result in better performance and efficiency but require more sophisticated battery management systems to ensure proper charging and discharging of each cell. It’s important to note that nickel-metal batteries have been largely replaced by Lithium-ion batteries due to their lighter weight, higher energy density and longer cycle life.
Factors Affecting Electric Car Battery Voltages
Electric car battery voltages can be affected by several factors. One of the most significant is temperature. Extreme hot or cold conditions can cause the battery’s voltage to fluctuate, affecting the electric car’s performance.
Another factor is the age of the battery. As the battery ages, its capacity to hold a charge diminishes, leading to lower voltages. A third factor is the charging method used.
Fast charging can cause the battery’s voltage to spike, leading to decreased battery life over time. In contrast, slow charging can help maintain the battery’s voltage levels and overall health. It’s essential to keep all these factors in mind when utilizing an electric car, as they affect the battery’s voltage and overall lifespan.
By taking proper care of the battery and considering these factors, electric car owners can prolong the battery life and get the most out of their vehicle.
Temperature
Temperature is a crucial factor affecting electric car battery voltages. When the temperature is too high or too low, it can impact the battery’s performance and overall lifespan. High temperatures can cause the battery to overheat, leading to accelerated degradation and decreased capacity.
On the other hand, low temperatures can reduce the battery’s ability to deliver power efficiently. This is why it’s essential to maintain a suitable temperature range for the battery to function optimally. Electric car batteries are often equipped with thermal management systems to monitor and control the temperature, preventing damage to the battery pack.
By maintaining the right temperature range, electric car owners can extend their battery’s lifespan and ensure maximum performance. So, if you’re an electric car owner, make sure to keep an eye on the temperature to keep your car running smoothly.
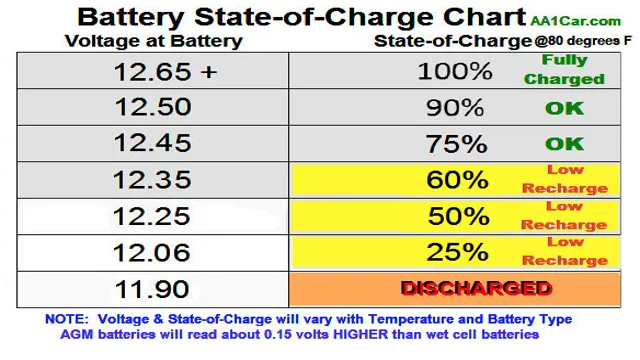
State of Charge
Keeping track of your electric car battery voltage is crucial to efficiently managing your vehicle’s overall State of Charge. As the name suggests, State of Charge indicates the percentage of charge stored in your battery. Several factors can affect your electric car battery’s voltage, including temperature, mileage, driving habits, and how often you charge it.
Driving at high speeds can result in a quicker loss of battery life than driving at lower speeds. Similarly, frequent acceleration and stop-and-go traffic can drain your electric car battery faster than smooth and consistent driving. If left unmanaged, these factors can cause your battery voltage to drop, resulting in reduced range and overall diminished performance.
Therefore, it’s essential to keep an eye on your battery voltage and take preventive measures to prolong its life for a better driving experience.
How to Check Electric Car Battery Voltages
If you own an electric car, it’s important to know how to check the battery voltages. Keeping an eye on the voltage can give you an idea of how much charge your battery has left and when it may need to be replaced. Fortunately, checking the voltage is a simple process that can be done with a multimeter.
First, locate the positive and negative battery terminals in your car. Connect the red lead from the multimeter to the positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal. Turn on the multimeter and switch it to the DC voltage setting.
The reading on the multimeter display will give you the voltage of your battery. Keep in mind that while a fully charged battery should read around 17 volts, a reading of 1
0 volts or lower may indicate that your battery needs to be charged or replaced. Regularly checking your electric car battery voltages can help you avoid unexpected breakdowns and ensure that your car runs efficiently.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric car battery voltages are more than just numbers on a screen. They represent the future of transportation and our society’s commitment to sustainable energy. So next time you hear someone talking about their electric car battery voltage, just remember that they’re not just showing off their fancy tech- they’re helping to pave the way towards a brighter, cleaner future.
“
FAQs
What is the average voltage of an electric car battery?
The average voltage of an electric car battery is around 300-400 volts.
How long does an electric car battery last?
The lifespan of an electric car battery depends on several factors such as usage, temperature, and maintenance. Generally, it lasts around 8-10 years or 100,000-200,000 miles.
Can you charge an electric car battery at home?
Yes, you can charge an electric car battery at home using a Level 1 or Level 2 charger. However, you may need to install a charging station for Level 2 charging.
How much does it cost to replace an electric car battery?
The cost of replacing an electric car battery varies depending on the make and model of the car and the capacity of the battery. Generally, it can range from $3,000 to $10,000. However, some manufacturers offer battery replacement programs or warranties that cover the cost of battery replacement.