Revolutionizing Green Transportation: The CO2 Battery-Powered Electric Cars
As we continue to make strides towards a greener future, electric cars have emerged as one of the most promising solutions. They’re eco-friendly, efficient, and fun to drive. However, the production of electric car batteries is not as environmentally friendly as one might think.
In fact, the batteries that power these vehicles are responsible for a significant amount of CO2 emissions. This begs the question: what impact do battery CO2 emissions have on the overall environmental impact of electric cars? To answer this question, we must first understand how batteries are made. The production of lithium-ion batteries involves mining for metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
The process of extracting these minerals can be energy-intensive and result in the emission of CO2 and other greenhouse gases. Additionally, the transportation of raw materials, the manufacturing process, and the end-of-life disposal of batteries can also contribute to emissions. So, how much CO2 do electric car batteries emit? Studies show that the production of batteries for electric cars emits anywhere from 70 – 200kg of CO2 per kWh of battery capacity.
This means that a mid-sized electric car with a 60 kWh battery emits between 2 and 12 tonnes of CO2 during production. However, it’s important to note that the emissions from battery production are still significantly lower than those of producing an Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) car over its lifetime.
In conclusion, while it’s clear that the production of electric car batteries does result in CO2 emissions, the overall environmental impact of electric cars is still far lower than that of traditional ICE cars. As technology continues to advance and we find ways to produce batteries more sustainably, the environmental impact of electric cars will continue to decrease. Nevertheless, it’s important for us to remain mindful of our individual impact on the environment and continue to advocate for sustainability in all aspects of our lives.
Understanding Battery CO2 Emissions
Electric cars are often seen as the solution to our environmental problems, as they are powered by electricity rather than gasoline. However, it is important to understand that the production of the batteries used in these cars does create carbon dioxide emissions. These emissions come from the manufacturing process of the battery cells, which involves mining, refining, transportation, and assembly.
The amount of CO2 emitted during this process can vary depending on the materials used and the location of the manufacturing plant. While electric cars still emit less CO2 when in use compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, it is important to consider the carbon footprint of the entire life cycle of the car, including the production and disposal of the battery. Overall, while electric cars do produce CO2 emissions during the battery production process, they are still a more environmentally friendly option compared to traditional gasoline vehicles.
CO2 Emissions During Battery Production
When it comes to creating sustainable technologies, it’s important to understand the impact they have on the environment. One key area of concern is the CO2 emissions produced during battery production. While batteries offer an eco-friendly way to power vehicles and other devices, they themselves require energy to create.
This energy is often generated from non-renewable sources, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. However, it’s important to note that battery production CO2 emissions can be reduced through the use of renewable energy sources in manufacturing processes. Additionally, efforts to improve battery efficiency and lifespan can also result in lowering overall CO2 emissions.
As we continue to push for a more sustainable future, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of all technologies, including batteries.

CO2 Emissions During Battery Charging
When it comes to understanding battery CO2 emissions during charging, it’s important to first understand the types of batteries most commonly used. Lithium-ion batteries are one such type which have become increasingly popular in recent years thanks to their ability to store large amounts of energy in a small space. However, it’s also important to consider the carbon footprint associated with charging these batteries.
CO2 emissions are released during the production of electricity used to charge lithium-ion batteries, so it’s important to consider the type of electricity that is being used. Renewable electricity sources such as solar and wind power can reduce CO2 emissions significantly. Additionally, it’s important to note that the level of CO2 emissions during battery charging can vary depending on the location and time of day.
Overall, understanding the carbon footprint associated with battery charging can help us make informed decisions about our energy usage and move towards a more sustainable future.
Measuring the CO2 Footprint of Electric Cars
When it comes to electric cars, one of the biggest advantages they have over traditional gas-powered vehicles is their reduced carbon footprint. But how do we measure just how much carbon dioxide (CO2) an electric car produces? One factor is the battery. The production of batteries requires significant energy, often resulting in the emission of greenhouse gases.
However, studies have shown that the CO2 emissions from producing an electric car battery are offset by the emissions saved from driving an electric car in the long run. Another consideration is the source of the electricity used to charge the car. If the electricity comes from renewable sources such as solar or wind power, the carbon footprint is drastically reduced.
But if the electricity comes from fossil fuels, then the emissions are comparable to those of a gas-powered car. Overall, while electric cars have their own environmental impacts, they are still a much cleaner option compared to internal combustion engine vehicles.
Comparing CO2 Emissions of Electric and Gasoline Cars
When it comes to measuring the carbon footprint of electric cars, it’s important to take into account not only the emissions produced during its use but also during its production and disposal. While it’s true that electric cars don’t have tailpipe emissions like gasoline cars, the production of their batteries does produce carbon emissions. However, studies have shown that even with the emissions produced during production, electric cars emit significantly less CO2 over their lifetime compared to gasoline cars.
In fact, a study in Norway found that even with their electricity sourced from fossil fuels, electric cars produce less CO2 than gasoline cars. So, when it comes to reducing your carbon footprint, switching to an electric car is a step in the right direction.
Factors Affecting Electric Car CO2 Emissions
When it comes to measuring the CO2 footprint of electric cars, there are a few factors that come into play. Firstly, the source of the electricity used to power the car plays a major role in determining its overall CO2 emissions. If the electricity is generated from renewable sources such as solar or wind power, then the CO2 emissions from the car will be significantly lower compared to if it is generated from fossil fuels.
Another factor that affects the CO2 emissions of electric cars is the type of battery used. Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in electric cars, require a significant amount of energy to manufacture and dispose of, which contributes to the car’s overall carbon footprint. However, research is being conducted to develop more eco-friendly battery technologies.
Overall, while electric cars have the potential to significantly reduce CO2 emissions, it is important to consider the various factors that contribute to their overall carbon footprint in order to make informed decisions about the environmental impact of electric vehicles.
Real-World CO2 Emissions of Popular Electric Car Models
Electric cars have been touted as a greener alternative to their fossil fuel-consuming counterparts, promising zero-emissions during driving. Yet, the production and electricity generation involved in the manufacturing and charging of electric cars still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. As such, it is important to measure the real-world CO2 emissions of electric cars, and many popular models have been put to the test.
Studies have shown that electric cars emit lower amounts of CO2 than traditional cars on average, but the exact amount varies depending on factors such as country of production, electricity sources, and manufacturing processes. It is important for consumers to consider these factors when choosing an electric car model to minimize their environmental impact and drive towards a more sustainable future.
Reducing the CO2 Footprint of Electric Cars
Electric cars are considered more environmentally friendly than traditional gas-powered vehicles, but they still contribute to carbon emissions through the production of their batteries. However, there are measures being taken to reduce the CO2 footprint of electric cars. One way is to use materials that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly in the production of the batteries.
This includes using recycled metals and reducing the amount of rare earth elements used in the battery production process. Another way to reduce the CO2 footprint of electric cars is through the use of renewable energy sources for charging the vehicle. By using solar panels or wind turbines to power the charging stations, the energy used to charge the vehicle is not only carbon-free but also reduces the overall carbon emissions of the vehicle.
These measures can ultimately reduce the CO2 footprint of electric cars, making them even more environmentally friendly.
Advances in Battery Technology
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as people seek to reduce their carbon footprint and help combat climate change. Advances in battery technology have been crucial in making these cars more practical and efficient. Lithium-ion batteries are the preferred choice for most electric cars, but there are concerns about the environmental impact of their production and disposal.
To address these concerns, researchers are developing new battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, that use more sustainable materials and are less harmful to the environment. These batteries also have the potential to store more energy, increase range, and reduce the cost of electric cars. With continued innovation, electric cars could soon become the norm, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality.
Renewable Energy Sources for Charging Electric Cars
As electric cars gain popularity, it’s essential to consider the carbon footprint they leave behind. Luckily, there are renewable energy sources that can be used to charge electric cars, reducing their CO2 impact. Solar power is an obvious choice, as it is an environmentally-friendly and sustainable source of energy.
By installing solar panels, you can generate electricity from the sun’s rays and charge your electric car with this energy. Wind energy is another renewable option, with wind turbines forming part of an ever-increasing number of energy installations worldwide. Hydroelectricity also presents an attractive option, using the flow of water to power turbines and generate clean, renewable electricity.
By using these renewable energy sources, there is an opportunity to reduce the environmental impact and promote a sustainable future.
Conclusion: The Future of Electric Cars and CO2 Emissions
In conclusion, the use of an electric vehicle powered by a CO2 battery is not only a practical and environmentally-friendly solution, but also a clever way to reduce carbon emissions without sacrificing convenience and performance. The future of transportation lies in innovation and advanced technology, and it’s exciting to see the progress being made in the realm of electric vehicles. With the CO2 battery, we’re one step closer to achieving a greener, cleaner world.
“
FAQs
How do electric cars help in reducing CO2 emissions?
Electric cars run on batteries that do not emit any greenhouse gases which directly contribute to CO2 emissions. Hence, they are considered an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline cars.
How long does the battery of an electric car last?
The lifespan of the battery in an electric car depends on several factors such as the type of battery, how often it is charged, how it is used, and the climatic conditions. On average, the battery life can range from 8 to 10 years.
How is the CO2 footprint of electric cars compared to gasoline cars?
While electric cars do not emit any CO2 during their use, the production of the batteries and the electricity needed to charge them can lead to CO2 emissions. However, studies have shown that even with the production emissions considered, electric cars still have a lower CO2 footprint than gasoline cars.
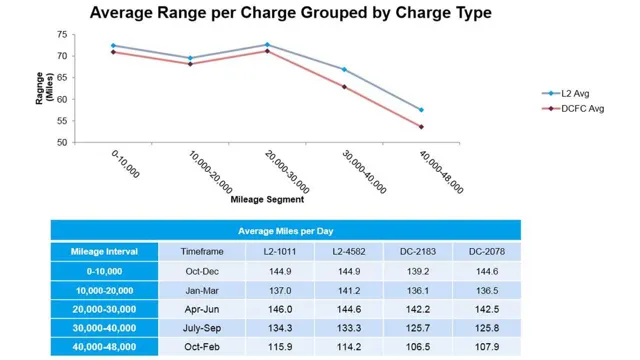
What is the range of an electric car on a single charge?
The range of an electric car on a single charge depends on the battery capacity and the make and model of the car. On average, electric cars can travel between 100 and 300 miles on a single charge. However, some high-end models can go up to 400 miles on a single charge.