The Shocking Truth: A Fascinating Look at the Early Days of Electric Cars
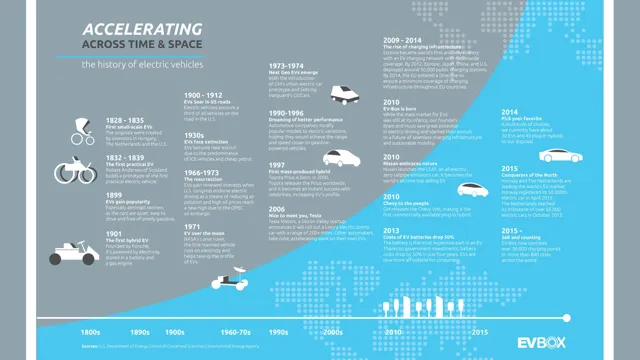
Have you ever wondered about the early history of electric cars? Before the popularization of gasoline-powered vehicles, there were electric vehicles humming down city streets. In fact, electric cars were the chosen mode of transportation for many people at the turn of the 20th century. Despite their early advantages, these early electric cars faded into obscurity as gasoline engines became more prevalent.
But why? To uncover this historical mystery, let’s take a closer look at the early days of electric cars. We’ll explore the various advantages they held over gasoline vehicles, such as their quiet operation and the absence of the exhaust fumes that plagued their gasoline counterparts. Despite these advantages, however, electric cars began to fall out of favor in the early 1900s, with the rise of cheaper, more accessible gasoline engines taking their place.
Even so, the world is experiencing a resurgence of electric cars in recent years, and it’s interesting to reflect on the long history of these environmentally-friendly vehicles. By examining the historical context that gave rise to electric cars, we can better understand the current challenges and opportunities facing this innovative technology. So, let’s dive into the fascinating history of early electric cars and discover what made them such a revolutionary force in the transportation world.
Invention of Electric Cars
The early history of electric cars goes back to the early 19th century, when inventors started experimenting with battery-powered vehicles. A Scottish inventor named Robert Anderson built the first electric car prototype in the 1830s, while French engineer Gustave Trouvé developed an electric tricycle in 188 However, it was Thomas Davenport, an American inventor, who built the first practical electric motor in 183
In the late 1800s, electric cars were quite popular in cities, as they were quiet and clean compared to the noisy and smelly gasoline-powered cars of the time. However, the invention of the electric starter for gasoline engines in 1912 made gas-powered cars easier to use and more popular. It was not until the 1990s that electric cars regained attention, as concerns about air pollution and global warming grew.
Today, electric cars are becoming more commonplace, thanks to advancements in battery technology and increasing awareness of the need for sustainable transportation.
Thomas Davenport’s Electric Motor
In the late 19th century, the invention of the electric motor by Thomas Davenport sparked the possibility of electric cars. The electric motor allowed for the creation of a viable and more sustainable alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. At the time, electric cars had several advantages over traditional cars, as they were quiet, didn’t produce emissions, and didn’t require a hand crank to start.
Unfortunately, electric car technology was hindered by the high cost of batteries and the limited distance an electric car could travel on a single charge. However, advancements in battery technology and the increasing demand for sustainable transportation options has led to a resurgence of interest in electric cars. With companies like Tesla leading the way, electric cars are once again on the forefront of automotive innovation and sustainability.
As we continue to prioritize environmentally conscious practices, electric cars may become the norm rather than the exception.

Robert Anderson’s Electric Carriage
In the late 1800s, Robert Anderson invented the world’s first electric carriage, laying the groundwork for the modern electric car. This groundbreaking invention came at a time when people were still using horse-drawn carriages and steam-powered locomotives for transportation. Anderson was one of the first to recognize the potential of electric power as a viable alternative to fossil fuels.
His electric carriage was powered by a battery stored beneath the passenger seat, which could travel up to a distance of six miles at speeds of up to four miles per hour. At the time, it was considered a marvel of technology and drew the attention of many curious onlookers. Although Anderson’s electric carriage wasn’t practical enough for long distance travel, it paved the way for future electric car inventions to come.
Today, electric cars have become increasingly popular and a more eco-friendly option than traditional gasoline cars, championing environmentally conscious transportation solutions.
Rise and Fall of Electric Cars
The early history of electric cars dates back to the 19th century, with inventors like Thomas Davenport and Robert Anderson creating early versions of electric vehicles. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric cars really took off, with companies like Baker Electric and Detroit Electric producing popular models. These electric cars were known for their ease of use and low maintenance requirements, making them a popular choice for the upper class.
However, the rise of the internal combustion engine and the mass production of gasoline-powered cars led to a decline in electric car popularity in the early 1900s. It wasn’t until the 1990s that electric cars started to make a comeback, with the introduction of models like the GM EV1 and the Toyota RAV4 EV. Today, electric cars are becoming more and more popular due to concerns over climate change and the increasing availability of charging infrastructure.
Despite their early rise and fall, it seems that electric cars are here to stay.
Competition with Gasoline Cars
The competition between electric cars and gasoline vehicles has been ongoing for over a century, but it wasn’t until the rise of the electric vehicle in the early 2010s that this competition truly picked up steam. In the beginning, electric cars were lauded as a cleaner and more efficient alternative to gasoline-powered automobiles. However, the high cost of batteries and limited range proved to be major obstacles in the widespread adoption of electric cars.
As a result, the popularity of electric cars declined in the mid-20th century with the emergence of cheaper gasoline vehicles. Nonetheless, with advancements in battery technology and Tesla’s early success in electric car manufacturing, electric cars look to make a comeback. While gasoline cars still reign supreme in terms of convenience and range, it’s only a matter of time before the advantages of electric cars outweigh those of their gasoline-powered counterparts.
It’s clear that the future belongs to electric cars, and sooner or later, those driving gasoline cars may be left in the rearview mirror.
Fate of Electric Cars in the 20th Century
“Electric Cars in the 20th Century” The 20th century saw the rise and fall of electric cars, but what led to their decline? In the early 1900s, electric cars were popular, especially in cities where their quiet and clean operation was a welcome relief from the noise and pollution of gas-powered vehicles. However, the proliferation of cheap oil and the invention of the electric starter for internal combustion engines led to the dominance of gasoline-powered cars. Additionally, electric cars’ limited driving range and long recharging times made them inconvenient for long-distance travel.
Despite advancements in battery technology, electric cars had become an afterthought and niche market by the 1930s. However, interest in electric cars resurfaced in the 1990s, and with the advent of lithium-ion batteries, electric cars became a serious challenger to gas-powered vehicles. Today, electric cars are more popular than ever, and with continued advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure, electric cars’ future is looking bright.
Role of Electric Cars during World War II
Electric cars played a significant role during World War II, mainly due to the fuel and material shortages caused by the war. In fact, electric vehicles saw a rise in popularity during this time, as they were more cost-effective and efficient than gasoline-powered cars. However, as the war came to an end, so did the popularity of electric cars.
The availability of gasoline increased, making it a more viable option for consumers. Cars with internal combustion engines also had a greater range and were more convenient for long-distance travel. As a result, the demand for electric cars declined rapidly, and the industry almost disappeared entirely.
Today, we are seeing a resurgence of interest in electric cars, as concerns about the environment and rising fuel costs have led consumers and manufacturers to consider alternative modes of transportation. These vehicles offer a cleaner and more sustainable option, which is crucial as we move towards a future that is more environmentally conscious.
Revival of Electric Cars
The early history of electric cars is fascinating. Although electric vehicles (EVs) seem like a modern innovation, they were actually first developed in the mid-19th century. In fact, the first electric car was built by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson as far back as 1832! However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric cars started to become more common on the roads.
At first, they were popular with wealthy city dwellers who appreciated their quiet, clean operation. However, their limitations in terms of battery range, speed, and charging infrastructure made them less practical for the average person. As internal combustion engines improved and oil became easier to extract and refine, gasoline-powered cars became the norm, and electric cars fell out of favor.
Nevertheless, in recent years, electric cars have experienced a major revival. Thanks to advances in battery technology, they now have longer ranges, faster charging times, and improved performance. Plus, with growing concerns about climate change, air pollution, and energy security, more and more people are turning to electric cars as a cleaner, greener alternative to traditional vehicles.
Adoption of Hybrid Electric Cars
The adoption of hybrid electric cars has been on the rise in recent years, bringing a revival of electric cars. With growing concerns about climate change and rising fuel costs, more and more people are turning to electric and hybrid cars as a way to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on fuel. These cars are ideal for city driving and short trips, as they use electricity for short distances and switch to gasoline for longer journeys.
The technology used in hybrid electric cars has come a long way in recent years, with more efficient battery storage and better charging infrastructure making it easier for people to own and use electric cars. With the success of companies like Tesla, electric cars are becoming more mainstream and accessible than ever before. As more people adopt hybrid electric cars, we will continue to see a positive impact on the environment and a decline in our dependence on fossil fuels.
This is a win-win situation for both drivers and the planet.
Introduction of Modern Electric Cars
Electric Cars
Future of Electric Cars
The early history of electric cars can be traced back to the 1800s when inventors started experimenting with battery-powered vehicles. In fact, the first known electric car was built by Thomas Davenport in 183 It wasn’t until the late 1800s and early 1900s that electric cars became more widely available and popular.
However, the introduction of gasoline-powered cars by Henry Ford and others caused a decline in the popularity of electric cars. Despite this setback, electric cars continued to be developed and improved over the years. With advancements in battery technology and a growing concern for the environment, electric cars are now on the rise once again.
The future of electric cars is looking bright, as more and more people are choosing electric vehicles for their eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness. It’s clear that the early history of electric cars paved the way for a brighter future in sustainable transportation.
Conclusion
In the early history of electric cars, we see a shining example of human beings’ desire to innovate and overcome obstacles. From humble beginnings to high tech advancements, electric cars have come a long way. Despite the initial setbacks, the technology has proven itself to be versatile and eco-friendly, deserving a second chance in today’s world.
It’s an integral part of the transportation industry today, and as we progress further into the future, we are sure to find even more ingenious ways to harness the power of electricity and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. So let’s all raise a glass to the early pioneers of this electric car revolution, and their steadfast commitment to creating a cleaner, greener future for us all.”
FAQs
What is the history of electric cars?
Electric cars have been around since the early 19th century, with some of the earliest designs being developed in Hungary, the United States, and the Netherlands. However, they did not become practical until the development of rechargeable batteries in the 1990s.
How do electric cars work?
Electric cars use an electric motor and a rechargeable battery pack to power the vehicle. When the battery is depleted, it can be recharged using an external power source.
What are the benefits of driving an electric car?
Electric cars are more environmentally friendly than traditional gas-powered cars, as they emit less pollution and use less fuel. They can also be more cost-effective in the long run, as electricity is cheaper than gasoline in many areas.
What is the range of an electric car?
The range of an electric car can vary depending on the model and battery type. Some electric cars can travel up to 300 miles on a single charge, while others may have a range closer to 100 miles. Advances in battery technology continue to improve the range of electric cars.