Electrifying Evolution: Tracing the Fascinating History of Electric Cars
If there’s one thing that’s clear about the automotive industry, it’s that technology never stops advancing. And with the increasing emphasis on sustainability, electric cars are becoming more and more popular. But how did this all begin? The history of electric cars is a fascinating and often overlooked topic that sheds light on just how far we’ve come in terms of vehicle technology.
From early prototypes in the 1830s to the first successful electric car in the late 1800s, we’ve come a long way in a relatively short amount of time. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the history of electric cars and explore the key moments that led us to where we are today. So buckle up and let’s take a trip down memory lane!
Early experiments with electric vehicles
The history of the electric car dates back as early as the 1830s when inventors started creating the first experiments with electric vehicles. While it wasn’t until much later that electric cars were mass-produced and considered as a feasible option for personal transportation, these early experiments laid the groundwork for the technology we have today. One such inventor was Thomas Davenport, who in the late 1830s built a small electric motor that could power a model car.
However, it was a Scottish inventor named Robert Anderson who is credited with creating the first crude electric vehicle prototype in the early 1830s. His electric carriage used non-rechargeable cells to power its electric motor. Early experiments with electric cars showed promise, but the technology was still quite limited.
Electric vehicles wouldn’t become popular until the early 1900s when advancements in technology could make electric cars more practical and accessible. Nonetheless, today’s electric cars have come a long way since those first early experiments.
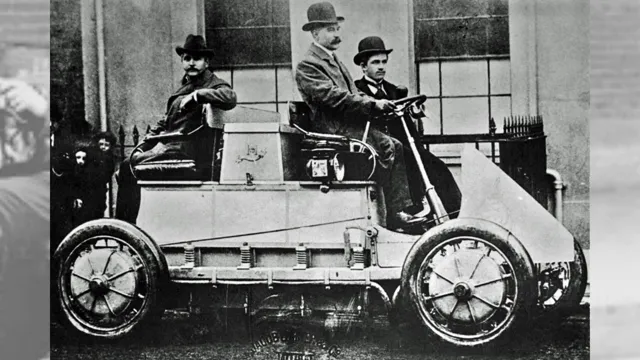
Thomas Davenport’s prototype in 1834
Electric vehicles have been a topic of interest for over a century now. Back in 1834, Thomas Davenport designed the first electric car prototype in the US. It was a small locomotive that ran on a circular electrified track and had a top speed of 4 miles per hour.
Although it was a primitive design, it marked the beginning of electric vehicle technology. Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, many other inventors and scientists continued to experiment with the concept of electric vehicles, but gasoline-powered cars eventually became more popular due to their longer range. However, with advancements in battery technology and concern for the environment, electric cars are making a comeback in recent times.
Now, electric cars have a longer range, better performance, and are more affordable than ever before. It’s exciting to see how far electric vehicles have come since Davenport’s prototype over 180 years ago, and it makes one wonder what the future holds for this innovative technology.

First practical electric car built in 1884
The first practical electric car was built way back in 1884 by Thomas Parker, an English inventor. However, experiments with electric vehicles had already begun decades earlier. In the early 1800s, inventors like Thomas Davenport and Robert Anderson were working on small electric cars, but they were not practical for everyday use due to their limited range and speed.
It wasn’t until the development of the rechargeable battery in the 1860s that electric cars began to become more viable. Even then, they were still considered a luxury item for the wealthy, as they were costly and required special charging infrastructure. Despite these limitations, electric cars continued to gain popularity throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
In fact, by 1900, electric cars made up around one-third of all vehicles on the road in America. However, with the rise of the gas-powered automobile and cheap oil, electric cars were quickly overtaken and largely forgotten until recent years. Fortunately, the humble beginnings of electric vehicles have paved the way for the modern, environmentally friendly electric vehicles we know today.
Growth and decline of electric cars in the early 1900s
The history of the electric car dates back to the early 1900s when they were introduced as a viable alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. At the time, electric cars were more popular than gas-powered cars because they were quieter, easier to operate, and required less maintenance. In fact, in 1900, electric cars made up one-third of all vehicles on the road in the United States.
However, the growth of electric cars was short-lived because they had limited range and were expensive to produce. With the discovery of oil in Texas in 1901, gasoline became the primary fuel source, and the electric car industry declined. It wasn’t until the 1990s that electric cars began to reemerge as a viable option with the introduction of more advanced battery technology.
Now, with concerns about climate change and the push towards renewable energy sources, electric cars are once again gaining popularity as a sustainable transportation option.
Electric cars peak at a third of all cars, but decline with introduction of gasoline engine
In the early 1900s, electric cars experienced significant growth and then a decline as gasoline-powered engines were introduced. At their peak, electric cars made up a third of all cars on the road, but their popularity dwindled as gas engines became more prevalent. Some of the reasons for their fall from grace included limitations in battery technology, limited range, and long charging times.
Additionally, gas-powered cars were cheaper and had more power than early electric cars. Despite these setbacks, electric cars continued to be popular in certain industries, such as urban transportation and delivery services. Eventually, advancements in battery technology and a renewed focus on sustainability brought electric cars back into the mainstream in recent years, and they are now seen as a viable alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles.
As we continue to face environmental challenges and a need for cleaner energy sources, electric cars are likely to see continued growth and adoption.
Resurgence of electric cars due to environmental concerns
Electric cars have been around for over a century, but they haven’t always been as popular as they are today. In the early 1900s, electric cars were actually quite common, but their popularity dwindled as gasoline-powered cars became more accessible and affordable. However, with the rise of environmental concerns such as global warming and air pollution, electric cars have once again come into the spotlight as a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
In recent years, we have seen a resurgence of electric car use, with more and more people opting for electric vehicles to reduce their carbon footprint and protect the planet. With advancements in battery technology and infrastructure, it’s easier than ever to charge and drive electric cars, making them a convenient and sustainable choice for many drivers. As we continue to prioritize the health of our planet, it’s likely that we will see the continued growth of electric cars as a sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
GM’s EV1 and California’s Zero Emission Vehicle mandate
The growth and decline of electric cars can be traced back to the early 1900s, when they first hit the market. At the time, gasoline-powered cars were also becoming increasingly popular, but electric cars were the preferred mode of transportation due to their quiet operation and lack of exhaust fumes. However, as the technology for gasoline-powered cars improved, electric cars began to decline in popularity.
Fast forward to the 1990s and GM’s introduction of the EV1, which was an attempt to bring electric cars back into the mainstream. The California Zero Emission Vehicle mandate required automakers to produce a certain number of zero-emission vehicles, and GM saw an opportunity to meet that demand. However, the EV1 ultimately failed due to limited range, high production costs, and lack of adequate charging infrastructure.
While electric cars have had their ups and downs over the years, recent advancements in technology have led to increased interest and demand for these vehicles. As we look toward the future, it is clear that electric cars will play a significant role in the transportation industry.
Modern electric vehicles and the future
The history of the electric car dates back to the late 1800s when inventors started experimenting with electric engines as an alternative to the internal combustion engine. The first electric car was developed by Thomas Davenport in 1835, but it was not until the late 19th century that electric cars saw actual production. At the time, electric cars had some advantages over gasoline-powered cars, such as low noise and emissions, and easy maintenance.
In the early 20th century, however, gasoline cars became more popular due to advancements in technology that made them more efficient and affordable. Electric cars remained a niche alternative until the 21st century, when their popularity resurged due to concerns about climate change and air pollution. Today, modern electric vehicles have come a long way with improved driving range and battery technology.
With their environmental benefits and increasing affordability, many industry experts believe that electric cars will be the future of transportation.
Tesla’s push for electric cars
Tesla’s push for electric cars has revolutionized the automotive industry. Their mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy, and they are accomplishing this through their sleek and modern electric vehicles. With each new release, Tesla continues to push the boundaries of what is possible with electric cars.
These vehicles use advanced battery technology to provide a longer range, faster acceleration, and a smoother ride than traditional gas-powered cars. The future looks bright for electric cars, as more and more people are seeing the benefits of owning one. Not only are they better for the environment, but they also save money in the long run on gas and maintenance costs.
As Tesla continues to lead the charge towards sustainable energy, we can expect to see more innovative electric cars on the road in the years to come.
Increasing popularity and availability of hybrid and fully electric vehicles
The rise of hybrid and electric vehicles is a significant transformation in the automotive industry. With the growing concern for the environment and the need to reduce carbon emissions, modern electric vehicles are becoming more popular and accessible. These vehicles offer excellent benefits such as high performance, energy efficiency, and lower maintenance costs.
In the future, more car manufacturers are expected to introduce new models of electric vehicles, and this will transform the way people think about vehicles and transportation. The increasing availability of electric charging stations will enhance the accessibility and convenience of using electric vehicles. Furthermore, the advancement of battery technology will improve the driving range and accelerate the adoption of electric cars.
It is exciting to see the future of electric vehicles and the possibilities that await us. With the growing need to protect our environment, electric vehicles are the best solution as they reduce our carbon footprint while still providing an enjoyable driving experience.
Conclusion: The future of the electric car
After a century of ups and downs, the electric car is finally back in the driver’s seat. Despite facing numerous obstacles throughout history, including technological limitations and a lack of public interest, the electric car has proven time and time again that it’s a force to be reckoned with. With advancements in battery technology, the growing demand for clean energy vehicles, and a renewed commitment from automakers to invest in electric cars, it’s clear that this is only the beginning of a bright new chapter in the history of the electric car.
So plug in, buckle up, and get ready for the ride of your life!”
FAQs
What is the history of the electric car?
The first electric car was built in 1837 by Robert Davidson, but it wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s that electric cars started to become more widely available.
How do electric cars work?
Electric cars run on an electric motor powered by a rechargeable battery. They use electricity stored in the battery to power the motor and move the car.
Are electric cars better for the environment than gasoline cars?
Yes, electric cars produce zero emissions while driving, so they are much better for the environment than gasoline cars, which emit harmful pollutants.
What is the range of an electric car?
The range of an electric car varies depending on the make and model, but most electric cars can travel between 100 and 300 miles on a single charge.