The Shocking Evolution of the Electric Car Battery: A Fascinating Journey Through History
Have you ever wondered about the history of the electric car battery? As our world moves towards more sustainable and eco-friendly modes of transportation, understanding the evolution of the electric car battery becomes increasingly important. The history of the electric car battery dates back to the late 1800s, with early experiments in rechargeable batteries, and the development of lead-acid batteries in the early 1900s. However, the major breakthrough in electric car battery technology came in the 1990s with the introduction of the nickel-metal hydride battery, which allowed for longer driving ranges and faster charging times.
Today, there are a variety of electric car battery options available, including lithium-ion batteries which dominate the market. These batteries offer even greater capacity and faster charging times than their predecessors, making electric cars increasingly practical for everyday use. However, as we continue to innovate in the realm of electric car battery technology, there are still many questions about the environmental impact of their production and disposal.
Despite these concerns, the electric car battery remains an important piece of the puzzle in our journey towards a more sustainable future. Join us as we explore the fascinating history of this powerful little device!
Early Years
The history of the electric car battery dates back to the early 19th century. While many experimenters worked on creating batteries, it was not until the late 1800s that the first rechargeable batteries were invented. Lead-acid batteries became the go-to for electric vehicles in the early 20th century, but their weight and limited range made them impractical for most drivers.
In the 1990s, the invention of the nickel-metal-hydride battery spurred interest in electric cars again, but it wasn’t until the 21st century that lithium-ion batteries revolutionized the industry. Today, electric car batteries continue to evolve, with rapid charging and longer ranges becoming more commonplace. As the world shifts towards more sustainable modes of transportation, the history of the electric car battery remains an important part of the story.
Lead-acid battery invented in 1859
The lead-acid battery, which is still widely used today, was invented by French physicist Gaston Planté in 185 It was the first rechargeable battery and a significant advancement in energy storage technology. The early years of the lead-acid battery were marked by experimentation and refinement, as scientists and engineers tried to improve the battery’s performance and make it more practical for commercial use.
Planté initially used pure lead and lead oxide electrodes, which were immersed in diluted sulfuric acid. He discovered that when he charged the battery, the lead oxide electrode became coated in lead dioxide, which improved its capacity to store energy. Over time, researchers found ways to make the battery more efficient, durable, and affordable, and it became an essential component of many industries, including telecommunications, transportation, and backup power systems.
Today, the lead-acid battery remains one of the most reliable and cost-effective energy storage solutions on the market, powering everything from cars to submarines to off-grid homes.
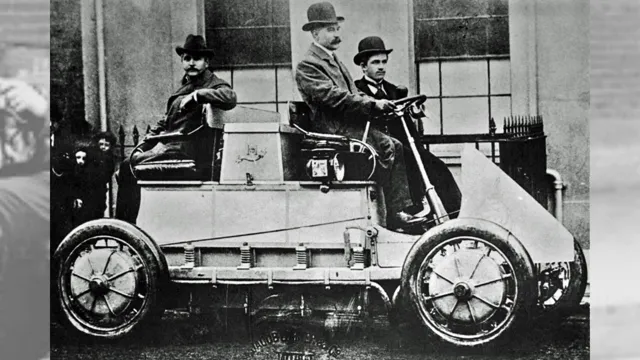
First electric car built in 1884
The early years of electric cars go back all the way to 1884 when the first one was built by British inventor Thomas Parker. The vehicle had a top speed of about 14 miles per hour and was powered by lead-acid batteries, very similar to the ones used in cars today. Parker’s electric car was a significant milestone because it showed that the technology was feasible and had great potential for future development.
The early electric cars, although crude by today’s standards, were much more practical than their gasoline counterparts and were more popular in the cities, especially in Europe. The electric car industry had a surge of growth during the early 1900s with many manufacturers producing several different models. However, the advent of the internal combustion engine and the discovery of cheap and abundant oil made gasoline cars more practical and affordable.
Nonetheless, Parker’s electric car laid the foundation for the electric cars of today, which are becoming more popular as people look for greener alternatives to traditional transportation.
Mid-20th Century
In the mid-20th century, there was a significant breakthrough in the history of the electric car battery. While lead-acid batteries had been the norm, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries were developed and became the new standard. These batteries were lighter, had higher energy densities, and were more efficient than lead-acid batteries.
However, the emergence of NiMH batteries was short-lived due to patent disputes between the companies that owned the technology. As a result, the development of electric vehicles stagnated for several years until the development of lithium-ion batteries, which are still used in electric cars today. Despite the setbacks, the mid-20th century was an important time in the development of electric vehicle battery technology, paving the way for the advancements we see today.
Nickel-cadmium battery introduced in 1947
The mid-20th century was a time of great technological advancements, with new and exciting inventions emerging left and right. One such invention was the nickel-cadmium (NiCd) battery, which was first introduced in 194 This battery was revolutionary for its time, as it was the first rechargeable battery to be widely available to consumers.
Prior to its introduction, most batteries were disposable, so the NiCd battery provided a much more efficient and cost-effective solution. It quickly became popular for a wide range of applications, from portable electronics to electric vehicles. Despite its popularity, the NiCd battery did have some drawbacks – it was relatively heavy and had a tendency to suffer from the “memory effect,” which could reduce its overall lifespan.
However, these drawbacks did little to diminish the impact that the NiCd battery had on the world of technology, and it remains an important milestone in the history of battery technology.
Nickel-metal hydride battery introduced in 1967
In 1967, scientists made a major breakthrough in the development of batteries with the introduction of the nickel-metal hydride battery. This new type of battery was created to address the limitations of existing batteries at the time, such as the lead-acid battery used in many automobiles. Nickel-metal hydride batteries offered a higher energy density, meaning they could store more electrical energy in a smaller size.
This made them ideal for use in portable electronic devices such as cameras and cell phones. Additionally, nickel-metal hydride batteries were believed to be more environmentally friendly than traditional batteries. Despite their many advantages over older battery technology, nickel-metal hydride batteries had some limitations of their own, such as a shorter lifespan and decreased performance in extreme temperatures.
However, they paved the way for further advancements in battery technology in the latter half of the 20th century.
Recent Advances
In recent years, there have been significant advances in the history of the electric car battery. The development of high-capacity lithium-ion batteries has revolutionized the electric car industry, making electric vehicles a more viable option for everyday drivers. This type of battery is incredibly energy-dense and can store a large amount of power in a small space, allowing electric cars to have longer ranges and faster charging times.
Additionally, the use of solid-state batteries has shown promise in overcoming some of the limitations of traditional lithium-ion batteries, such as safety concerns and performance degradation over time. With ongoing research and development in the field of electric car batteries, it is exciting to see what new advances will emerge in the future. As the demand for clean energy sources grows, the history of the electric car battery continues to evolve and innovate to meet the needs of modern society.
Lithium-ion battery introduced in 1991
The invention of the lithium-ion battery in 1991 revolutionized the way we think about portable electronics. These batteries are lighter, more compact, and have a higher energy density than their predecessors. This makes them perfect for modern devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and electric cars.
The recent advances in lithium-ion battery technology have focused on improving their efficiency, safety, and lifespan. Scientists are working on developing solid-state lithium-ion batteries, which are safer and more durable than traditional batteries. They are also experimenting with new materials for the cathode and anode, which can increase the battery’s energy density.
In addition, researchers are exploring ways to make lithium-ion batteries more environmentally friendly by using sustainable materials and recycling them more efficiently. These advances are critical for achieving a sustainable future, and the lithium-ion battery will undoubtedly play a significant role in this effort.
Improvements in energy density and cost
Recent advances in battery technology have allowed for significant improvements in energy density and cost, making batteries more efficient and cost-effective. For instance, new types of lithium-ion batteries use cobalt, nickel, and manganese to increase energy density, which allows for smaller and lighter batteries to store and deliver more energy. Additionally, the usage of silicon and graphene in battery components increases their energy capacity and allows for faster charging times.
Moreover, the rise of renewable energy systems has led to more research into improving the performance of energy storage technologies, which has also helped to drive down the cost of batteries. These developments are essential for the transition to a cleaner energy future, as they will encourage more widespread adoption of battery technologies and make renewable energy systems more cost-effective and efficient.
Future Prospects
The history of the electric car battery is a fascinating one, and the future prospects for this technology are equally exciting. In the early days of electric vehicles, lead-acid batteries were the norm, but they had limitations in terms of weight, range, and charging time. The development of nickel-cadmium batteries in the 1970s and 1980s brought some improvement, but it wasn’t until the breakthrough of lithium-ion batteries in the 1990s that electric cars could match the performance of their gasoline-powered counterparts.
Today, electric car batteries continue to improve in terms of energy density, charging speed, and cost. The emergence of solid-state batteries, which promise even higher energy density and safety, could be the next big breakthrough in this field. With electric cars becoming more affordable and popular, and with governments around the world setting ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions, the future looks bright for the electric car battery industry.
Development of solid-state batteries
Solid-state batteries have the potential to revolutionize the energy storage industry. These batteries have several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries, including higher energy density, faster charging times, and increased safety. As a result, solid-state batteries are being developed for use in a range of applications, from electric vehicles to electronic devices like smartphones and laptops.
While solid-state batteries are still in the development stage, several companies are making significant progress in improving their performance and lowering their costs. Researchers are working to optimize the materials used in solid-state batteries, with the goal of creating batteries that are both efficient and affordable. If successful, solid-state batteries could be a game-changer in the energy sector, offering a more sustainable and efficient method of energy storage.
Push towards sustainability and renewable energy
The push towards sustainability and renewable energy is gaining momentum, as individuals and businesses alike are increasingly recognizing the importance of reducing carbon footprints and protecting the environment. As we look towards the future, there are many promising prospects for sustainability and renewable energy. One exciting development is the emergence of new technologies, such as advanced solar panels, wind turbines, and batteries.
These innovations are making it increasingly feasible to rely entirely on sustainable energy sources for our power needs. In addition, government policies and regulations are starting to reflect the importance of sustainability and renewable energy, with many countries providing incentives for businesses that prioritize sustainability. Finally, consumer demand is driving the shift towards sustainability, with more and more people actively seeking out environmentally-friendly products and services.
All of these factors are contributing to a bright future for sustainability and renewable energy, and we can look forward to a more sustainable world as a result.
Conclusion
The history of the electric car battery is an electrifying tale of innovation, setback, and renewed hope. From the early days of lead-acid batteries to the revolutionary lithium-ion technology, the journey to the perfect electric car battery has been a challenging one. But thanks to the tireless efforts of scientists, engineers, and eco-conscious individuals, the electric car battery has emerged as a shining star in the fight against climate change.
So let’s raise a charge to the bright future of the electric car battery, and may it continue to power our world towards a cleaner, more sustainable tomorrow!”
FAQs
What is the history of electric car batteries?
The first rechargeable battery was invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. However, it wasn’t until the 1990s that electric car batteries began to gain mainstream attention with the invention of nickel-metal hydride batteries by General Motors and the subsequent development of lithium-ion batteries.
How do electric car batteries work?
Electric car batteries work by storing electrical energy that is used to power an electric motor. When the motor is turned on, the battery releases its stored energy, which is converted into mechanical energy that propels the car forward.
What are the advantages of electric car batteries?
Electric car batteries offer a number of advantages over traditional gasoline engines, including lower emissions, quieter operation, and better fuel efficiency. Additionally, electric cars require less maintenance since they have fewer moving parts than traditional combustion engines.
What are the disadvantages of electric car batteries?
Despite their advantages, there are also some disadvantages to electric car batteries, such as limited driving range, long recharge times, and high upfront costs. Additionally, the production of the batteries themselves requires significant amounts of energy and natural resources.