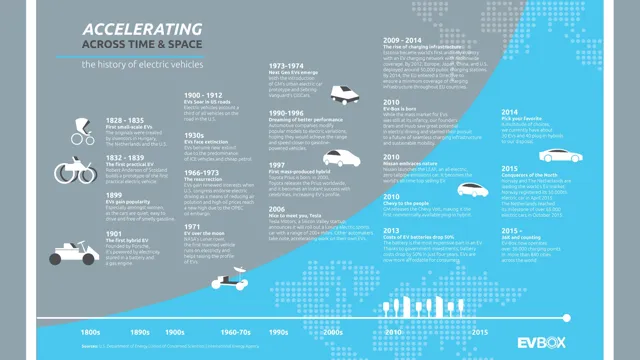
Revolutionizing the Road: A Look into the Fascinating History of the First Electric Cars
Do you ever wonder what the first electric cars were like? Back in the late 1800s, the idea of an automobile was still relatively new, with only a few experimental models being crafted by daring inventors. But, among them were those who saw the potential of electric power as a way to revolutionize transportation and improve air quality. These early electric cars were truly ahead of their time, utilizing rechargeable batteries and powerful electric motors to provide a quiet and eco-friendly alternative to the noisy and smoggy gas-powered vehicles of the day.
Let’s take a closer look at the history of these pioneering machines and their place in the evolution of electric transportation.
Early developments in electricity-powered vehicles
The history of the first electric cars dates back to the early 19th century when inventors began experimenting with electricity-powered vehicles. In 1828, Anyos Jedlik, a Hungarian inventor, built a small-scale model car, powered by an electric motor, that could reach a speed of 25 miles per hour.
In 1834, Thomas Davenport, an American blacksmith, built the first real electric car that used a series of cells to power a small motor. However, it was impractical for everyday use as it required constant recharging. Several other inventors, including Robert Anderson, Gustave Trouvé, and William Morrison, made significant contributions to the development of electric cars during the late 1800s and early 1900s.
The history of the first electric cars reveals the pioneering efforts of inventors who helped pave the way for the modern electric vehicles we have today.
The invention of the first electric car in 1884
The invention of the first electric car in 1884 was a groundbreaking achievement in the history of transportation. While electricity had been discovered and studied since the early 19th century, the concept of using it to power vehicles was still in its infancy. Thomas Parker, an English inventor, was the first to successfully design and build an electric car that could travel up to 18 miles per hour.
However, due to the limited technology of the time, the batteries used in these vehicles were heavy and expensive, making them impractical for most consumers. Despite these setbacks, other inventors continued to experiment with electricity-powered vehicles in the coming years, leading to further advancements in the technology and eventually bringing electric cars to the mainstream market. Today, with the increasing demand for eco-friendly and sustainable modes of transportation, electric cars have once again become a major focus of innovation and development.
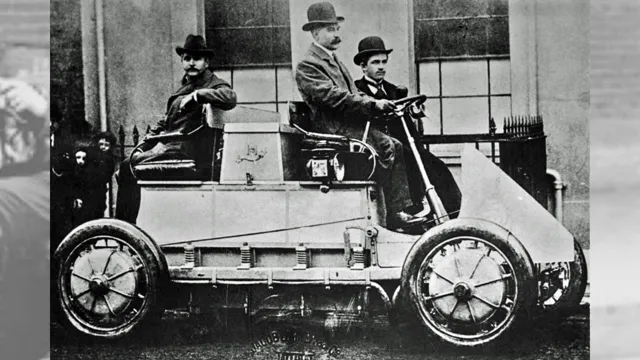
Increased popularity in the early 20th century
Electricity-powered vehicles started gaining popularity in the early 20th century due to several developments. One of the first electrified cars was invented by Thomas Parker in 188 The electric vehicle he created was equipped with rechargeable batteries and ran on four electric motors.
But it was only after the invention of the lead-acid battery in 1901 by Gaston Planté that electric cars became more practical and efficient. Around the same time, several automobile manufacturers, including Baker Electric and Detroit Electric, started producing electric cars. In 1912, the Edison Electric Car Company even introduced the Model 50, which had a range of up to 80 miles per charge.
The increased availability of electricity in homes and businesses also made electric vehicles more convenient to use. With these advancements, electric cars were poised to challenge gasoline-powered vehicles in popularity.
Challenges faced by the early electric cars
When we think of electric cars, we often think of modern-day cars like Tesla models or the Nissan Leaf. However, the history of the first electric cars goes back to the 1800s. While these early electric cars faced many challenges such as limited range, difficulty recharging, and high cost, they were a promising development in the transportation industry at the time.
One major issue faced by early electric cars was battery technology. The batteries used in these cars were heavy and had a limited range, making long-distance travel difficult. Additionally, recharging the batteries took much longer than refueling a traditional gas-powered car, making the process inconvenient for drivers.
Despite these obstacles, the early electric cars paved the way for modern electric vehicles and the ever-improving technology that comes with them.
Limited driving range and battery technology
One of the most significant challenges faced by early electric cars was their limited driving range and battery technology. In the early days of electric cars, battery technology was not readily advanced enough to produce batteries with high enough capacity to power cars for long distances. As a result, many early electric cars could only travel a few miles before needing to be recharged.
This limitation made electric cars unsuitable for long-distance travel and made them a niche option for city driving. Additionally, the performance of electric cars was severely impacted by weather conditions, such as cold temperatures, which decreased battery life and reduced driving range even further. Today, technological advancements have allowed for more efficient and higher-capacity batteries that can power electric cars for much longer periods.
However, the early challenges faced by manufacturers and drivers of electric cars remain an important part of the history of this revolutionary technology.
Competition with gasoline-powered cars
During the early days of electric cars, the biggest challenge was competing with gasoline-powered vehicles. For starters, electric cars had a much shorter range, limited by the capacity of their batteries which were heavier and less powerful than modern ones. Moreover, gas cars were already widely available, and gas stations were popping up everywhere, making it more convenient for people to refuel their automobiles.
On the other hand, charging infrastructure for electric cars was virtually non-existent for most of the 20th century. Additionally, electric cars were often more expensive to produce and purchase than gas cars, due to the limited availability of the materials needed to build their batteries. However, in recent years, advancements in battery tech and government incentives have helped make electric cars more affordable, and the construction of more charging stations has made them more accessible to the general public.
As a result, electric cars are now gaining in popularity and are projected to outsell gas vehicles in the near future.
Decline of electric cars in the mid-20th century
The mid-20th century witnessed a decline in the popularity of electric cars. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that these early electric cars faced several challenges that contributed to their downfall. One significant challenge was the battery technology used at the time, which was expensive and inefficient.
The limited range of early electric vehicles also posed a problem, making them inconvenient for long trips. Additionally, advancements in gasoline-powered engines led to cars that were faster, more powerful, and easier to refuel, outcompeting electric vehicles on the market. Furthermore, automakers failed to invest in the necessary infrastructure for charging electric cars.
Without sufficient charging stations or battery-swapping stations, car buyers were hesitant to choose electric vehicles over gasoline-powered cars. Despite these challenges, the electric car industry continued to innovate and evolve, leading to the electric vehicle revolution we are experiencing today.
Revival of electric cars in the 21st century
The history of the first electric cars goes back to the late 19th century, when the world was seeing rapid growth in the automobile industry. At the time, electric vehicles were actually more common than gasoline-powered ones, due in part to their smooth and quiet ride. However, advances in gasoline engine technology and improvements in infrastructure, such as the construction of gas stations, eventually made gasoline-powered cars the dominant force.
But in recent years, the electric car has made an impressive comeback, thanks to increased awareness of environmental issues and advances in battery technology. Today’s electric cars are sophisticated, eco-friendly machines that can go further on a single charge than ever before. It’s exciting to think about what the future holds for the electric car, as more and more people embrace sustainable transportation.
Advancements in battery technology and government incentives
As battery technology continues to improve and governments offer incentives, electric cars are experiencing a revival in the 21st century. With more efficient batteries, electric vehicles can now travel longer distances and charge faster than ever before. Governments around the world are offering incentives like tax credits, rebates, and free charging stations to encourage the adoption of electric cars.
Additionally, many countries have implemented regulations to reduce carbon emissions, prompting car manufacturers to produce more electric and hybrid cars. As a result, electric vehicles are becoming more accessible and affordable to the average consumer. While electric cars still face challenges like range anxiety and limited charging infrastructure, the advancements in battery technology and government support suggest that they will play a significant role in the future of transportation.
Leading electric car manufacturers today
The 21st century has seen a revival in the popularity of electric cars, thanks to the efforts of leading car manufacturers like Tesla, Nissan, and BMW. Electric cars have come a long way from their humble beginnings in the 19th century, and now offer greater range, performance, and affordability than ever before. Tesla, for instance, is known for its premium electric vehicles that have set the standard for electric car technology and performance.
Nissan’s Leaf, on the other hand, offers a more affordable option for those looking to transition to electric, while BMW’s i3 combines cutting-edge technology with sleek design. With more car manufacturers jumping on the electric bandwagon, it’s clear that electric cars are here to stay. Whether you want to reduce your carbon footprint or simply want to enjoy the benefits of electric driving, electric cars offer an exciting and sustainable future for the automotive industry.
Future of electric cars
The history of the first electric cars dates back to the early 1800s, where inventors started experimenting with battery-powered vehicles. The first electric car was built in Scotland in the 1830s, featuring a top speed of 4 miles per hour and a range of roughly 10 miles. However, the limited capabilities of the batteries at the time hindered the growth of these electric vehicles.
Fast forward to today, and electric cars have advanced significantly in terms of technology and capability. With longer ranges, faster charging times, and more affordable prices, electric cars are becoming an increasingly viable option for drivers looking to make the switch to sustainable transportation. The future of electric cars looks bright, with continued advancements in battery technology and infrastructure development.
Expected growth in the electric car market
The electric car market is expected to see significant growth in the coming years. With advancements in technology and increased focus on sustainability, more and more people are opting for electric cars over traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. In fact, a report by BloombergNEF predicts that electric vehicles will account for 58% of new passenger car sales by 2040.
This surge in popularity is due to multiple factors, such as increased battery capacity, improved charging infrastructure, and government incentives. Additionally, electric cars offer a quieter, smoother ride and have lower operating costs compared to their gasoline counterparts. As the world shifts towards renewable energy and consumers become more environmentally conscious, the future of electric cars looks bright.
It won’t be long before they become a common sight on the road, paving the way for a cleaner and greener future.
Potential impact on the automotive industry and the environment
The future of electric cars looks bright and promising, with potentially game-changing advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure. This will undoubtedly have a massive impact on both the automotive industry and the environment. With consumers becoming more environmentally conscious and governments implementing stricter carbon emissions regulations, the demand for electric vehicles is steadily increasing.
The automotive industry is starting to take notice, with more and more major car manufacturers investing heavily in the development of electric vehicles. In addition, the growing popularity of electric cars will also impact the environment positively by reducing the carbon footprint of transportation. As battery technology improves, electric cars will become more practical for longer journeys, making them a viable option for many more people.
It’s clear that the future of the automotive industry is electric and eco-friendly, which is good news for everyone.
Conclusion
After delving into the history of the first electric cars, it’s clear that the road to clean and sustainable transportation wasn’t always a smooth ride. From the early days of horseless carriages to the modern advancements in battery technology, the electric car has come a long way. Despite facing numerous setbacks, pioneers such as Thomas Davenport, Robert Anderson, and Thomas Parker paved the way for a brighter future in transportation.
Today, we continue to see the benefits of electric cars in reducing emissions and increasing efficiency. As we move towards a more sustainable future, it’s clear that the electric car is not just a passing trend, but a vital part of the automotive landscape.”
FAQs
When were the first electric cars invented?
The first electric cars were invented in the 1830s.
Who invented the first successful electric car?
The first successful electric car was invented in 1884 by Thomas Parker.
How did the early electric cars differ from modern electric cars?
Early electric cars had limited range and speed, whereas modern electric cars can travel hundreds of miles on a single charge.
When did electric cars become popular again?
Electric cars became popular again in the 21st century, as concerns about climate change and air pollution increased.