Unveiling the Truth: Are Electric Car Batteries Really Biodegradable?
Electric cars are often lauded as a more environmentally-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. But as with any new technology, questions arise regarding its impact on the environment. One concern that has been raised is whether or not electric car batteries are biodegradable.
After all, if they are not, then what is the long-term impact of these batteries on the environment? In this blog post, we will delve into this topic, exploring what electric car batteries are made of and whether or not they can be disposed of in an eco-friendly manner. So, buckle up and let’s dive in!
What Are Electric Car Batteries Made Of?
Are electric car batteries biodegradable? Unfortunately, they are not. Electric car batteries are made up of a collection of materials that include heavy metals like cobalt, lithium, and nickel. These materials can pose a significant risk to the environment if they are not taken care of properly.
In addition, it is essential to note that extracting and refining these materials can have a negative impact on the environment. While it is vital to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, it is also crucial to ensure that the materials used in electric vehicle batteries are disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner. However, with advancements in technology, researchers are exploring ways to make batteries more sustainable and less harmful to the environment.
So, while electric car batteries may not be biodegradable now, there is hope and possibilities for a more sustainable future.
Lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the heart of most electric cars. They’re made up of several components, including electrodes, a separator, and an electrolyte. The electrodes are typically made of a metal oxide and carbon, while the separator – which keeps the positive and negative electrodes from touching each other – is typically a thin polymer film.
The electrolyte, on the other hand, is a liquid or gel-like substance that allows the ions to flow between the electrodes. The most common type of electrolyte used in electric car batteries is a lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent. This allows for efficient ion movement and overall battery performance.
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density and long lifespan, making them a popular choice for electric cars. However, they can be sensitive to high temperatures and can sometimes pose a fire risk if damaged or punctured. Despite these drawbacks, they remain the most widely used type of electric car battery in production today.

Nickel-metal hydride batteries
Electric car batteries come in different types, each utilizing different materials and chemistries. One common type is the nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) battery, which was used in older hybrid cars and is still employed in some electric vehicles today. These batteries use a combination of nickel (as the positive electrode) and a hydrogen-absorbing metal alloy (as the negative electrode) to store and release electrical energy.
Compared to lead-acid batteries, NiMH batteries have higher energy densities, longer lifespans, and less environmental impact. However, they are also heavier, bulkier, and less efficient than newer lithium-ion batteries. Moreover, NiMH batteries suffer from issues of memory effect and self-discharge, which reduce their overall performance over time.
Despite these drawbacks, NiMH batteries remain a reliable and cost-effective option for certain applications, such as in municipal or commercial fleets.
The Biodegradability of Electric Car Batteries
Many people are becoming increasingly concerned about the impact that electric car batteries have on the environment, specifically with regards to their biodegradability. Unfortunately, the answer is not a simple yes or no. While some components of electric car batteries can be biodegradable, such as the plastic casings, the more significant problem is with the metals and chemicals inside the battery.
Due to their potentially hazardous nature, these components need to be properly disposed of, which often involves recycling or repurposing. It is essential to ensure that electric car batteries are recycled correctly, not only to protect the environment but also to recover valuable resources. Therefore, while electric car batteries may not be entirely biodegradable, there are responsible methods of disposal to reduce their environmental impact.
Challenges with recycling
Recycling has always been a challenge, but the biodegradability of electric car batteries poses a unique problem. Electric car batteries are made up of toxic and non-biodegradable materials like lithium-ion, which can take up to 200 years to decompose. That means that if these batteries are not recycled properly, they could end up sitting in a landfill for centuries to come.
To make matters worse, recycling electric car batteries is a costly and complex process that involves separating and purifying the different materials used to make the battery. However, it is essential that we find a way to recycle these batteries properly, not just because it’s the right thing to do, but also because we need to conserve our natural resources. By doing so, we can reduce our environmental footprint and create a more sustainable future.
Potential for reuse and repurposing
As electric vehicles become more prevalent on our roads, the question of the biodegradability of electric car batteries arises. Unlike traditional car batteries, electric car batteries contain rare and expensive materials such as lithium and cobalt which are not easily disposable after their useful life expires. However, these batteries have potential for reuse and repurposing.
For example, old electric car batteries can be given a second life in a stationary energy storage system, where they can provide backup power to buildings or renewable energy grids. Additionally, the materials used in these batteries can be recycled and reused in other industries, thus reducing the demand for newly mined materials. While it may take time and investment to develop efficient recycling processes, the potential benefits of repurposing electric car batteries cannot be ignored.
As society moves towards a more sustainable future, finding ways to reuse and recycle these batteries is critical.
Alternatives to traditional batteries
As electric vehicles become more popular, the biodegradability of their batteries is a topic of concern. Unlike traditional car batteries that can leak harmful chemicals into the environment, the components in electric car batteries are much less toxic and can be safely disposed of. However, the issue of biodegradation mainly pertains to the disposal of batteries at the end of their useful life.
While some electric car batteries can be recycled, others may end up in landfills, where they can take hundreds of years to decompose, potentially causing harm to the environment. Overall, while electric car batteries offer a more environmentally-friendly alternative to traditional car batteries, it is still crucial to consider their biodegradability in the long term for sustainable transportation.
Environmental Impact of Electric Car Batteries
When it comes to the environmental impact of electric car batteries, one question that often arises is whether they are biodegradable. Unfortunately, the answer is no. Electric car batteries are not biodegradable, meaning that they cannot be broken down over time by natural processes.
Instead, they contain a variety of materials that can be harmful to the environment if not properly disposed of. These materials include metals like nickel and cobalt, which can be toxic in high doses, as well as chemicals like lithium and electrolytes, which can be corrosive and harmful to ecosystems. Because of this, it’s important to recycle electric car batteries rather than simply throwing them away.
With proper recycling techniques, the valuable materials in these batteries can be repurposed and reused, reducing the need for new mining and manufacturing and helping to mitigate the environmental impact of this technology.
Reducing the carbon footprint of production
One of the biggest selling points of electric cars is their reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. However, the environmental impact of electric car batteries cannot be ignored. The production of these batteries requires a significant amount of energy and resources, including rare minerals and metals that may be sourced unsustainably in some cases.
Additionally, the disposal of these batteries at the end of their lifespan can lead to further environmental damage if not handled correctly. It’s important for car manufacturers to take steps to reduce the carbon footprint of battery production, such as implementing more sustainable sourcing practices and developing more efficient production processes. As consumers, we can also do our part by properly disposing of our old batteries and choosing to support companies that prioritize environmentally-friendly practices.
Ultimately, while electric cars have the potential to greatly reduce our carbon footprint, we must also be mindful of their overall environmental impact and take steps to minimize it.
Impact of improper disposal
Electric car batteries have undoubtedly brought about a significant reduction in the carbon footprint, which is commendable. However, improper disposal of these batteries poses a severe threat to the environment. The batteries typically contain a range of toxic chemicals such as lead, lithium, and sulphuric acid which can create a devastating impact on the surrounding ecosystem if not disposed of properly.
When improperly disposed of, the toxic chemicals can leach into the soil and water bodies, polluting them and leading to bioaccumulation in the food chain. This can result in long-term health hazards for both animals and humans. Therefore, it is essential to take responsible measures when disposing of electric car batteries to prevent any catastrophe.
Proper disposal methods include recycling which involves reusing the rechargeable battery components after it can no longer be used for driving the vehicle.
Conclusion: The State of Biodegradable Electric Car Batteries
In conclusion, while electric car batteries are not technically biodegradable, advancements in technology are allowing for more sustainable and environmentally-friendly ways to dispose of and recycle them. As we continue to shift towards a clean energy future, it’s important to consider not just the benefits of electric cars, but also their potential impact on the planet. So let’s keep charging ahead with innovation and responsible usage, and maybe one day even our car batteries will be able to return to the earth just as easily as the fruits and veggies in our compost pile.
“
FAQs
What materials are used in electric car batteries?
Electric car batteries are made of a combination of metals such as lithium, cobalt, nickel and manganese, along with polymer electrolyte and various other materials to control the battery’s performance.
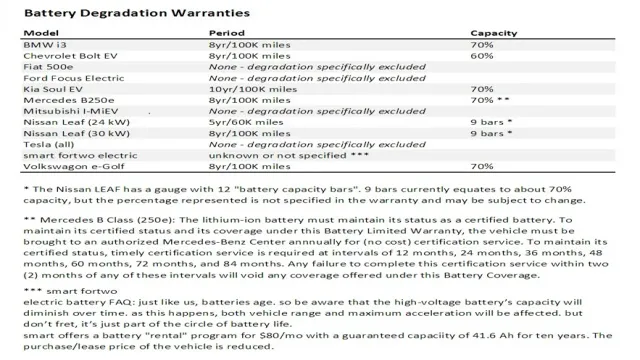
How long do electric car batteries last?
The lifespan of an electric car battery depends on a number of factors such as usage patterns, temperature, and charging habits. Typically, electric car batteries are designed to last anywhere from 8 to 10 years or more before needing to be replaced.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, electric car batteries can be recycled. The materials used in the battery, such as the metals and electrolytes, can be extracted and reused to make new batteries or other products. Recycling electric car batteries helps to reduce waste and preserve valuable resources.
Are electric car batteries biodegradable?
No, electric car batteries are not biodegradable. The materials used in the battery, such as the metals and polymers, do not break down naturally over time. Proper disposal of electric car batteries is important to prevent environmental damage and ensure safe handling of the battery materials.