The Evolution of Transportation: Uncovering the Fascinating History of Gas and Electric Cars
Gasoline and electric-powered cars have become commonplace on our roads today, but have you ever wondered how these two types of vehicles came to exist and how they developed over time? The history of gas and electric cars goes back centuries, with each having their own unique impact on the transportation industry. Gasoline cars date back to the late 1800s, when they were first introduced as a more convenient alternative to the horse and carriage. It wasn’t until the early 1900s that gasoline-powered cars started to become more widely available, and by the 1920s, they had become the standard mode of transportation.
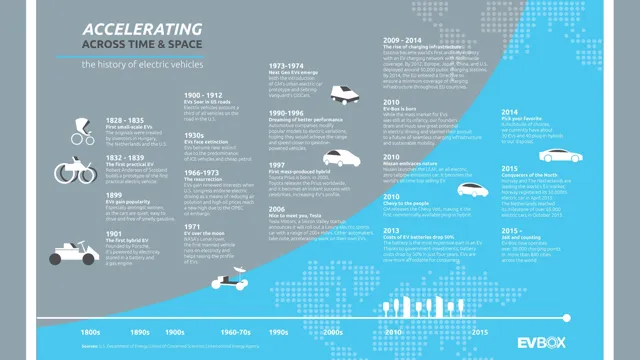
On the other hand, electric cars have a history that dates back even further. The first electric car was invented in the 1830s, but it wasn’t until the late 1800s that they started to see commercial success. However, electric cars fell out of popularity due to the limited range and the high cost of batteries.
Both types of cars have experienced various highs and lows over the years, with gas cars experiencing booming sales during times of cheap gas prices, and electric cars experiencing resurgences in popularity with the advancement of technology and the push for more eco-friendly transportation options. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the history and evolution of gas and electric cars, and explore the impact they’ve had on transportation as we know it today. So settle in and hang on, as we take a trip down memory lane and dive into the fascinating world of gas and electric cars.
Early Days of Gasoline Cars
Back in the early days of the automobile industry, gasoline cars and electric cars were both popular options. Gasoline cars were powered by internal combustion engines, which allowed for greater speed and range. However, they also emitted harmful pollutants and required frequent maintenance.
On the other hand, electric cars were quiet, clean, and required less maintenance. As a result, they were often favored by women drivers. However, electric cars were limited in terms of speed and range, which made them less practical for long trips.
Despite their limitations, both gasoline and electric cars played an important role in the history of the automobile industry, paving the way for the development of more advanced and efficient vehicles in the future.
19th Century Inventions
Gasoline cars were a revolutionary invention of the 19th century that completely changed the way people traveled. The earliest models were clunky and slow, but they quickly improved as the technology advanced. One of the first gasoline cars was invented by Carl Benz in 1885, called the Benz Patent Motorwagen.
It was a three-wheeled vehicle that had a top speed of only 10 miles per hour. However, this car was the start of a new era, and it opened up a world of possibilities for transportation and travel. As the popularity of gasoline cars grew, so did their speed and efficiency.
By the end of the 19th century, cars were being used for all sorts of purposes, from racing and sport to everyday transportation. Gasoline cars were a true milestone in the history of transportation that made it possible for people to travel in ways that they never could before.

Ford’s Model T Revolution
In the early days of gasoline cars, the automobile industry was still in its infancy. Cars were expensive and only the wealthy could afford them. However, this all changed with the release of Ford’s Model T in 190
With its affordable price of $825, the Model T revolutionized the automobile industry and made cars accessible to the average person. It was a sturdy and reliable vehicle that could carry up to five passengers, making it perfect for families. The Model T was also easy to drive and maintain, and it quickly became the most popular car on the market.
In fact, by 1913, half of all the cars in America were Model Ts. This popularity was due, in part, to Ford’s innovative assembly line production system, which made the production of the car faster and more efficient than ever before. The Model T ignited a passion for automobiles that still exists today, and it forever changed the way we travel and live our lives.
The Emergence of Electric Cars
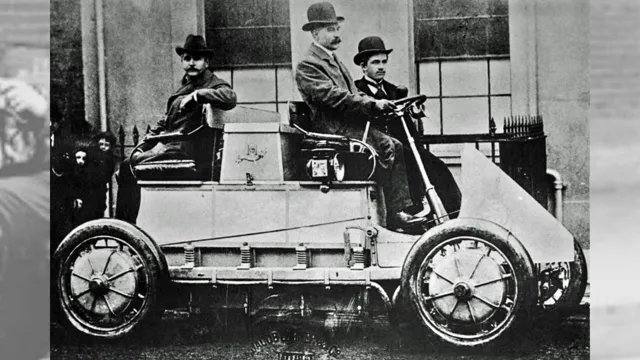
Over the past couple of decades, electric cars have emerged as a popular alternative to gas-powered vehicles. However, the history of electric cars dates back to the early days of automobiles. In fact, electric cars were some of the first automobiles on the road, with the first electric car being built in the late 1800s.
At the time, electric cars were popular for their quiet operation and ease of use. However, as gasoline became more readily available, and cars became more powerful, electric cars fell out of favor. It wasn’t until the 1990s that electric cars began to re-emerge as a viable alternative to gas-powered vehicles.
With advancements in battery technology, electric cars can now travel longer distances and operate more efficiently. As concerns over climate change and air pollution continue to grow, electric cars are becoming an increasingly popular choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Early Electric Vehicles
The emergence of electric cars traces back to the late 1800s when inventors like Thomas Davenport and Robert Davidson created the first electric vehicles. These early electric cars featured simple designs with lead-acid batteries to power the motor. Although they were expensive and only wealthy individuals could afford them, electric vehicles gained popularity in cities where they were ideal for short trips and low-speed drives.
Despite their limitations compared to gasoline-powered cars, electric vehicles continued to evolve and improve with technological advancements. The main challenge with electric vehicles was the battery’s capacity to store energy, but this started to improve in the early 1900s with the introduction of nickel-iron batteries. However, the competition with gasoline-powered cars hindered the growth of electric vehicles, and by the 1920s, the production of electric cars came to a halt.
Nonetheless, the legacy of these early electric vehicles is still evident today as manufacturers continue to produce electric cars with advanced features and uses.
Rise and Fall of Electric Cars
Electric cars have been around for more than a century, but it wasn’t until the last decade that they began to take center stage. With climate change on the rise and people becoming more mindful of their environmental impact, electric cars quickly gained popularity. They were seen as the solution to pollution, and many car enthusiasts eagerly hopped on the electric bandwagon.
The rise of electric cars was marked by Tesla, which not only produced arguably the most popular electric car but also changed people’s perspective on electric cars. However, electric cars are not a new phenomenon. In the early 1900s, electric cars were widely popular, but their popularity declined with the advent of gasoline-powered vehicles.
But the emergence of electric cars in the twenty-first century ignited a new era of eco-friendliness, pushing electric cars back into the spotlight as a feasible alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles.
Modern Electric Car Comeback
Electric cars have been making a comeback in recent years as the push for sustainable transportation becomes more prominent. Unlike traditional cars that run on gasoline, electric cars run on electricity from batteries that can be recharged. This means they produce significantly less carbon emissions, making them more environmentally friendly.
The emergence of modern electric cars with longer ranges and faster charging times has also made them more practical for everyday use. With advances in technology and growing concerns over climate change, it’s no surprise that more and more people are turning to electric cars as their go-to mode of transportation.
Gas vs. Electric: A Comparative History
Gas-powered cars have been around since the late 1800s, but electric vehicles actually predate them by a couple of decades. However, the early electric cars were limited in speed and range, and gas quickly emerged as the dominant fuel source for automobiles. In the early 20th century, gasoline engines continued to improve in power and efficiency, while electric cars remained a niche market.
This trend continued until the 1970s, when oil shortages led to a resurgence of interest in electric vehicles. However, it wasn’t until the 21st century that the mass production of electric cars really took off. Today, the choice between gas and electric vehicles depends on factors like cost, performance, and the availability of charging stations – and with the push towards renewable energy, electric cars are becoming an increasingly popular option.
Environmental Impact
When it comes to choosing between gas and electric appliances, environmental impact is a crucial factor to consider. The history of these two energy sources has been shaped by their differing environmental effects. Gas appliances have been popular for centuries due to their efficiency and affordability.
However, gas burning leads to the emission of harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, which contribute to poor air quality and climate change. Electric appliances, on the other hand, have a much lower environmental impact as they don’t emit any harmful pollutants during use. But, for a long time, the production of electricity was heavily reliant on fossil fuels, causing significant harm to the environment.
However, with the growing popularity of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, electric appliances have become the more sustainable option. Nowadays, eco-conscious consumers are switching to electric alternatives, making a positive impact on the environment. Overall, as the world becomes increasingly focused on reducing its carbon footprint, electric appliances seem to be the way forward.
Efficiency & Cost
When it comes to energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness, the choice between gas and electric has been a debated topic for decades. Gas has been around since the late 1800s and provided a cheaper alternative to coal for heating and cooking. However, with the rise of electricity in the early 1900s, electric appliances started to become more popular due to their convenience and cleanliness.
In the 1940s and 1950s, electricity became widely available, and with advancements in technology, electric appliances became more energy-efficient than gas-powered ones. Today, the debate continues, with gas being more affordable in some regions and electricity being cheaper in others. The decision ultimately depends on the availability and cost of gas and electricity in your area and the specific needs of your household.
The Future of Cars: Where Do We Go From Here?
The history of gas and electric cars has been incredibly interesting to see, and as we look towards the future, there’s still so much more to explore. With electric cars growing in popularity, it’s important to remember the impact of gas cars on our society. They’ve given us mobility and flexibility, but the negative effects on the environment cannot be ignored.
However, electric cars are not the complete solution to all of our problems. There’s still a demand for a fast and long-range option that electric cars can’t provide yet. The future of cars will likely be a hybrid of both technologies, with electric cars improving and gas cars becoming more efficient and eco-friendly.
Plus, with the continued development of autonomous technology, we may see a shift in how we even use cars. All in all, we must continue to innovate and find ways to make transportation more sustainable for future generations.
Conclusion
In the end, the rivalry between gas and electric cars can be traced back over a century, with each method of powering vehicles vying for dominance. Gasoline was initially the frontrunner, but as concerns for the environment and sustainability have grown, electric cars have become more and more prevalent. While gas-powered vehicles will likely be on the roads for many years to come, the shift towards electric cars and other alternative modes of transportation seems inevitable.
Who knows what the future holds, but one thing is for certain – the journey towards an all-electric future will be electrifying!”.
FAQs
What is the history of gas-powered cars?
Gas-powered cars have a history that dates back to the 19th century when the first gasoline-powered car was invented by Karl Benz in 1885.
When did electric cars become popular?
Electric cars were first invented in the 19th century but they only became popular in the 21st century due to advancements in technology and the need to reduce emissions.
What are the advantages of electric cars over gas-powered cars?
Electric cars have several advantages over gas-powered cars including being more environmentally friendly, having lower operating costs, and offering a smoother and quieter ride.
What are the disadvantages of electric cars?
The disadvantages of electric cars include limited range, longer charging times, and higher upfront costs than gas-powered cars. However, these issues are gradually being addressed with advancements in technology.
How have gas and electric cars affected the environment?
Gas-powered cars have contributed heavily to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, while electric cars have been touted as a cleaner alternative, with greatly reduced emissions, especially if the electricity used to charge them comes from renewable sources.