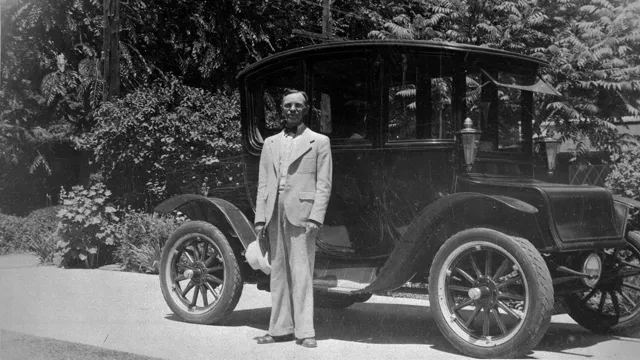The Electrifying Journey of Electric Cars: Uncovering Their Fascinating Background History
Electric cars are increasingly gaining popularity as people become more aware of the harmful effects of traditional gasoline cars on the environment. However, the concept of electric cars is not new and dates back over a century. In fact, the first electric car was invented in the late 1800s, long before gasoline-powered vehicles became mainstream.
In this brief history of electric cars, we will delve into their evolution over the years, from their inception to modern-day electric vehicles. Get ready to witness the transformative journey of electric cars from a strange, quirky innovation to one of the hottest topics in the automotive industry today.
Early Inventions and Development
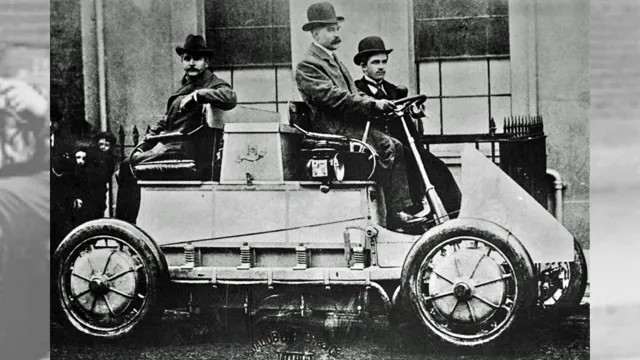
The background history of electric cars dates back to the 19th century when inventors first experimented with electric vehicles. Robert Anderson created the first electric car prototype in Scotland in 183 However, the development of electric cars only gained momentum during the early 20th century.
Thomas Parker, a British inventor, built the first practical electric car in 188 Over the next few decades, electric cars became more popular in urban areas due to their quiet engines and lack of emissions. However, the invention of the gasoline-powered combustion engine ultimately overshadowed the electric car industry.
It was only in the 1990s when concerns about climate change and gasoline prices reignited interest in electric cars. Today, electric cars are more advanced and popular among environmentally-conscious consumers, and the technology continues to evolve to make them more accessible and practical.
Thomas Davenport’s Electric Motor
Thomas Davenport’s Electric Motor was one of the earliest inventions in the field of electromagnetism. Davenport, an American blacksmith and inventor, developed his electric motor in the early 1830s. His invention used a battery to provide electric current to a coil, which would then produce a rotational force.
This initial development paved the way for new advancements in the field, which led to the widespread use of electric motors in practically every industry today. While Davenport’s initial motor design was simple, it was revolutionary for its time and showcased the immense potential of electromagnetism. His invention remains an integral part of the history of technology and an inspiration for generations of inventors to come.

Introduction of the Lead-Acid Battery
The lead-acid battery, which is still commonly used today, has a long history of development and innovation. Early inventions and discoveries by Gaston Planté, a French physicist in the 1850s, laid the groundwork for the lead-acid battery. Planté noticed that when a battery was charged, lead plates became coated with a layer of lead oxide, which could then be used to produce electricity.
Over the years, other scientists and inventors made improvements to Planté’s design, such as the addition of sulfuric acid to increase the battery’s power output. By the late 1800s, the lead-acid battery had become a standard source of electrical power, used in everything from telegraph systems to automobiles. The lead-acid battery’s durability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness have kept it in widespread use for over a century.
The Rise of Electric Cars in the 20th Century
The history of electric cars dates back to the early 20th century when they were a common sight on roads worldwide. In fact, they even outnumbered gas-powered vehicles in some cities. However, due to advancements in the gasoline engine, the growth of mass production, and the drop in gasoline prices, electric cars fell from favor and lost their popularity.
The term “gas-guzzler” became synonymous with power and speed, while electric vehicles were associated with durability and reliability, but also slowness and lack of power. Fast forward to modern times, and the awareness of global warming and air pollution has led to a revival of the electric car industry. With technological advancements, electric cars have become more powerful, efficient, and accessible to the general public.
It’s safe to say that electric cars are on the rise again.
Development of Modern Batteries
The development of modern batteries has been a crucial factor in the rise of electric cars in the 20th century. With the invention of rechargeable and more efficient batteries, the idea of electric cars became more practical. Early electric cars in the late 1800s and early 1900s had limited ranges due to their heavy lead-acid batteries, but advancements in technology have resulted in modern lithium-ion batteries that can power electric vehicles for hundreds of miles on a single charge.
Nowadays, batteries are at the core of electric cars, providing the power needed to run motors, cool the vehicles, and even power headlights and other accessories. It’s incredible how far we’ve come in just a century, and as battery technology continues to evolve, there are boundless possibilities for the future of electric cars.
Early Electric Cars vs. Gas-Powered Cars
Electric cars have been around since the early days of automobiles, but their popularity has waxed and waned over the years. In the early 20th century, electric cars were actually more popular than cars powered by gasoline engines. These early electric cars had several advantages over their gas-powered counterparts.
They were much quieter and easier to operate, and they didn’t require messy and time-consuming refueling. However, the electric cars of this era had a limited range, typically only about 30-40 miles on a single charge. As gasoline cars became more efficient and affordable, they gradually surpassed electric cars in popularity.
In recent years, however, electric cars have seen a resurgence in popularity, thanks to improvements in battery technology and environmental concerns. Today’s electric cars offer a much greater range than their predecessors, and they are increasingly seen as a practical and eco-friendly alternative to gasoline cars.
Decline and Rediscovery of Electric Cars in the 20th Century
The 20th century saw a notable rise of electric cars in the automotive industry. This was mainly due to the advances in battery technology and the growing concern for the environment. Electric cars were viewed as the future of transportation, with their emissions-free and quiet operation.
In fact, in the early 1900s, electric cars were more popular than gasoline-powered cars. Manufacturers such as Baker, Columbia, and Detroit Electric were producing thousands of electric cars annually. They were especially popular among city dwellers who valued the convenience of not having to refuel at gas stations.
However, the rise of cheaper and more efficient gasoline-powered cars, combined with the availability of cheap oil, led to the eventual decline of electric cars. But their rediscovery in the 21st century marked a new era in the automotive industry, bringing back the focus on eco-friendly transportation.
Electric Cars Today
The history of electric cars dates back to the early 19th century when inventors such as Thomas Davenport and Robert Anderson were experimenting with electric vehicle prototypes. However, the first practical electric car was invented in 1884 by British inventor Thomas Parker. It was followed by the production of electric taxis in England and the United States in the early 1900s.
These early electric vehicles had limited range and were expensive compared to gasoline-powered cars at the time. Moreover, the discovery of oil reserves and the mass production of gasoline vehicles led to the decline of electric cars by the 1920s. It was not until the 1990s that electric cars made a comeback with the production of the General Motors EV1 and the Toyota RAV4 EV.
Recent advances in battery technology, government incentives, and public awareness of environmental issues have led to a surge in the production and sales of electric cars. Today, electric cars are becoming increasingly popular and are expected to play a major role in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change.
Modern Advancements in Battery Technology
Modern advancements in battery technology have paved the way for a new era of transportation – electric cars. With the ability to store more energy, last longer, and charge quicker than ever before, electric cars have become a viable option for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint. Electric cars are no longer just a novelty; they are becoming increasingly popular and are now more accessible to the average consumer.
The rise of electric vehicles can be attributed to the advancements in lithium-ion batteries, which are lighter, more efficient and eco-friendly. Not only are electric cars better for the environment, but they are also cheaper to run and maintain than their conventional counterparts. With modern battery technology constantly improving, it’s only a matter of time before we see electric cars dominating our roads.
So, are you ready to make the switch to electric and join the future of transportation?
Popularity of Electric Cars in the Global Market
Electric cars have come a long way since they were first introduced to the global market. Today, they have gained immense popularity, and their adoption rate continues to grow. One of the primary reasons for this is the increasing concern about the impact of conventional vehicles on the environment.
With electric cars, drivers can drastically reduce their carbon footprint and help mitigate climate change. Additionally, the cost of electric cars has been gradually decreasing, making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers. The advancements in technology have also resulted in more efficient batteries that allow electric cars to travel longer distances.
As a result, electric cars have become a practical alternative to their gas-powered counterparts. Governments across the world are also incentivizing the use of electric cars through tax credits, discounts, and other measures, which has further contributed to their mainstream acceptance. All these factors have made electric cars an attractive option for environmentally conscious drivers who are willing to make the switch.
The Future of Electric Cars
The history of electric cars dates back to the early 1800s, with initial prototypes developed by inventors such as Robert Anderson and Thomas Davenport. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric cars became more popular with the advent of rechargeable batteries. In fact, electric cars were among the most popular cars on the road until the early 1900s, when the gasoline-powered car began to dominate the market.
Despite several attempts to revive the popularity of electric cars over the decades, it wasn’t until the 21st century that electric cars found a more significant market share. Today, with increasing concerns about the environmental impact of gasoline cars, electric cars are seen as a viable alternative that is both environmentally friendly and economically feasible. The future of electric cars looks bright, with advancements in battery technology and infrastructure improvements making electric cars even more accessible to the average consumer.
Growth Potential and Impact on the Environment
The growth potential for electric cars is huge, and it’s not just because they’re environmentally friendly. As the technology behind electric cars continues to improve, we can expect to see more and more people opting for a sustainable and efficient mode of transportation. This doesn’t just benefit the environment, but it also has the potential to revolutionize our cities, reducing air pollution and traffic congestion.
As batteries become more powerful, electric cars will cover longer distances on a single charge, making them more practical for long trips. The future of electric cars will undoubtedly benefit both consumers and the environment, and it’s exciting to see the potential for growth. However, it’s important to recognize that the production of batteries for electric cars can have a significant impact on the environment, and steps need to be taken to ensure that this is minimized.
Overall, electric cars have the potential to be a game-changer for both travel and the environment, and we can’t wait to see what the future holds for this technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of electric cars is a tale of great innovation, perseverance, and progress. From the early days of experimentation with batteries and electric motors, to the mass production of vehicles like the Tesla Model S, it’s clear that electric cars are here to stay. With the growing urgency to combat climate change and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, electric cars are more important than ever.
And who knows, one day we may look back on the age of gasoline-powered cars as a primitive and outdated era. After all, there’s nothing quite as clever and witty as embracing a sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.”
FAQs
When was the first electric car invented?
The first electric car was invented in 1837.
What was the range of the earliest electric cars?
The earliest electric cars had a range of about 50 miles on a single charge.
When did electric cars become more popular?
Electric cars became more popular in the late 1990s and early 2000s, when the Toyota Prius and Tesla Roadster were introduced.
What is the current state of the electric car market?
The electric car market has been rapidly growing in recent years, with many new models and advancements in battery technology.