Revving up the Future: Unleashing the Power of Batteries for Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as the world moves towards a more sustainable future. One of the biggest challenges in making this transition is finding ways to power these vehicles. The most common way to power electric cars is with lithium-ion batteries, which are able to store energy from the electric grid and power the car’s electric motor.
However, as electric cars become more prevalent on our roads, there is a growing need for more efficient and sustainable ways to charge them. From solar panels to wireless charging stations, there are many innovations being developed to ensure that electric cars can be powered in a sustainable and convenient way. In this blog post, we will explore some of the most promising developments in the field of electric car charging, and discuss how these innovations could help to make electric cars even more practical and accessible in the years to come.
Battery Basics
Batteries that power electric cars are sometimes a mystery to many people. While most know that they store electricity to power the car, the science behind how they work is not widely understood. These batteries are lithium-ion, which means that they use lithium-ion cells to store the energy.
When a car is plugged into an outlet to charge, the energy is transferred from the outlet to the battery. The lithium-ion cells become charged and are then able to store the energy until it’s needed to power the car. The amount of energy that can be stored in these batteries varies depending on the size of the battery and the specific car model.
However, it’s important to note that while electric cars are becoming more common, the technology behind the batteries that power them is still evolving. As the technology advances, it’s likely that electric cars will become even more efficient and more accessible to the average person.
How Electric Cars Work
When it comes to electric cars, the battery is at the forefront of how it all works. These batteries essentially act as the car’s fuel tank, storing the energy needed to power the electric motor. Most electric car batteries today use lithium-ion technology, which is similar to the batteries in our smartphones and laptops.
However, the batteries in electric cars are much larger and more powerful, with the ability to store a significant amount of energy. Essentially, when you plug your electric car in to charge, you’re filling up your “fuel tank” with electricity. It’s important to note that batteries can vary in size and capacity, which can affect the range of the car.
For example, a larger battery will typically offer longer range, whereas a smaller battery may have a shorter range but can be more affordable. Overall, the battery is a crucial component in electric cars and plays a significant role in their functionality and overall performance on the road.
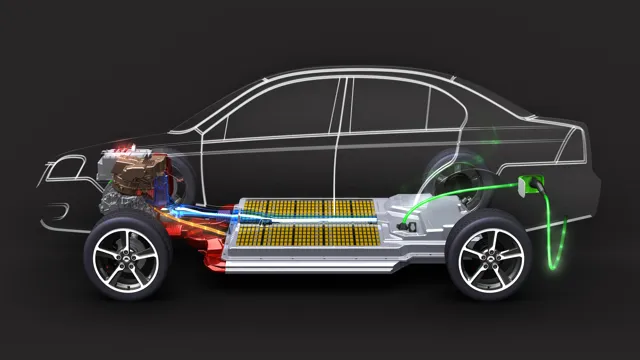
Battery Capacity & Range
Battery capacity is a fundamental aspect of electric vehicles (EVs) that greatly impacts their range. Simply put, battery capacity refers to the amount of energy that can be stored in an EV’s battery. This energy is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Higher capacity batteries can store more energy, which in turn allows the vehicle to travel further on a single charge. Some EVs have battery capacities as low as 20 kWh, while others have batteries that can store up to 100 kWh or more. Of course, the higher the battery capacity, the more expensive the EV will be.
However, it is important to remember that battery capacity and range are directly related. So, if you want an EV with a longer range, you will need to invest in a higher capacity battery.
Types of Batteries
When it comes to batteries that power electric cars, there are mainly two types that are widely used: lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly found in modern electric vehicles due to their high energy density and long lifespan. They are also lighter and smaller than lead-acid batteries, making them a popular choice among automakers.
Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand, have been used for decades and are still in use in some older electric vehicles. They are cheaper than lithium-ion batteries, but are heavier and have a shorter lifespan. Ultimately, the choice between these two battery types depends on the specific needs and goals of each vehicle and its manufacturer.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have become a popular choice for powering various electronic devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles. But did you know that not all lithium-ion batteries are created equal? There are actually several types of lithium-ion batteries, each with its own unique characteristics and performance capabilities. One common type of lithium-ion battery is the cylindrical cell, which is often used in laptops and power tools.
Another type is the prismatic cell, which is used in larger devices like electric vehicles. There are also pouch cells, which are thin and flexible, making them ideal for use in wearable devices. The type of lithium-ion battery used in a particular device depends on factors such as size, power requirements, and cost.
Understanding the different types of lithium-ion batteries can help you make informed decisions when purchasing electronic products.
Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
When it comes to batteries, there are several types available in the market. One such type is the Nickel-Metal Hydride battery. Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries (NiMH) are rechargeable batteries that have a higher energy density compared to Nickel-Cadmium batteries.
They are an excellent choice for portable devices that require lots of power, such as digital cameras, laptops, and smartphones. Additionally, NiMH batteries are more environmentally friendly than other types of batteries because they don’t contain toxic metals like lead and cadmium. Moreover, they also don’t suffer from “memory effect,” a phenomenon common in Nickel-Cadmium batteries where they need to be fully discharged before recharging.
NiMH batteries can also hold their charge for extended periods, making them an excellent choice for emergency devices like flashlights and radios. Overall, NiMH batteries offer a cost-effective, long-lasting, and eco-friendly solution to power your devices.
Solid State Batteries
Solid state batteries are a relatively new type of technology that promises to revolutionize the battery industry. Unlike traditional batteries that use a liquid or gel electrolyte to move ions between the anode and cathode, solid state batteries use a solid electrolyte. This gives them some unique advantages, including a higher energy density, faster charging times, and increased safety.
There are several types of solid state batteries, including lithium-ion, lithium-sulfur, and sodium-ion batteries. Each type has its unique advantages and disadvantages, so research is ongoing to find the best applications for each type. Solid state batteries have the potential to power everything from smartphones to electric cars, making them an exciting area of research for scientists and engineers.
Charging Your Electric Car
When it comes to electric cars, it’s all about the batteries that power them. Electric cars rely on high-capacity lithium-ion batteries that allow them to travel long distances without producing harmful emissions. However, just like any other battery, these need to be charged to keep the vehicle running.
The good news is that there are now many options for charging your electric car, from fast-charging stations found at public locations to home charging units that can be installed in your garage. With a little bit of planning, you can ensure that your electric car always has the energy it needs to take you wherever you need to go. So, next time you’re out on the road in your electric car, rest easy knowing that there are plenty of ways to keep those batteries charged and ready to go!
Home Charging Options
When it comes to electric cars, one of the biggest considerations for potential buyers is how they will charge their vehicle. Fortunately, there are several options available, with home charging being the most convenient and cost-effective solution. There are two main types of home chargers – level 1 and level
Level 1 chargers use a standard household outlet and can take up to 20 hours to fully charge an electric car. Whereas, level 2 chargers require a 240V outlet and can fully charge a car in 4-6 hours. Installing a level 2 charger may require an electrician, but it’s an investment worth considering for the convenience it offers.
Not only does home charging eliminate the need to find and use public charging stations, it also allows for time-of-use charging, where electricity rates can be cheaper during off-peak times. So, whether you opt for a level 1 or level 2 charger, home charging is the way to go when it comes to charging your electric car.
Public Charging Stations
Charging your electric car has never been easier, thanks to the increasing availability of public charging stations. These stations are strategically located in areas where electric car drivers are likely to frequent, such as shopping malls, restaurants, and city centers. Using a public charging station is simple – all you need to do is plug in your car and wait for it to charge.
Most public charging stations provide fast charging options, allowing your vehicle to recharge within a matter of hours. However, it’s important to note that not all public charging stations are created equal, and some may not be compatible with your specific electric car model. To avoid any frustration or inconvenience, make sure to research the types of public charging stations available in your area and which ones are compatible with your vehicle.
By doing so, you can make the most of the public charging infrastructure and enjoy a smooth and hassle-free driving experience.
Future of Electric Car Batteries
The world is rapidly transitioning towards renewable energy sources, and electric cars are at the forefront of this shift. And the batteries that power electric cars are undergoing constant advancements to enhance their performance, safety, and cost-efficiency. Today, we already have advanced lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles that offer high energy density, reliability, and durability.
But there’s always room for improvement, and researchers around the world are experimenting with various materials and designs to create better batteries. From solid-state batteries to silicon-based anodes, these new technologies promise to deliver more range, faster charging times, longer lifespan, and lower costs. The future of batteries that power electric cars seems very bright, and we can expect to see more innovative breakthroughs in the coming years, making electric cars more accessible, convenient, and sustainable for everyone.
Conclusion
In conclusion, batteries truly are the lifeblood of electric cars, providing the essential power needed to get us from point A to point B. Without them, we’d be stranded and our dreams of a greener future would remain out of reach. So let’s all give a (charged up) round of applause to these tiny, but mighty, energy storage devices.
Thanks for keeping us moving and for keeping the environment a little bit brighter.”
FAQs
What are the main types of batteries used in electric cars?
The main types of batteries used in electric cars are lithium ion, lead acid, and nickel-metal hydride.
How long do the batteries in electric cars typically last before needing to be replaced?
The lifespan of the batteries in electric cars depends on factors such as usage and temperature. On average, they can last anywhere from 5 to 10 years.
Can the batteries in electric cars be recycled?
Yes, the batteries in electric cars can be recycled. The process involves breaking down the cells and extracting the valuable materials, such as lithium and cobalt, for reuse.
How long does it take to charge the batteries in an electric car?
The time it takes to charge an electric car battery depends on the charging method used. Level 1 charging with a standard 120-volt outlet can take up to 24 hours, while Level 2 charging with a 240-volt charging station can take anywhere from 3 to 8 hours. Fast charging can get an electric car to 80% charged in as little as 30 minutes.