Powering the Future: Battery Electric Cars vs. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are often seen as the future of sustainable transportation, but they have a worthy competitor in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). The debate between BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles) and FCVs (Fuel Cell Vehicles) has been ongoing for years, with both sides presenting compelling arguments for their technology. On one hand, EVs have become increasingly popular thanks to advancements in battery technology, and on the other, FCVs offer longer driving ranges and quicker refueling times.
The question remains: which technology will ultimately win out? In this blog, we’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of both BEVs and FCVs and try to draw some conclusions about the future of sustainable transportation.
What is a Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)?
When it comes to eco-friendly vehicles, two options come to mind: battery electric cars (BEVs) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). The primary difference between BEVs and FCVs lies in how they generate electricity to power their motors. BEVs rely on large batteries to store electrical energy produced by an onboard charger that’s plugged into an electrical outlet, while FCVs generate electricity through a chemical process between hydrogen and oxygen.
Although both types of eco-friendly vehicles produce zero emissions, there are a few drawbacks to each. BEVs have limited range, and recharging them can take quite a while, while FCVs have limited access to refueling stations and may require significant infrastructure investments. Ultimately, both types have their benefits and drawbacks, and the decision between a BEV and FCV will depend on a driver’s specific needs and circumstances.
Low Emissions and Running Costs
A Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) is a type of electric vehicle that runs solely on battery power. Unlike hybrid vehicles, which have both a battery and a traditional combustion engine, BEVs rely entirely on their batteries for power. This means that BEVs have zero tailpipe emissions, making them a great choice for people who are passionate about environmental sustainability.
Additionally, BEVs have lower running costs than traditional combustion engine vehicles because electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline or diesel. While BEVs may have a higher upfront cost, the savings on fuel and maintenance costs over time can make them a more cost-effective choice in the long run. Plus, as the technology continues to develop, many experts predict that the price of BEVs will continue to drop, making them more accessible to consumers.
Overall, BEVs represent a promising future for environmentally conscious drivers looking to save money on fuel and maintenance costs.
Reliance on Charging Infrastructure
A Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) is a type of vehicle that runs entirely on electric power from a rechargeable battery. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, BEVs produce zero harmful emissions and offer lower operating costs due to the lack of fuel needed. However, the reliance on charging infrastructure remains a concern for many potential BEV owners.
Charging stations for BEVs are not yet as ubiquitous as gas stations, which can lead to range anxiety for drivers. Nonetheless, the push for more charging infrastructure is a priority for governments and private companies to increase the appeal and adoption of BEVs. With improvements in battery technology, the range of BEVs is also increasing, alleviating concerns about long-distance travel.
In the end, BEVs offer a promising alternative to traditional vehicles and are worth considering for their environmental and economic benefits.
What is a Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV)?
Battery electric cars and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) serve the same purpose of being emissions-free transportation options. However, they differ in how they produce and store energy. While battery electric cars rely on rechargeable batteries to power an electric motor, FCVs utilize hydrogen gas and an electrochemical process to generate electricity for their motor.
The biggest advantage of FCVs is their faster refueling time and longer driving range, making them suitable for long-distance travel. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations is not as widespread as electric charging stations, and the manufacturing of hydrogen is still limited. On the other hand, electric cars have more charging options and can run on renewable energy, making them more energy-efficient and cheaper to maintain.
Ultimately, the choice between a battery electric car and an FCV depends on personal preference and availability of infrastructure.
Zero Emissions and Fast Refueling
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV) Have you ever heard of a Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV)? These cars are among the most exciting emerging technologies in the automobile industry. Unlike traditional gas-powered cars, FCVs generate electricity by converting hydrogen and oxygen into water, producing zero harmful emissions. Not only are they environmentally friendly, but FCVs can be refueled in just a few minutes, much faster than charging an electric car.
Additionally, FCVs have a much longer range than battery-electric vehicles, meaning you can drive farther without needing to refuel. However, there are still some challenges to be addressed, such as a limited infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations. But as this technology continues to develop, the FCV may become a leading solution to the growing demand for a cleaner, more efficient means of transportation.
High Upfront Costs and Limited Infrastructure
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV) If you’re exploring the world of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), you’re not alone. FCVs are an emerging technology that is generating buzz in the automotive industry. Instead of relying solely on gasoline or diesel, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water and heat as byproducts.
While FCVs offer several benefits, such as zero emissions and incredible range, there are also some drawbacks to consider. One of the main issues is the relatively high upfront cost to purchase an FCV, as well as the limited infrastructure for hydrogen fueling stations. However, with advancements in technology and increased investment in hydrogen fueling infrastructure, FCVs may become a more accessible and common form of transportation in the future.
So, are you ready to join the FCV revolution?
Comparison and Contrast
When it comes to choosing between a battery electric car and a hydrogen fuel cell, there are some key differences to consider. Both types of vehicles are environmentally friendly, producing no emissions while on the road. However, there are some factors that set them apart.
Battery electric cars rely solely on a rechargeable battery to power the car, while hydrogen fuel cell vehicles use a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity. One advantage of hydrogen fuel cells is that they can be refueled much faster than electric cars can recharge their batteries. However, there are currently fewer hydrogen fueling stations available for consumers compared to electric charging stations.
Another factor to consider is the cost. Battery electric cars can be more affordable upfront, but may require expensive battery replacements after a number of years. On the other hand, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles can be more expensive to purchase initially, but have longer lifespans and may require less maintenance.
Ultimately, the choice between a battery electric car and a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle will depend on individual preferences and needs.
Environmental Impact
When looking at the environmental impact of different products or practices, it’s important to compare and contrast to make informed decisions. For example, let’s compare the impact of disposable plastic water bottles vs reusable ones. Disposable bottles may seem more convenient, but they have a hugely negative impact on the environment.
They take hundreds of years to decompose and often end up in landfills or the ocean where they harm marine life. Reusable bottles, on the other hand, can last for years and significantly reduce waste. Similarly, let’s consider the impact of gasoline-powered cars vs electric ones.
Gasoline cars emit harmful pollutants into the air and contribute to climate change, while electric cars emit no pollutants and run on renewable energy if charged properly. While electric cars may have a higher upfront cost, they save money in the long run and have a much smaller environmental impact. By comparing and contrasting the environmental impact of different products or practices, we can make more sustainable and responsible choices for our planet.
Economic Considerations
When it comes to economic considerations, there are several factors to weigh before making a decision. One of the most common approaches is to compare and contrast the various options to determine the most advantageous course of action. This can involve looking at the costs and benefits of each choice, as well as considering the potential risks and rewards.
For example, if a company is deciding whether to invest in a new production facility or to expand an existing one, they may compare the upfront costs and expected returns of each option. On the other hand, if an individual is trying to decide whether to buy or lease a car, they may compare the monthly payments, insurance costs, and the overall cost of ownership. By taking a more detailed look at the options and comparing their various features, it is possible to make more informed decisions that take into account the unique needs and circumstances of each situation.
Overall, careful comparison and contrast can be a valuable tool in navigating the complex world of economics.
Conclusion: Which is Better for You?
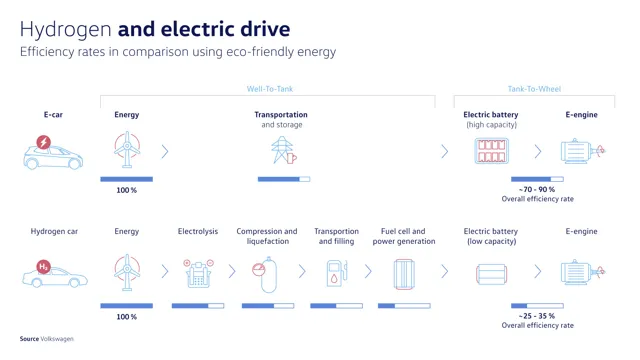
In the battle of battery electric cars versus hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, it seems that the battery electric car has won the war for the present. These vehicles are more widely available, have lower costs and are more efficient in terms of the energy used. However, this doesn’t mean that hydrogen fuel cells won’t play a key role in our transportation future.
Their potential and promise make them a viable option for long-range travel and commercial vehicles. So, as we continue to advance our technology, it may not be a question of which is better, but rather how we can best utilize both to create a sustainable and efficient transportation system. It’s a race to the finish line, but it’s looking like both battery technology and hydrogen fuel cells will be crossing it together.
“
FAQs
What is the primary difference between a battery electric car and a hydrogen fuel cell car?
The primary difference is the source of power – battery electric cars rely on electricity stored in a battery, while hydrogen fuel cell cars generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
Which is more energy-efficient – a battery electric car or a hydrogen fuel cell car?
Generally, battery electric cars are more energy-efficient, as there are fewer steps involved in the process of generating and delivering electricity to the motor. Hydrogen fuel cell cars, on the other hand, need to convert hydrogen gas into electricity, which can result in energy loss.
Are hydrogen fuel cell cars more expensive than battery electric cars?
Yes, currently hydrogen fuel cell cars tend to be more expensive than battery electric cars. This is due in part to the fact that the technology is newer and less widely adopted, as well as the challenges associated with storing, transporting, and distributing hydrogen fuel.
What is the range of a typical battery electric car compared to a hydrogen fuel cell car?
Range can vary widely depending on the specific make and model, but generally battery electric cars have a shorter range than hydrogen fuel cell cars. However, battery electric cars are more widely available and have more charging infrastructure in place, which makes them more practical for many drivers.