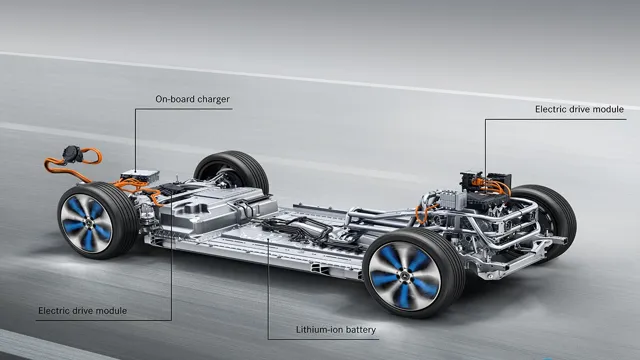
10 Revolutionary Battery Technologies that are Powering the Electric Cars of the Future
Electric vehicles have come a long way in the past few years, and the technology behind them is evolving at a rapid pace. One of the most crucial parts of any EV is its battery, as it provides the power needed for the car to move. Battery tech in EVs has become a hot topic, as researchers and engineers work to create better, longer-lasting batteries that can drive EVs further than ever before.
In this blog, we’ll explore the latest developments in EV battery tech and how they’re changing the game for drivers and manufacturers alike.
Current State of EV Batteries
Battery technology in electric cars has come a long way in recent years, with improvements made in terms of range, charging time, and overall efficiency. Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used type of battery in electric cars, due to their high energy density and relative affordability. However, there is still room for improvement, with several new battery technologies currently being developed and tested.
For example, solid-state batteries have the potential to offer higher energy densities, longer lifetimes, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of other materials such as sodium, magnesium, and even air as potential alternatives for batteries in electric cars. As battery technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see further advancements in the performance and efficiency of electric cars, making them an even more attractive option for environmentally-conscious consumers.
Average Range per Charge
Electric vehicle (EV) batteries have come a long way in terms of the average range per charge. In the early days, EVs typically had a range of less than 100 miles on a single charge, which limited their appeal for many commuters. However, with advancements in battery technology, many EVs now offer ranges of up to 300 or even 400 miles per charge.
This is a game-changer for electric mobility, as it makes EVs a practical option for a growing number of drivers. Of course, the exact range of an EV battery can vary depending on a range of factors, such as driving style, weather conditions, and the terrain. However, with the current state of EV batteries, range anxiety is becoming less and less of an issue for EV drivers.

Charging Time
The current state of EV batteries has brought us a long way from the early days of electric cars, where charging time was a major concern for potential buyers. Now, thanks to technological advancements, many EV batteries can be charged to 80% in less than an hour, making it much more convenient for drivers to keep their cars charged. However, it’s worth noting that different models and brands of EVs can have varying charging times, so it’s important to do your research before buying.
In general, though, it’s safe to say that EV batteries have come a long way in terms of charging time, and the future looks bright for even faster and more efficient charging methods.
Battery Lifespan
Battery Lifespan One of the biggest concerns among electric vehicle (EV) owners is the lifespan of the battery. While older EV models had battery life spans of around eight years, advancements in technology have brought that number up to around 10 years for newer models. Additionally, many automakers offer warranties on their EV batteries for 8-10 years or 100,000-150,000 miles.
However, it’s important to note that factors such as temperature, usage patterns, and charging habits can all affect the lifespan of an EV battery. To get the most out of your battery, it’s recommended to avoid frequent fast charging, limit exposure to extreme temperatures, and try to avoid draining the battery completely. By taking proper care of your EV battery, you can expect it to last for many years and thousands of miles.
Types of EV Batteries
Battery technology in electric cars has come a long way since the early days of EVs. Today, there are several types of batteries that are used in electric cars, each with their own pros and cons. The most common type of battery used in EVs is lithium-ion, which is known for its high energy density and fast charging times.
However, there are other types of batteries that are being developed and tested, including solid-state batteries and flow batteries. Solid-state batteries offer the promise of even higher energy densities and faster charging times, while flow batteries are being explored for their potential to offer longer ranges and reduced charging times. As battery technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more advancements in the years to come, making electric cars an even more practical and convenient way to get around.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
When it comes to EV batteries, lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used type. These batteries are known for their high energy density, which means they can store a lot of energy in a small space. There are two main types of lithium-ion batteries used in EVs, which are nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) and nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC).
NCA batteries are known for their high energy density, but they are also quite expensive. On the other hand, NMC batteries are more affordable and offer a good balance of energy density and safety. The choice of battery type depends on factors such as cost, performance, and safety.
Regardless of the battery type, it’s important to consider the charging and discharging habits to ensure the longevity of the battery and the overall performance of the EV. Overall, lithium-ion batteries are the most popular choice due to their high energy density and suitability for EVs.
Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are a type of EV battery that are gaining popularity due to their potential advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries. These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid electrolyte found in lithium-ion batteries. This makes them less flammable and potentially safer.
Additionally, solid-state batteries have the potential for increased energy density, which would mean longer ranges for EVs. However, there are still challenges in scaling up production and reducing costs for solid-state batteries before they can be widespread in the market. Nonetheless, with further research and development, solid-state batteries could revolutionize the EV industry.
Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
Lithium-sulfur batteries are a type of electric vehicle battery that is gaining popularity because of its high energy density. These batteries use sulfur as a cathode and lithium as an anode, which means that they are able to store more energy than traditional lithium-ion batteries. This is because sulfur is a lightweight and abundant element that can store two electrons per atom, while lithium can only store one.
However, lithium-sulfur batteries still have some challenges to overcome, such as their low cycle life and tendency to degrade quickly. Researchers are working on improving these batteries’ durability and safety by developing new electrolyte solutions and protective coatings. Overall, lithium-sulfur batteries have the potential to revolutionize the electric vehicle industry by making electric cars affordable, efficient, and practical for everyday use.
Future of EV Batteries
Battery technology in electric cars is constantly evolving, with manufacturers investing heavily in research to improve energy storage and extend driving range. Currently, most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, which are efficient, but can be expensive and have limitations in terms of charging time and lifespan. However, researchers are exploring new materials, such as solid-state and lithium-sulfur, which could offer significant improvements in performance and safety.
Solid-state batteries, for example, are expected to offer greater energy density and faster recharge times, while lithium-sulfur batteries could reduce weight and increase energy storage. Furthermore, advancements in battery recycling and reuse could lead to a more sustainable and cost-effective future for electric cars. As the demand for electric vehicles increases and technology advancements continue, the future of EV batteries looks promising.
Increased Energy Density
The future of EV batteries is rapidly evolving thanks to increased energy density. With the advancement of technology, batteries are becoming more powerful, allowing EVs to travel longer distances without needing to recharge. Increased energy density means more energy is stored in the same-sized battery, improving the driving range and performance of EVs.
This is made possible through the development of new materials and manufacturing processes. As a result, EVs are becoming more viable for everyday use as they become more efficient and reliable. With these advancements, we can expect to see an increase in the adoption of EVs and a decrease in our reliance on fossil fuels.
The future of transportation looks electrifying!
Lower Costs
The future of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is looking bright for not only the environment but also for drivers’ wallets due to the expected lower costs. With the advancements in technology and production, EV batteries are becoming more affordable for consumers. As more companies invest in EVs and their batteries, the economies of scale will come into play, leading to further cost reductions.
This will ultimately make owning and maintaining an EV more accessible for the average consumer. Moreover, with the increasing demand for renewable energy, we can see the shift towards cleaner energy sources. With these clean energy sources, EV batteries will become more sustainable, and the cost of production will decrease even further.
In conclusion, the future looks bright for EV batteries, with increased affordability and sustainability on the horizon. So, if you’re thinking of buying a vehicle, perhaps it might be time to consider an EV for a more eco-friendly and cost-effective option.
Impact on EV Industry
The development of battery technology in electric cars has had a significant impact on the EV industry. With advancements in battery technology, electric cars can now travel longer distances than ever before, making them more practical for everyday use. This has increased the demand for electric cars, leading to more investment in the EV industry.
Additionally, the development of fast charging technology has reduced the time it takes to charge an electric car, making them even more convenient to use. As battery technology continues to improve, we can expect to see even more innovative features in electric cars, such as longer battery life and faster charging times. This will further drive the adoption of electric cars and ultimately lead to a greener, more sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolution of battery technology in electric cars has been truly electrifying. From the early days of short range and long recharge times, to the present day of longer range and faster charging times, it’s clear that progress is being made at an energy-charged pace. And as battery technology continues to improve, we can look forward to a future where electric cars are not just a viable option, but a preferred mode of transportation.
So if you want to keep up with the times, it’s time to ditch the gas guzzler and plug in to the electrifying world of electric cars.”
FAQs
What is battery technology in electric cars?
Battery technology in electric cars is the technology used to power the vehicle’s electric motor by storing energy in rechargeable batteries.
How do batteries work in an electric car?
Batteries in an electric car work by converting stored chemical energy into electrical energy, which is then used to power the electric motor.
What is the range of an electric car battery?
The range of an electric car battery varies depending on the type of battery and the vehicle. Most electric cars have a range of 100-300 miles on a single charge.
How long does it take to charge an electric car battery?
The time it takes to charge an electric car battery depends on the type of charger and the size of the battery. It can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours to fully charge an electric car battery.