Revolutionizing Electric Cars: The Advancements in Battery Technology
Battery technology has come a long way in recent years, and now it’s powering some of the most impressive machines on the planet. Electric cars are just one example of how far battery technology has come. But how do these batteries work? And what makes them different from the batteries you might find in your phone or laptop? In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the battery tech powering electric cars, exploring the science behind it while also looking at the practical implications for drivers and manufacturers alike.
Whether you’re an EV enthusiast or simply curious about the technology behind the vehicles we drive, this post will provide you with a comprehensive introduction to battery tech for electric cars. So, buckle up, and let’s dive in!
History of EV Batteries
Battery technology used in electric cars has come a long way since the early days of EVs. In the 1990s, lead-acid batteries were commonly used in electric cars, but they had limited range and were heavy. Nickel-metal hydride batteries replaced lead-acid batteries in the early 2000s and became the industry standard for several years.
They offered better range and were lighter, but still had some limitations. However, over the last few years, lithium-ion batteries have become the go-to technology for electric cars. Lithium-ion batteries are much lighter and have a higher energy density, which means they can store more energy in a smaller size.
This has helped increase the range of electric cars and make them more practical for everyday use. While the technology has come a long way, there is still room for improvement, and researchers are constantly looking for ways to make EV batteries even better.
From Lead-acid to Li-ion
Electric Vehicle (EV) Batteries The history of EV batteries is a fascinating one that dates back several decades. In the early days of electric vehicles, lead-acid batteries were the primary source of power. These batteries were reliable but heavy and had limited range.
However, with the advent of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, the game changed. Li-ion batteries are lighter, more efficient, and have a longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries. Their energy density allows for more range on a single charge, making them the preferred choice for modern EVs.
As technology continues to advance, the future of EV batteries seems bright. With innovations like solid-state batteries on the horizon, the possibilities are endless. The quest for the perfect EV battery continues, and we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the coming years.
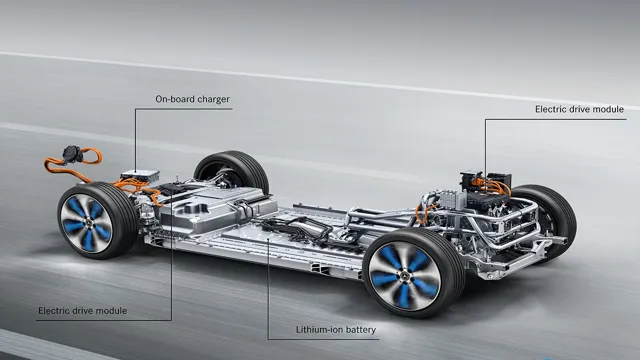
Current EV Battery Techs
Battery technology used in electric cars has come a long way in recent years, with several different types of batteries being used today. The most commonly used battery is the lithium-ion battery, which can be found in virtually all electric vehicles on the market. Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, meaning they can store a lot of energy in a small amount of space.
Another popular type of battery is the nickel-metal hydride battery, which is used in hybrid electric vehicles. Despite being less energy-dense than their lithium-ion counterparts, nickel-metal hydride batteries are more reliable and are less prone to overheating. Finally, some electric vehicles make use of solid-state batteries, which have the potential to be lighter, cheaper, and more energy-dense than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
As battery technology continues to improve, we can expect to see more advancements in electric vehicle technology, including longer-range vehicles, faster charging times, and more affordable prices.
Cobalt-free and Solid-state Batteries
As electric vehicles continue to gain popularity, advancements in battery technology have become more important than ever. Two emerging types of batteries, cobalt-free and solid-state batteries, have been making waves in the EV world. Cobalt-free batteries use substitutes for cobalt, which is expensive and sometimes produced using unethical practices.
Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, which can increase energy density and reduce the risk of fire. While these new battery techs show promise for the future, they still face challenges in terms of scalability and cost. Nonetheless, they could potentially offer a more sustainable and efficient solution for powering electric vehicles in the years to come.
Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Battery Management Systems, EV Battery Techs One of the most crucial components of an electric vehicle (EV) is the battery management system (BMS). This technology is responsible for monitoring the health of the battery, regulating the flow of energy in and out of the battery, and ensuring that the battery operates within safe parameters. BMS technology has come a long way since the inception of the EV industry, and there are currently several different types of BMS in use.
Some of the most popular EV battery techs include nickel-cadmium (NiCad), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), and solid-state batteries. Each battery technology has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the type of BMS used may differ depending on the type of battery. Despite the variety of battery technologies available, Li-ion batteries currently dominate the EV market due to their high energy density and long cycle life.
As the electric vehicle industry continues to grow, advancements in BMS technology will likely play a critical role in improving battery performance, efficiency, and safety.
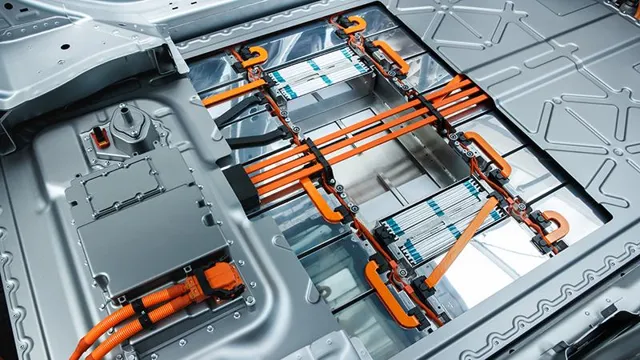
How EV Batteries Work
When it comes to electric cars, the battery technology used is a crucial component. These batteries work by storing energy that is used to power the car’s electric motor. They are typically made up of multiple lithium-ion cells that are wired together to create a larger battery pack.
The cells themselves contain a cathode and an anode, which are separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is charged, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, creating a flow of electrons that can be used to power the car. When the car is in use, the process is reversed, and the flow of electrons moves in the opposite direction.
The type of battery technology used in electric cars is constantly evolving, and new advancements are being made all the time to increase their efficiency and range. As electric cars become more prevalent, battery technology will continue to play an essential role in their growth and development.
Chemical Reactions Inside Batteries
Electric vehicle batteries work using chemical reactions that occur inside them. Inside the battery, there are two electrodes (an anode and a cathode), separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is charged, the electrons flow from the positive (+) cathode to the negative (-) anode and are stored as chemical energy.
When the battery is discharged, the flow is reversed, and the electrons flow from the negative anode to the positive cathode, providing electrical energy to power the EV. These chemical reactions are what make electric vehicles operate, and it’s the rechargeable nature of the batteries that makes them so practical for everyday use. EV batteries have come a long way in recent years, and with advancements in technology, they’re becoming more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly.
As we move towards a cleaner, sustainable future, the importance of electric vehicle batteries in powering our transportation needs will only continue to grow.
Electricity Generation and Storage
EV batteries are the heart of electric vehicles. But, how do these batteries work? EV batteries are made of hundreds of individual battery cells that work in tandem to provide power to the vehicle. Each cell consists of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and an electrolyte.
When the battery is charged, lithium ions from the positive electrode move through the electrolyte to the negative electrode, creating an electrical current. When the battery powers the vehicle, the process is reversed, with lithium ions moving from the negative electrode to the positive electrode. This movement of ions is what powers the electric motor.
When an EV is charging, the battery management system makes sure that the cells are charged evenly to prevent any damage. Understanding how EV batteries work is crucial to understanding how electric vehicles operate. With the rapid expansion of EVs, the demand for better and safer battery technology continues to increase.
As the technology advances, EV batteries will become even more efficient, affordable, and accessible to everyone.
Future of EV Batteries
Without a doubt, the battery technology used in electric cars is improving rapidly. Over the past few years, there have been significant advancements in battery technology, leading to longer ranges and quicker charging times. One of the most promising technologies is solid-state batteries.
These batteries have the potential to increase energy density and reduce the risk of fires. Another area of development is fast-charging solutions. Companies are looking to reduce charging times to just minutes, making them almost as convenient as filling up a gas tank.
These innovations hold enormous promise for the future of electric vehicles. With continued research and development, we can expect to see even more efficient and effective battery technology used in electric cars. As demand for EVs continues to grow, developing more advanced and economical batteries will be essential for the industry’s continued success.
Emerging Battery Techs and Innovations
The future of EV batteries is looking bright, with emerging battery techs and innovations promising longer range and shorter charging times. One exciting development is solid-state batteries, which use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, providing improved energy density and reduced risk of fire. Another emerging technology is lithium-sulfur batteries, which have the potential to store up to five times more energy than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Additionally, advanced charging methods such as wireless charging and ultrafast charging are being developed to further streamline the charging process for electric vehicles. As these battery technologies continue to improve, the feasibility and practicality of widespread electric vehicle adoption will only increase.
Sustainability and Recycling
The future of EV batteries promises more sustainability and recycling options than ever before. As electric vehicles become increasingly popular, there are mounting concerns about the environmental impact of disposing of the batteries. Fortunately, innovative solutions are being developed to address these concerns.
One promising development is the use of recycled materials in manufacturing new batteries. This not only reduces the amount of waste generated but also lowers the extraction of critical resources used in battery production. Another option is to reuse EV batteries for energy storage in homes and buildings, extending the lifetime of the batteries and reducing the need to manufacture new ones.
With these and other sustainability initiatives taking place, the electric vehicle industry is poised to become even more environmentally friendly in the years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, battery technology is the backbone of electric cars. It’s the powerhouse that fuels these sleek, eco-friendly machines. Without it, we would be stuck with gas-guzzling beasts that choke the environment with their emissions.
Just like a life without coffee is unimaginable, a world without batteries in electric cars is impossible. So, the next time you see an electric car whizzing by, give a nod to the battery and feel good about doing your bit for the planet. After all, battery technology has come a long way, and it’s here to stay!”
FAQs
What type of battery technology is commonly used in electric cars?
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used type of battery technology in electric cars.
How long do the batteries in electric cars last before needing to be replaced?
The lifespan of electric car batteries varies, but most manufacturers offer warranties for 8-10 years or 100,000 miles.
What factors can affect the range of an electric car’s battery?
The range of an electric car’s battery can be affected by factors such as temperature, driving habits, and use of accessories like air conditioning.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, electric car batteries can be recycled. The materials used in the batteries, such as lithium and cobalt, can be recovered and used again in new batteries or other products.