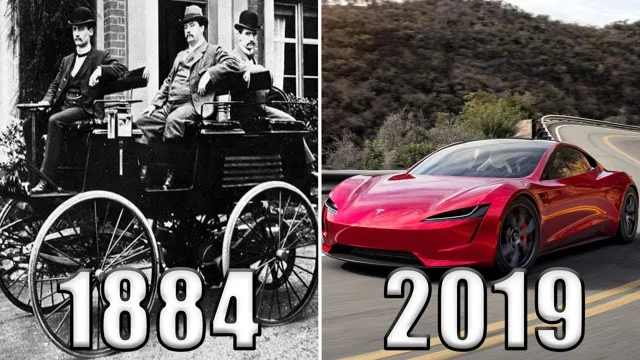
The Shocking Evolution of Electric Cars: A Brief History
Do you know when the first electric car was invented? It may surprise you to learn that electric cars have been around for more than a century. In fact, they were among the first automobiles ever made. While they may have taken a back seat to gasoline-powered cars in the past, electric cars have been steadily gaining in popularity over the last few decades as consumers become more concerned about the environment and the rising cost of oil.
In this blog post, we’ll take a brief look at the history of electric cars, from their early beginnings to the modern electric vehicles of today. So sit back, and let’s take a ride through time as we discover the fascinating history of electric cars.
Early Electric Cars
Electric cars have been around longer than many people realize. In fact, the first electric car was created in the late 1800s! But while electric cars were popular in the early days of automobiles, they eventually fell out of favor due to the rise of gasoline-powered cars. It wasn’t until the 1990s and 2000s that electric cars began to gain traction once again.
Today, electric cars are becoming more and more popular as people are looking for more environmentally-friendly transportation options. While electric cars might still not be as common as gas-powered cars, their popularity is certainly on the rise. So, while the early electric cars may have been forgotten about for some time, they are now experiencing a resurgence in popularity and may soon become more common on roads around the world.
First electric car invented in the 1830s
Electric cars are not a new invention, and in fact, the first electric car was invented in the 1830s. Scottish inventor Robert Anderson built the first crude electric carriage around 1832, and it could travel up to 3 miles at a time. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s and early 1900s that electric cars really started to gain in popularity.
Many early electric cars were designed for women, as they were considered cleaner, quieter, and easier to operate than gasoline-powered cars. The Baker Electric, for example, was a popular choice for affluent women in the early 1900s. However, with the invention of the Ford Model T in 1908, gasoline-powered cars quickly became the norm, and electric cars fell out of favor.
It wasn’t until the 1990s that electric cars started to make a comeback, and today, more and more people are opting for electric vehicles as a way to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on gas.

Electric vehicles popular in the late 19th century
Electric vehicles were actually very popular in the late 19th century, but they lost favor to gasoline cars by the 1920s. In the late 1800s, electric cars were preferred for short distances due to the ability to create a self-starter electric motor that could power the car. But the downside was that electric cars were expensive, and electric batteries struggled to store enough energy to provide sufficient range.
Despite that, the first land speed record was set by an electric vehicle on 18 December 1898, when an electric-powered car went faster than any other vehicle on earth. In the 1910s, gasoline-powered vehicles became cheaper, and the invention of the electric starter made them easier to operate, cornering the market with their convenience and affordability. However, recently, with the advances in technology and concern for the environment, more and more people are turning to electric vehicles as a cleaner and more sustainable option for transportation.
As a result, the electric vehicle market is now growing rapidly, and new developments in battery technology and charging stations are making them more accessible and practical than ever before.
Decline of Electric Cars
A brief history of electric cars reveals that they have been around for over a century. The first electric car was invented in the late 1800s, and electric cars were actually quite popular at the start of the 20th century. However, as gas-powered cars became more popular and accessible, electric cars declined in popularity.
Throughout the 20th century, electric cars had their ups and downs, but it wasn’t until the 2000s that they began to make a comeback, thanks to advancements in battery technology and concerns about climate change. At first, it seemed like electric cars were poised to be the wave of the future, but in recent years, their popularity has declined once again. The high cost of electric cars, a lack of charging infrastructure, and lower gas prices have all contributed to this decline.
Despite these challenges, electric cars will likely continue to play an important role in the future of transportation.
Introduction of the gasoline engine led to decline
With the introduction of the gasoline engine, electric cars began to decline. As gasoline engines became more popular, electric cars became less and less common. This decline continued for many years until electric cars were nearly forgotten.
The gasoline engine was simply more convenient, more powerful, and more reliable than electric cars of the time. While electric cars still exist today, it wasn’t until recent advances in technology that they began to gain popularity again. Now, with the rise of electric cars, we are seeing a shift towards more sustainable forms of transportation.
People are becoming more aware of the impact that gasoline engines have on our environment, and they are looking for alternatives. Electric cars are not only better for the environment, but they are also more efficient and cost-effective than gasoline-powered vehicles. The future of transportation is electric, and it’s an exciting time to see how this technology will continue to evolve.
Lack of infrastructure for charging
The decline of electric cars stems from the lack of infrastructure for charging. While electric cars promise to be a green and efficient way to travel, their success is hindered by the practicality of charging them. Unlike traditional cars, electric cars require recharging every few hundred miles, which can be a hassle without accessible charging stations.
In addition, public charging stations are often occupied or not conveniently located, leading to frustration for electric car drivers. As a result, many people are hesitant to make the switch to electric cars and stick with traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. It’s like having a phone with a battery that lasts for days, but nowhere to charge it.
Without adequate infrastructure for charging, the potential benefits of electric cars remain out of reach for many drivers. The solution may lie in investing in widespread charging infrastructure to make electric cars a more viable option for drivers. Until then, gas-powered cars will likely remain the more convenient and practical choice for most people.
Modern Day Electric Cars
Electric cars have come a long way since their inception in the late 1800s. The early electric vehicles boasted top speeds of only 20 miles per hour and limited range due to their heavy lead-acid batteries. However, with advancements in technology and the need for eco-friendly transportation options, the modern-day electric car has come a long way.
The latest electric vehicles have impressive ranges ranging from 200-300 miles with a speed of over 100 miles per hour. Moreover, as opposed to early electric vehicles, modern electric cars use sophisticated lithium-ion batteries that are far lighter than their predecessors, resulting in superior performance and extended range. Tesla is a prime example of a company that has revolutionized the electric car industry, with its electric vehicles boasting luxury features and a range of up to 402 miles.
The rise of electric cars has allowed for cleaner transportation and a more sustainable future – a win for both consumers and the environment.
Tesla’s impact on electric car resurgence
The last decade has seen a significant resurgence of interest in electric cars, and much of this can be attributed to Tesla’s impact in the industry. Modern-day electric cars, like those produced by Tesla, have come a long way from their early counterparts, which had limited driving range and took far too long to charge. Today’s electric cars like the Tesla Model S and Model 3 offer high-performance, long-range capabilities, and faster charging times.
Tesla’s Supercharger network is one of the biggest reasons for the success of electric cars, giving drivers peace of mind that they can charge their cars up on long trips. Tesla’s sleek design and technological prowess also make electric cars more appealing to a broader audience. In short, Tesla has made electric cars cool and practical, and their impact on the industry is undeniable.
As Tesla continues to push the boundaries with new innovations, we can expect the popularity of electric cars to continue to grow.
Government incentives for electric vehicles
Modern day electric cars have garnered attention from both consumers and governments due to their positive impact on the environment. In recent years, several countries have introduced incentives to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). These incentives range from tax credits and rebates to free public charging and reduced toll fees.
Governments are recognizing the need to reduce carbon emissions and are playing an active role in promoting the production and adoption of electric cars. For instance, in the United States, the federal government provides a tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of an EV. Various cities across the globe have also taken steps to provide access to a charging network to make EVs more practical for everyday use.
These incentives not only benefit the environment but also make EVs more attractive to consumers through lower costs, improved infrastructure, and innovative technology. As we move towards a greener future, these government incentives are a step in the right direction towards cleaner air and a sustainable world.
The Future of Electric Cars
Before discussing the future of electric cars, it’s important to understand their brief history. The invention of the electric car dates back to the 19th century, but it wasn’t until the early 2000s that they started gaining traction in the market. The first models were limited in range, and their high costs made them inaccessible to the majority of consumers.
But with advancements in battery technology and increased production, electric cars have become more affordable and their range has significantly improved. Today, there are more than 7 million electric cars on the road worldwide, and this number is projected to increase exponentially in the coming years. As the world shifts towards sustainable energy sources, the future of transportation seems to be electric.
With growing concerns about climate change and the need to reduce carbon emissions, electric cars will play a crucial role in shaping a cleaner, healthier future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of electric cars has been one of ups and downs, with moments of great promise and periods of relative neglect. But with increasing demand for environmentally-friendly vehicles and advancements in technology, it seems that electric cars are finally primed to take over the road. So buckle up and charge your batteries, because the future of transportation is electric and it’s going to be one electrifying ride!”
FAQs
When were electric cars first invented?
The first electric car was built in the 1830s by Robert Anderson of Scotland.
What was the first mass-produced electric car?
The first mass-produced electric car was the Baker Electric in 1899.
When did electric cars become less popular?
Electric cars lost popularity in the early 20th century due to the development of gasoline-powered cars and the discovery of vast oil reserves.
Why are electric cars gaining popularity again?
Electric cars are gaining popularity again due to increasing concerns about climate change and the environmental impacts of gasoline-powered cars.
How far can electric cars typically travel on a single charge?
The range of electric cars varies, but most can travel between 100 and 300 miles on a single charge.
What are the benefits of driving an electric car?
Electric cars produce zero emissions, are cheaper to operate than gasoline cars, and have lower maintenance costs. They also offer a quieter and smoother driving experience.


![The Shocking History of Battery-Only-Powered Cars: Unveiling the Rise of Electric Automobiles [PDF]](https://electriccarwiki.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/history-of-the-electric-automobile-batteryonly-powered-cars-pdf.webp)