Revolutionizing Electric Cars: Could D Cell Batteries be the Future Power Source?
If you’re curious about whether D cell batteries can power electric cars, you’re not alone. With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and the focus on renewable energy, it’s natural to wonder if there are alternative sources of power that can be used to fuel these eco-friendly cars. D cells are commonly used in flashlights, toys, and other small devices, but are they powerful enough to support an electric car? In this blog, we’ll delve into this fascinating topic and explore the feasibility of using D cell batteries as a power source for electric vehicles.
So, buckle up and let’s dive in!
Understanding the power requirements of an electric car
While D cell batteries may be a useful alternative source of power for small appliances, they are not practical for electric cars. Electric cars require a high amount of power to run, and D cell batteries simply cannot provide enough energy to keep the vehicle moving for any length of time. In fact, electric cars use high-capacity lithium-ion batteries that can store energy efficiently and safely.
Additionally, these batteries must be properly maintained to ensure optimal performance and longevity. While it may be tempting to find alternative power sources for your electric car, it’s important to remember that these vehicles are designed to run on specific types of batteries for safety and performance reasons.
Calculating the power output of D cell batteries
As electric cars become more prevalent on our roads, it’s crucial to understand their power requirements. One way to measure the power output of a battery is by calculating its voltage, current, and capacity. For example, D cell batteries typically have a voltage of
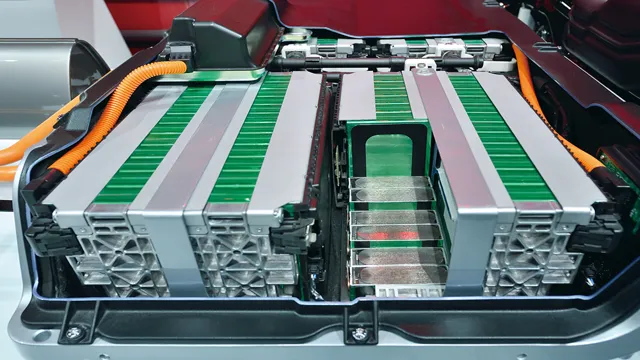
5V, a capacity of around 12000mAh, and can discharge at a current of up to 3A. These power requirements are great for small devices, but electric cars need much more power than a pack of D cell batteries can provide. In fact, the battery packs used in electric cars are made up of thousands of individual cells that can deliver the power needed to move a vehicle that weighs several thousand pounds.
To put it in perspective, the battery pack of a Tesla Model S can provide up to 85 kilowatt-hours of power, which is equivalent to over 5,000 D cell batteries! Understanding the power requirements of an electric car is crucial to ensure that the battery pack can provide enough power to drive the vehicle and that it can be charged safely and efficiently.

Comparing D cell batteries to other power sources for electric cars
Electric cars require a significant amount of power to run, and understanding the power requirements of an electric car is crucial to selecting the right power source. When comparing D cell batteries to other power sources for electric cars, it’s important to note that D cell batteries are not a feasible option due to their low energy density and limited lifespan. Electric cars require high-capacity batteries that are capable of delivering consistent power over extended periods.
Lithium-ion batteries have become the preferred power source for electric cars due to their high energy density and extended lifespan. While gasoline-powered cars rely on a combustion engine that converts fuel into energy, electric cars draw their power from a battery that stores and delivers energy to the motor. This fundamental difference in power source is what makes electric cars a far more environmentally-friendly and sustainable option.
So, when it comes to powering an electric car, it’s clear that D cell batteries simply don’t have what it takes.
The limitations of using D cell batteries for electric cars
While the idea of using D cell batteries to power an electric car may seem tempting due to their affordability and accessibility, it’s important to understand the limitations this approach presents. D cell batteries are simply not designed to provide the energy required to propel a vehicle on the scale of an electric car. The burstiness of D cell batteries means that they can deliver a significant burst of power but only for a short period, whereas an electric car needs consistent and sustained power to operate effectively.
Additionally, the energy density of D cell batteries is much lower compared to Lithium-ion or other advanced batteries used in electric cars. This means that electric cars powered by D cell batteries wouldn’t be able to travel far distances, and the batteries would require replacement frequently. In the end, while it may be an intriguing idea, using D cell batteries to power an electric car is not a viable option for practical purposes.
Addressing safety and environmental concerns
Electric cars have been touted as a greener and cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline cars. However, as with any new technology, there are still safety and environmental concerns that need to be addressed. One specific concern is the use of D cell batteries in electric cars.
While these batteries are commonly found in household appliances, they are not well-suited for the demands of electric cars. D cell batteries have limited capacity, meaning they can only power a car for a short distance before needing to be recharged. Additionally, these batteries contain toxic chemicals and heavy metals that can be hazardous to the environment if not disposed of properly.
As a result, electric car manufacturers are looking for alternative battery technologies that can provide longer-range and are more environmentally friendly.
Analyzing the cost-effectiveness of using D cell batteries for electric cars
Although D cell batteries may seem like a cost-effective solution for electric cars, they come with several limitations that make them impractical. D cell batteries operate at a lower voltage, which means they require many more batteries to power an electric car compared to lithium-ion batteries. This not only increases the weight of the car but also takes up valuable space, making it challenging to fit additional components that contribute to an electric car’s functionality.
Additionally, D cell batteries do not have a high energy density, which means they won’t last as long as lithium-ion batteries, making them unsuitable for long-distance travel. In the end, while D cell batteries may appear as a cheap alternative, their limitations outweigh their benefits. For long-term cost-effectiveness and practicality, lithium-ion batteries remain the best option for electric cars.
Exploring potential technological solutions
Electric cars have revolutionized the automobile industry, but their limited range remains a challenge. One of the more significant drawbacks is the reliance on D cell batteries, which can be both bulky and heavy. While D cell batteries have been a viable source of energy for electric cars, they come with several limitations, including efficiency, cost, and weight.
The use of these batteries can severely impact the vehicle’s acceleration and speed, making it less practical for long-term use. Despite the numerous advances in electric car technology, the reliance on D cell batteries is a significant challenge that requires urgent attention. Finding alternative technologies that offer better energy density, longer-range, faster charging times, and safer battery management systems is essential.
As the world moves toward a more sustainable future, the automotive industry must explore potential solutions for electric cars capable of addressing these challenges.
Conclusion: Is it feasible to power an electric car with D cell batteries?
In conclusion, while it may be possible to power a small toy car with D cell batteries, it is highly unlikely that you could manufacture an electric car for everyday use that runs on them. It would be like trying to power a rocket ship with sparklers- it might work for a brief moment, but it is simply not feasible in the long run. So, let’s stick to the more practical methods of powering our cars and leave the D cell batteries for their intended use- small electronic devices and toys.
“
Summarizing key takeaways
While D cell batteries may be reliable and widely available, they are not suitable for powering electric cars for several reasons. Firstly, their size and weight make them impractical for use in a vehicle, as they take up a lot of space and add unnecessary weight. Additionally, D cell batteries have a relatively low energy density, which means they cannot store as much energy as other types of batteries.
This results in reduced range and poorer performance for electric cars. Furthermore, D cell batteries have a shorter lifespan compared to other rechargeable battery options, and they are not as environmentally friendly due to their higher pollution and carbon emissions. While D cell batteries have their uses in other applications, they are simply not suitable for powering electric cars efficiently and sustainably.
It is important to explore other battery options that are specifically designed for electric vehicles, to ensure they can meet the demands and expectations of modern drivers.
Discussing potential future developments
As we move towards a more sustainable future, electric cars are becoming increasingly popular. However, one major limitation is the use of D cell batteries. While these batteries are readily available and affordable, they are not designed for the high demands of electric vehicles.
Electric cars require a significant amount of power to run, and D cell batteries simply are not capable of providing the power needed for long distances. Additionally, the batteries are quite heavy, adding to the overall weight of the vehicle and decreasing its efficiency. There is hope for future developments, particularly with advancements in the field of battery technology.
However, until then, we may need to look to other power sources or battery types that are better suited to the demands of electric cars if we want to continue on the path towards a greener, more sustainable future.
Exploring alternative power sources for electric cars
As we continue to seek out more sustainable alternatives for powering our automobiles, the possibility of using D-cell batteries to power electric cars has been a topic of discussion. While it may seem unconventional, the idea of using D-cell batteries to power an electric car is not entirely far-fetched. However, it should be noted that D-cell batteries are not designed for such use and do not produce nearly enough energy to power an electric car.
Electric cars require a significant amount of electricity to operate, and the energy provided by D-cell batteries would not be enough to sustain the vehicle’s power needs for an extended period of time. While it is important to explore alternative power sources for electric cars, we must recognize the limitations of certain power sources and focus on developing technology that is both sustainable and practical. Perhaps one day, we will discover a way to use D-cell batteries to power electric cars, but for now, it remains an interesting idea that is not quite feasible.
FAQs
What is the power source of an electric car?
The power source of an electric car is typically a rechargeable battery pack composed of multiple individual cells.
Can D-cell batteries be used to power an electric car?
No, D-cell batteries are not practical to power an electric car due to their low energy density and limited capacity.
How many cells are typically in an electric car battery pack?
The number of cells in an electric car battery pack varies, but typically ranges from a few hundred to a few thousand cells.
Can the battery pack of an electric car be swapped for a fully charged one?
Yes, some electric cars have the capability for the battery pack to be swapped out for a fully charged one, allowing for quicker charging and longer driving range.