Revving up the future: Can electric car battery packs be recycled?
Electric cars have grown in popularity in recent years, with more people opting for the environmentally-friendly alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. However, with the rise in the number of electric cars comes the issue of what happens to their battery packs when they reach the end of their life. While electric car batteries are designed to last for many years, they will eventually need to be replaced, leaving many wondering what can be done with the old ones.
This is where the question of recycling electric car battery packs comes into play. Is it possible to recycle them, and is it worth it? The answer is yes, it is possible to recycle electric car battery packs, and it is also very important to do so. Electric car batteries contain valuable metals and materials that can be reused to make new batteries and other products.
Recycling them not only preserves these precious resources but also helps to reduce the environmental impact of mining for new materials. However, recycling electric car battery packs is not a simple process. The batteries must be safely dismantled, and the various materials separated out to be reused.
This can be a time-consuming and costly process, and not all recycling facilities are equipped to handle electric car batteries. Additionally, some of the materials used in electric car batteries, such as lithium and cobalt, can be dangerous if not handled properly. Despite the challenges, recycling electric car battery packs is a necessary step in the move towards a more sustainable future.
It not only reduces the strain on natural resources but also helps to protect the environment from the harmful effects of mining and disposal. So, the next time you’re considering purchasing an electric car, keep in mind the importance of recycling its battery pack when the time comes.
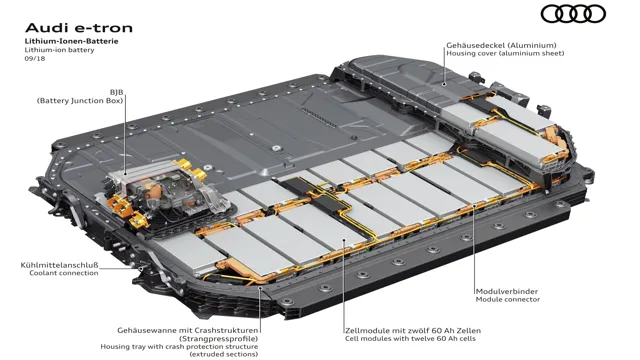
Battery Pack Composition
Yes, electric car battery packs can be recycled! In fact, recycling is becoming an increasingly important part of electric car production, as the demand for these vehicles continues to rise. The battery packs themselves are made up of a variety of materials, including metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, as well as plastics and other components. These materials can all be extracted and reused, reducing the need for new resources and minimizing waste.
Additionally, recycling battery packs can help to prevent harmful chemicals and pollutants from seeping into the environment, which can have a significant impact on both wildlife and human health. So the next time you’re considering purchasing an electric car, rest assured that its battery pack can be recycled and given new life for future use!
What metals are in electric car batteries?
When it comes to electric cars, the battery pack is undoubtedly one of the most integral components. Many people often wonder what metals are used in the construction of these battery packs. Well, the answer is quite complex.
Most modern electric car batteries are made using a lithium-ion chemistry, which typically includes materials like cobalt, nickel, manganese, and aluminum. These metals are utilized in varying amounts depending on the specific battery design and brand. Additionally, some manufacturers are looking to move away from cobalt due to the ethical concerns surrounding it, and instead, they are using more nickel or iron in their batteries.
Ultimately, the composition of an electric car battery’s metal makeup is dependent on the manufacturer’s design and the latest technology trends. Regardless of the specific metals used, the overall goal is to create a long-lasting battery with high energy density and minimal environmental impact.

How much of these metals can be recycled?
When it comes to recycling, the composition of a battery pack can greatly impact just how much of its materials can be reused. Most commonly found in electric vehicles, a lithium-ion battery pack contains a variety of metals, including cobalt, nickel, and copper. While all of these metals have value and can be recycled, the process is not always easy or efficient.
For example, cobalt is often found in low concentrations within the battery cells, which makes it more difficult and expensive to extract for reuse. Additionally, if the battery has been damaged or reached the end of its life cycle, it may not be possible to recycle all of its materials. Essentially, the amount of each metal that can be recycled from a battery pack largely depends on the specific composition and condition of the battery, as well as the recycling technology available.
Current State of Recycling
When it comes to the current state of recycling, there’s a lot to consider. One question that often arises is whether or not electric car battery packs can be recycled. The short answer is yes – they can be recycled.
However, the process isn’t as simple as just tossing the battery pack in a recycling bin. Electric car batteries are typically made up of a variety of different materials, including metals and chemicals, which can make recycling them a complex process. That said, the recycling industry is making strides in finding ways to recycle electric car batteries in a sustainable way.
By properly dismantling and separating the various components of the battery pack, recyclers can extract valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can then be repurposed for use in new batteries or other products. While the process has a ways to go, the fact that electric car battery packs can be recycled is a step in the right direction towards more eco-friendly transportation options.
What is the current rate of electric car battery recycling?
Electric car battery recycling The current rate of electric car battery recycling has been steadily increasing over recent years. As the world shifts towards sustainable energy sources and electric vehicles become more popular, there has been a greater focus on finding ways to recycle or repurpose the batteries that power these cars. While the exact rate varies depending on location and industry, studies have shown that most of the materials in electric vehicle batteries, such as copper, aluminum, and lithium, can be easily recycled.
As a result, there has been a growing trend towards battery recycling among manufacturers and governments worldwide. This not only helps to reduce waste and environmental impact but also provides a sustainable source of raw materials for new battery production. While there is still room for improvement, the current state of electric car battery recycling is promising and suggests a brighter future for the sustainability of electric vehicles.
Which countries are leading in battery recycling?
Battery recycling is becoming increasingly important as the world’s demand for batteries continues to grow. Proper disposal of batteries prevents toxic chemicals from leaching into the soil and water supply. Currently, Belgium and Sweden are leading the way in battery recycling, with both countries recycling over 95% of all batteries.
These countries have implemented laws and systems that encourage the responsible disposal of batteries and the recovery of valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Other countries, such as the United States, are also working towards improving battery recycling efforts, but they have a long way to go. The U.
S. recycles less than 5% of all batteries, but new legislation and public awareness campaigns are helping to increase those numbers. As the world continues to move towards renewable energy, battery recycling will become even more crucial, and it is up to governments, manufacturers, and consumers to ensure that this valuable resource is used responsibly.
Are there any challenges in recycling battery packs?
Recycling battery packs is becoming increasingly important in today’s environmentally conscious society. However, there are some challenges that need to be addressed in the current state of recycling. One major challenge is that the process of recycling battery packs can be complex and costly.
Batteries contain hazardous and flammable materials that require special handling and disposal. Additionally, battery packs are often made from a variety of materials, which can make them difficult to dismantle and separate for recycling. Another challenge is the lack of infrastructure and regulations around recycling battery packs.
In some areas, there may not be any facilities that are equipped to handle this type of recycling, or there may be inconsistent regulations on how batteries should be disposed of. Overall, while recycling battery packs can be a challenge, it is crucial for the health of our planet and we must continue to work towards solutions that allow for safe and sustainable recycling practices.
Future of Electric Car Battery Recycling
Can electric car battery packs be recycled? Absolutely! As the popularity of electric cars increases, so does the need for a proper recycling system. The future of electric car battery recycling looks bright as more and more companies are working on developing efficient and cost-effective recycling processes. The batteries have valuable metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can be recovered and reused.
Recycling these batteries will not only prevent the toxic waste from ending up in landfills but also help in reducing the reliance on mining these metals. The recycled materials can be used to make new batteries or even other electronic devices like smartphones and laptops. As more people opt for electric cars, recycling the batteries will become more important than ever to ensure the sustainability of the environment and reduce the carbon footprint.
Are there any promising technologies to improve battery recycling?
Electric car battery recycling has become a pressing concern in the automotive industry. To address this issue, researchers have been exploring new technologies to make battery recycling more efficient and cost-effective. One promising development is pyrometallurgy, which involves breaking down batteries at high temperatures to recover valuable metals.
Another approach involves using hydrometallurgy, where batteries are dissolved in a liquid solution to extract metals. One company has developed a process that uses microbes to break down batteries and recover metals, which could potentially reduce the amount of waste generated from battery recycling. While these technologies are still in the early stages of development, they offer hope for a more sustainable future for electric car battery recycling.
How can consumers and manufacturers contribute to battery recycling?
The future of electric car battery recycling looks promising, but it’s not just up to manufacturers to make this process a reality. Consumers also play a critical role in contributing to a sustainable approach for battery disposal. One way to do this is by opting for EV models that prioritize recycling and sustainability.
Some manufacturers have already stepped up their efforts and are offering take-back programs, where they accept used batteries for recycling and repurposing. Consumers can also look for recycling centers in their local area and bring their old batteries there. By doing this, they not only contribute to environmental protection but also help reduce the demand for minerals used in battery production.
As a result, we can reuse valuable materials found in car batteries, mitigating the environmental impact of producing new ones. It’s imperative that both manufacturers and consumers work together towards finding innovative solutions that address the challenges present in recycling batteries, turning this process into a sustainable one.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, the question of whether electric car battery packs can be recycled is one that has been asked quite frequently in recent times. The answer, fortunately, is a resounding yes! With advancements in technology, recycling electric car batteries has become easier than ever before, making it a more sustainable and environmentally friendly option than simply disposing of them. So, the next time you’re considering buying an electric car, remember that not only are they better for the environment, but their batteries can be recycled too! Now that’s what we call a clever and witty way to save the planet, one electric car at a time.
“
FAQs
Why is it important to recycle electric car battery packs?
Electric car battery packs contain valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can be reused and help reduce the demand for new materials. Recycling also prevents these materials from ending up in landfills and potentially harming the environment.
How are electric car battery packs typically recycled?
The process of recycling electric car battery packs involves removing the valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The remaining materials, like plastic and aluminum, can also be recycled separately. These materials can then be reused in new battery packs or other products.
Is it economically feasible to recycle electric car battery packs?
The economics of recycling electric car battery packs depend on the market demand for the materials inside the batteries. As the demand for these materials increases, the financial incentive for recycling also increases. However, the costs of recycling still need to be lower than the costs of producing new batteries for recycling to be economically feasible.
What happens to electric car battery packs that are not recycled?
If electric car battery packs are not recycled, they can end up in landfills and potentially harm the environment. Batteries can release toxic chemicals that can seep into the soil and groundwater. Additionally, not recycling battery packs means that valuable materials are not being reused and the demand for new materials is not being reduced.