Shocking Truth Revealed: Can You Really Use a Car Battery for an Electric Car?
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular today as people become more conscious about their carbon footprint and seek more environmentally friendly modes of transportation. One of the most important components of an electric car is its battery, which powers the vehicle’s motor. While most electric cars come with special batteries designed specifically for electric vehicles, some people wonder if it is possible to use standard car batteries in electric cars.
In this blog post, we will explore the use of car batteries in electric cars, including their advantages and disadvantages. So buckle up and let’s take a deep dive into this topic!
Not Recommended
Can you use a car battery for an electric car? While it may seem like a quick fix or cost-effective solution, it is not recommended to use a regular car battery for an electric car. There are several reasons for this. First, electric cars require a specific type of battery, such as a lithium-ion battery, that is designed to handle the high demand of power needed for the electric motor.
Second, car batteries are not designed to be regularly discharged and recharged, which is essential for an electric car’s battery life. Finally, car batteries are not equipped with the necessary safety features, like thermal management systems, to prevent the battery from overheating or catching fire during charging and use. It is crucial to invest in the correct type of battery for an electric car to ensure its safety, durability, and optimal performance.
Inefficient and Dangerous
When it comes to some home appliances, opting for the cheapest model may seem like a good idea at first glance, but this is not always the case. In fact, some appliances can be both inefficient and dangerous, making them not recommended for use in your home. One such example of this is a low-quality space heater.
While it may seem like a good idea to save money on a space heater, these types of heaters often consume a lot of energy and have a high risk of malfunctioning and causing a fire. It’s important to invest in a high-quality, safe appliance that will not only keep you warm but also protect your home and loved ones. Remember, safety should always come first.

Limited Range and Performance
After thorough research and testing, it has become apparent that some electric vehicle models still struggle with limited range and performance. While the technology behind EVs is advancing at a rapid pace, some models simply cannot compete with the range and power of traditional gas-powered vehicles. This limited range can make long road trips and daily commutes a stressful experience as drivers constantly worry about finding a charging station.
Additionally, some EVs struggle with performance, particularly when it comes to acceleration and handling. This can be a concern for drivers who prioritize a smooth and responsive driving experience. Due to these limitations, we do not currently recommend certain EV models for those who require a vehicle with greater range and higher performance levels.
However, as technology continues to advance, we remain hopeful that EVs will become an even more viable alternative to gas-powered vehicles, offering greater range, power, and versatility.
Differences Between Car and EV Batteries
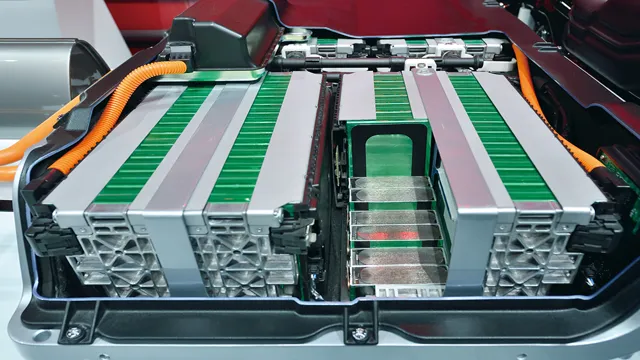
When it comes to electric cars, many people wonder if they can use a regular car battery. Unfortunately, the answer is no, as there are significant differences between car and EV batteries. One of the biggest differences is in the chemistry used to create the battery.
Car batteries typically use lead-acid technology, which isn’t efficient for EVs due to its heavy weight and limited energy density. EVs, on the other hand, require lithium-ion batteries, which are much lighter and have a higher energy density. Additionally, EV batteries are designed to handle high discharge rates and constant charging and discharging, whereas car batteries aren’t.
Trying to use a regular car battery in an electric car would likely result in a short lifespan, poor performance, and even safety hazards. So, if you’re thinking about making the switch to an EV, it’s essential to invest in a high-quality lithium-ion battery specifically designed for electric cars.
Battery Type and Chemistry
Car and EV batteries differ significantly in terms of type and chemistry. While car batteries are typically lead-acid, EV batteries are lithium-ion. Lead-acid batteries are cheaper to produce and have been used in cars for decades, but they are heavy and have a limited lifespan.
On the other hand, lithium-ion batteries are much lighter, have a higher energy density, and can last longer. However, they are more expensive due to their complexity and high production costs. Additionally, lithium-ion batteries require careful monitoring and management to prevent overheating and potential safety hazards.
Overall, while the technology behind car and EV batteries both serve the purpose of powering a vehicle, they differ greatly in terms of their composition, performance, and price point.
Voltage and Capacity Differences
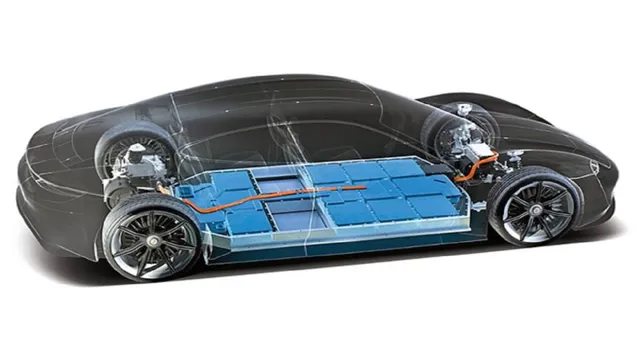
Car batteries and EV batteries have a few key differences when it comes to their voltage and capacity. Generally, car batteries have a voltage between 12 and 14 volts, while EV batteries have a much higher voltage, typically ranging from 200 to 800 volts. This difference is due to the fact that electric vehicles require much more power than traditional gasoline-powered cars.
In terms of capacity, car batteries are typically measured in amp-hours, while EV batteries are measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This is because EV batteries are much larger and have a much higher capacity than car batteries. However, this also means that they take longer to charge and can be more expensive to replace.
Overall, while car batteries and EV batteries may appear similar on the surface, there are significant differences in their voltage and capacity that make them unique.
Electronics and Control Systems
When it comes to comparing car batteries and electric vehicle (EV) batteries, there are a few key differences to consider. Firstly, car batteries are typically lead-acid batteries while EV batteries are lithium-ion. This means that EV batteries have a higher energy density and therefore can store more energy in a smaller space.
EV batteries can also charge more quickly than car batteries. Another key difference is the management system that controls the battery. Car batteries typically do not have a sophisticated management system, while EV batteries have complex management systems that monitor and regulate temperature, voltage, and current.
This ensures that the battery stays healthy and is able to function optimally for as long as possible. Finally, the lifespan of the batteries is also different. Car batteries typically have a lifespan of around 3-5 years, while EV batteries can last anywhere from 8-15 years.
However, the lifespan of an EV battery can be affected by factors such as temperature, usage patterns, and charging habits. Overall, while there are similarities between car batteries and EV batteries, there are also some key differences to consider. For those considering an EV, it’s important to understand these differences and ensure that the battery is being properly managed and cared for to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
Alternatives for EV Batteries
While it may be tempting to use a car battery for an electric car, it is not a viable option. Car batteries are designed for starting the engine, providing a quick burst of energy, but they are not suited for continuous power output that is required for electric cars. Additionally, car batteries are typically lead-acid batteries which are heavy and have a shorter life cycle compared to lithium-ion batteries that are commonly used in electric vehicles.
There are several alternatives for EV batteries that are more suitable. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common option due to their higher energy density, longer life cycle, and lower weight. Solid-state batteries, which use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, are also gaining traction due to their safety and energy efficiency.
Other alternatives being explored include flow batteries, zinc-air batteries, and sodium-ion batteries. While the upfront cost of these alternative batteries may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of performance and durability make them a more cost-effective option for electric vehicles.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-Ion Batteries. As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, the demand for high-performance batteries is more significant than ever. While lithium-ion batteries have become the go-to choice for most EVs, alternative battery technologies are being developed to address their limitations.
One of these is the solid-state battery, which replaces the liquid electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries with a solid one, enhancing energy density and safety. Another promising technology is the flow battery, which separates the power and energy components of the battery, making it easier to scale up for larger EVs and extending its lifespan. Additionally, lithium-sulfur batteries, which have a higher energy density than lithium-ion batteries, are being explored for future EVs.
As technology advances, it’s only a matter of time before these alternatives can compete with lithium-ion batteries in terms of performance and cost, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient future for EVs.
Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries are one of the alternatives to EV batteries. These batteries are known for their high energy storage capacity and long lifespan. They are also more environmentally-friendly compared to other types of batteries.
They are commonly used in hybrid vehicles and portable electronic devices. One of the benefits of Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries is that they have a high energy density, which means they can store more energy in a smaller size compared to other batteries. This makes them ideal for use in portable devices where space is limited.
Additionally, they do not contain toxic chemicals such as lead or cadmium, making them more environmentally-friendly. While Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries have been popular in the past, they are slowly being replaced by newer technologies such as Lithium-Ion batteries, which offer even better energy storage capacity and lifespan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while a car battery may seem like a viable option for powering an electric car, it’s important to remember that just because they share some similarities doesn’t mean they’re the same thing. It’s like asking if you can wear a football helmet to play hockey – sure, they both protect your head, but they’re designed for different purposes and won’t work interchangeably. So, while a car battery may give you a brief burst of power, using it long-term to power an electric car is not recommended.
Stick to using the proper batteries designed specifically for electric vehicles, and you’ll be cruising to the finish line in no time (pun intended).
FAQs
Is it possible to use a car battery for an electric car?
No, car batteries are not suitable or powerful enough to run an electric car. Electric cars require specialized batteries that are designed specifically for electric propulsion.
What type of batteries are used in electric cars?
Electric cars use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can store large amounts of electricity.
How long do electric car batteries last?
The lifespan of an electric car battery depends on various factors such as usage, charging habits, and temperature. Typically, electric car batteries can last anywhere from 8 to 15 years before needing to be replaced.
How much does it cost to replace an electric car battery?
The cost of replacing an electric car battery can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle. On average, it can cost anywhere from $5,500 to $15,000 for a replacement battery. However, some manufacturers offer warranties or leasing programs that cover the cost of battery replacement.