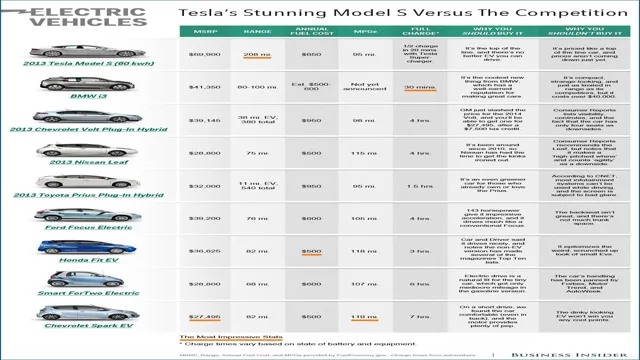
The Shocking Truth About Child Labor in Electric Car Battery Production: Why We Need to Take Action Now
In an age of increasing awareness of the impact of our daily choices, electric cars seem like a no-brainer for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint. However, the process of creating these vehicles is not without its ethical concerns. Reports have surfaced of child labor being used to mine cobalt, a crucial component in electric car batteries.
This raises important questions about the ethics of our eco-friendly choices and how they may inadvertently contribute to exploitation and suffering. In this blog post, we’ll explore the issue of child labor in the electric car industry and consider what steps can be taken to ensure that the production of sustainable energy doesn’t come at the expense of vulnerable communities.
Overview: Child Labor in the Mining Industry
Child labor in the mining industry is a major concern, especially when it comes to the production of electric car batteries. Many of the minerals necessary for these batteries, such as cobalt, are often mined in developing countries where child labor laws are not enforced. This has led to a significant number of children working in dangerous and hazardous conditions in order to satisfy the demand for these minerals.
It’s a tragic reality that children as young as six years old are working in mines, putting themselves at risk for injury, illness, and even death. Many of these children are forced to work long hours for very little pay, with no access to education or basic necessities. The issue of child labor in the mining industry is a complex and multifaceted problem that requires global cooperation to solve.
It’s vital that we take action to address these issues and ensure that the production of electric car batteries is not responsible for perpetuating child labor.
Statistics on Child Labor in Mines
Child labor in mines is a severe problem that remains prevalent in many developing countries around the world. The mining industry demands hard work and long hours, and children are often exploited for their cheap labor and small size, which allows them to fit into tight spaces that adult workers cannot. The International Labor Organization estimates that more than a million children are engaged in mining activities globally, with some being as young as five years old.
Children working in mines receive little or no education, leading to poor literacy rates and limiting their future job prospects. These children work in dangerous conditions, exposed to toxic materials and heavy machinery, leading to health problems and even death. While many countries have laws against child labor, enforcement remains weak, and children continue to suffer.
The issue of child labor in mining is complex and multifaceted, requiring collaborative efforts from governments, businesses, and civil society to address and combat effectively.

Examples of Companies Using Child Labor
Child labor is a topic that has been gaining more attention in recent years. Although it is illegal in most countries, there are still many companies that use children as laborers. One industry where child labor is particularly prevalent is the mining industry.
Mining requires a lot of physical labor and is often done in dangerous conditions. Children are often used because they are small and can fit into tight spaces and mines where adults cannot. Additionally, child labor is usually cheaper than adult labor, making it an attractive option for companies.
Unfortunately, children who work in mines often have little access to education and are at a high risk of injury or even death due to the hazardous conditions. Despite efforts to stop child labor, it is still a major issue in the mining industry and needs to be addressed.
Electric Car Batteries and Child Labor
It is a well-known fact that the production of electric car batteries often involves the use of child labor, particularly in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The mining of cobalt, a crucial component in these batteries, is notorious for relying on children as young as 6 years old to extract it from the mines, often working in hazardous conditions for very low wages. This exploitation of children is not only an ethical concern but also poses a serious public relations issue for companies that claim to be environmentally conscious.
As consumers become more socially aware, the demand for clean energy is increasing, and the industry must address the inherent moral dilemma of relying on child labor to produce the very product that is meant to save the planet. Companies must take a more active role in verifying their battery supply chains, investing in more sustainable alternatives and ensuring compliance with ethical and fair labor practices to reduce the impact of child labor on their products.
Which Materials Used in Batteries Involve Child Labor?
When it comes to batteries, many of us are unaware of the human costs involved in their production. Electric car batteries, in particular, are a cause of concern for their potential involvement with child labor. Several materials used in these batteries, such as cobalt and lithium, are sourced from countries where child labor is still prevalent.
In places like the Democratic Republic of Congo, children work in hazardous mines to extract cobalt. These children are exposed to toxic fumes, dust, and the risk of cave-ins, among other dangers. Similarly, children in Bolivia and Chile work in lithium mines, primarily in poverty-stricken areas with little access to education or health services.
It is crucial for companies and consumers to be aware of where these materials come from and ensure that ethical sourcing practices are in place to eliminate the involvement of child labor.
Current Efforts to Eliminate Child Labor in Battery Production
The electric car industry has been booming in recent years, with the rise in demand for battery-powered vehicles. However, there have been concerns regarding the use of child labor in the production of electric car batteries. Battery production requires a large amount of cobalt, a mineral that is predominantly mined in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
Unfortunately, the mining industry in the DRC has long been associated with child labor, with some estimates suggesting that up to 40,000 children are involved in the country’s cobalt industry. This has led to global efforts to eliminate child labor in battery production, with major companies such as Apple, Tesla and Volkswagen pledging to do better and implement strict measures to ensure that their supply chains are free from child labor. Steps such as implementing thorough audits, working with NGOs, and providing education and support for mining communities have been put in place to combat this issue.
While progress has been made, there is still a long way to go to ensure that electric car batteries are produced ethically and sustainably, without harming children and their communities.
Alternative Materials to Consider
When it comes to electric car batteries, many alternative materials are being considered to reduce the environmental impact and reliance on rare materials. However, it is important to also consider the ethical implications of these materials. One major issue is the use of child labor in the mining of cobalt, a key ingredient in many battery types.
While efforts are being made to address this issue, such as promoting responsible mining practices and increasing transparency in supply chains, it is still a concerning reality. That’s why it’s important to consider not only the material’s environmental impact, but also its ethical impact. As consumers, we have the power to demand transparency and ethical practices from companies, and to choose products that align with our values.
By doing so, we can help promote a more sustainable and ethical future.
What You Can Do to Help
As consumers, we all play a role in the demand for electric cars, and with that comes a responsibility to ensure that the production of their batteries does not involve child labor. To help eradicate child labor for electric car batteries, the first step is to research and only support companies that are transparent about their supply chain and take steps to ensure their products are ethically sourced. Pressure can be put on companies to prioritize child labor-free practices through petitions, social media campaigns, and boycotts.
Another way to help is by supporting organizations that work towards ending child labor, such as the International Labor Organization and the Global March Against Child Labour. Although it may seem overwhelming, small efforts by all of us can lead to impactful change, ensuring that the future of electric cars is not built on the exploitation of vulnerable children.
How to Research Companies’ Policies on Child Labor
Child labor is a pervasive issue that affects millions of children around the world. It is, therefore, essential to research companies’ policies to prevent and eradicate this problem from our society. However, knowing where to start can be daunting.
One of the best approaches is to check the company’s website for information on its employment policies, code of conduct, or social responsibility section. Some businesses also publish annual sustainability or corporate responsibility reports that can provide invaluable insights into their labor practices. Additionally, non-profit organizations and advocacy groups that focus on children’s rights can be excellent sources of information.
They often publish reports that highlight companies accused of exploiting child labor and positive examples of firms that prioritize ethical labor practices. By doing this research, you can make informed decisions and support businesses that prioritize children’s welfare and well-being over profits.
Supporting Ethical Eco-Friendly Companies
As consumers, we have the power to support ethical eco-friendly companies and make a positive impact on the environment and society as a whole. One simple way to do this is to research companies before making a purchase and choosing to support those that have sustainable and ethical practices. This can involve looking for certifications such as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance, or B Corp, which prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
We can also consider purchasing from local and small businesses, reducing our carbon footprint from shipping and supporting our local communities. Another way to support eco-friendly companies is by reducing waste through the use of reusable products such as water bottles, shopping bags, and food containers. Although these small actions may seem insignificant, collectively they can make a significant difference in creating a more sustainable and ethical world.
Let’s use our purchasing power for good and support businesses that prioritize the well-being of people and our planet.
Conclusion: The Importance of Ending Child Labor in All Industries
It’s shocking to think that the future is powered not just by electricity, but also by the exploitation of children. Child labor is a dark reality behind the production of electric car batteries, and this inconvenient truth cannot just be charged to some far-off factory. As consumers and citizens, we must hold ourselves and corporations accountable to ensure that progress is achieved through ethical means.
After all, we cannot truly claim to have a sustainable future if it is built upon the backs of innocent children.”
FAQs
What is child labor?
Child labor refers to work that is mentally, physically, socially, or morally dangerous and harmful to children. It deprives children of their childhood, their potential, and their dignity.
Why is child labor used in electric car battery production?
Child labor is often used in electric car battery production because it is cheap and allows companies to reduce their production costs. Children are also easier to manipulate and control, making them ideal for tasks that require small hands and nimble fingers.
Which countries are most affected by child labor in the electric car battery industry?
The countries most affected by child labor in the electric car battery industry are usually those with weak labor laws and a high demand for raw materials. These include countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia, and South Africa.
What can be done to reduce child labor in the electric car battery industry?
To reduce child labor in the electric car battery industry, companies must take responsibility for their supply chains and ensure that they are not using child labor. Consumers can also play a role by supporting companies that have a strong ethical track record and avoiding those that do not. Finally, governments must enforce labor laws and provide incentives for companies to behave ethically.