Cobalt: The Hidden Hero Behind Effective and Sustainable Electric Car Batteries
Electric cars are becoming more and more popular as people push for environmentally friendly transportation options. One of the key components of a successful electric car is its battery. And one of the key components of an electric car battery is cobalt.
But what is cobalt, and why is it so important in the world of electric cars? Cobalt is a metal that is used in a lot of different industries, from aerospace to healthcare. But it’s become particularly important in the production of electric car batteries. That’s because cobalt is a crucial component of the cathode, which is one of the two electrodes that allow a battery to store charge.
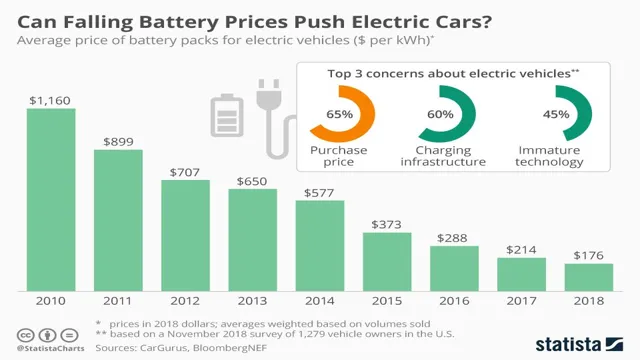
Simply put, without cobalt, an electric car battery wouldn’t be able to hold as much energy or last as long. But there’s a catch. Cobalt is also one of the most expensive and controversial metals in the world.
Much of the world’s cobalt supply comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo, where it’s often mined using child labor and under dangerous conditions. This poses a major ethical issue for automakers and battery manufacturers, who are under pressure to find alternative sources of cobalt. Despite these challenges, the electric car industry continues to grow and evolve.
Companies are exploring new battery designs that use less cobalt, or even eliminate it completely. And as technology improves and the market becomes more competitive, it’s likely that cobalt will become less of a bottleneck for the electric car industry. Either way, it’s clear that cobalt will play a critical role in shaping the future of transportation and sustainability.
What is Cobalt?
Cobalt is a metal used in the batteries that power electric cars. It is a rare and expensive resource, which makes it a valuable commodity in the green energy industry. Cobalt’s unique properties make it an essential component for producing high-performance lithium-ion batteries, which can store and release electrical energy quickly and efficiently.
However, despite its advantages, cobalt mining has been criticized for its environmental impact and reliance on child labor in some countries. Consequently, researchers are working to find alternative materials to replace cobalt in batteries, which would reduce environmental damage and promote social responsibility in resource extraction. Nonetheless, for the time being, cobalt remains an integral part of electric vehicle technology and could play a pivotal role in paving the way for a sustainable energy future.
Properties and Applications
Cobalt is a transition metal that sits on the periodic table between iron and nickel. It is hard, brittle, and has a silvery-blue appearance. Cobalt has numerous properties that make it useful in various applications.
Its magnetic properties, for instance, make it an essential component in the creation of magnets. Additionally, cobalt is corrosion-resistant and can withstand high temperatures, making it a preferred material for the production of jet engines and gas turbines. It is also an excellent alloying agent for other metals and is commonly used in the production of superalloys used in aircraft engines.
Cobalt compounds are used in the production of pigments and dyes, as well as in the manufacturing of rechargeable batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries. Furthermore, cobalt is an essential nutrient for both humans and animals, playing a crucial role in the production of red blood cells. Overall, Cobalt is a versatile and significant metal that has various applications in different fields.

Cobalt in Electric Car Batteries
Cobalt is a crucial component in the production of electric car batteries. This mineral possesses several unique properties that make it ideal for use in battery manufacturing. Cobalt helps to improve the stability and reliability of lithium-ion batteries, which are widely used in electric vehicles.
It also helps to increase battery capacity, allowing electric cars to travel longer distances without needing to recharge. However, cobalt is rare and expensive, making it a challenge for battery manufacturers to produce cost-effective electric vehicles. As a result, some car manufacturers are exploring alternative materials, such as nickel and manganese, for battery production.
While these materials may reduce the reliance on cobalt, they can also lead to a decrease in battery performance and safety. Therefore, it is crucial for the industry to continue exploring new ways to use cobalt more efficiently to produce sustainable, affordable, and high-performance electric vehicles.
Why is Cobalt Essential?
Cobalt is an essential element in the production of electric car batteries. It comprises about 10-15% of the total weight of the battery and plays a significant role in increasing its lifespan, energy density, and performance levels. Cobalt helps in stabilizing the battery’s structure, preventing it from overheating, and reducing its charge time.
Despite its importance, cobalt is a scarce and expensive mineral that is primarily mined in the Democratic Republic of Congo, where child labor and exploitation remain prevalent. As electric cars continue to rise in popularity, the demand for cobalt is expected to soar, raising concerns about its sustainability and ethical implications. Battery manufacturers are exploring alternative materials such as nickel, manganese, and aluminum to reduce their reliance on cobalt and develop more environmentally-friendly batteries.
Cobalt vs Other Metals
When it comes to powering electric car batteries, cobalt continues to be the go-to metal. Compared to other metals like lithium and nickel, cobalt is more durable and stable, ensuring better performance and a longer lifespan for the batteries themselves. However, concerns about the ethical implications of cobalt mining, particularly in regions like the Democratic Republic of Congo, have caused some to hesitate in their support of the metal.
While efforts are being made to develop cobalt alternatives, for now, it remains an essential component of electric car batteries and a crucial factor in the transition to a greener future.
Cobalt Supply and Demand
Cobalt has become an essential ingredient in Electric Vehicle (EV) batteries, and it’s dramatically impacting the cobalt supply and demand. The rise of EVs has led to soaring demand for cobalt, as it’s a crucial component in the rechargeable lithium-ion batteries used in these cars. Cobalt helps increase the cell’s energy density and improves battery life, making it an ideal choice for EV battery manufacturing.
However, there’s a growing concern over cobalt supplies; currently, over 60% of the world’s cobalt comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where child labor and other supply chain issues have raised ethical concerns. Thankfully, companies are recognizing this and becoming more conscious of their cobalt supply chains, seeking alternative sources to reduce their reliance on the DRC. As EVs continue to rise in popularity, we can expect to see even more pressure on the cobalt market, making it increasingly important to address concerns around cobalt supply and demand.
Future of Cobalt in Electric Car Batteries
Cobalt has been an essential component of electric car batteries for years, but concerns are mounting about the sustainability of its production. Cobalt is primarily mined in the Democratic Republic of Congo, where human rights abuses and child labor have been reported. This has prompted automakers to explore alternative materials for their batteries, such as nickel or manganese.
However, cobalt remains a critical ingredient in the current generation of batteries due to its stability and ability to hold a charge. As electric car adoption continues to accelerate, the demand for cobalt is expected to increase significantly. To address these issues, companies are researching new ways to produce sustainable cobalt, such as recycling and mining in more environmentally responsible ways.
It remains to be seen what the future of cobalt in electric car batteries will look like, but the industry is moving towards more responsible practices, ensuring the longevity of both the technology and the planet.
Innovations and Alternatives
The future of cobalt in electric car batteries is a much-talked-about topic these days. As we all know, cobalt plays a crucial role in the rechargeable lithium-ion batteries used in electric cars. However, cobalt’s ethical and environmental concerns have been a matter of controversy for the past few years.
But with the advancements in technology, scientists have been exploring alternative materials for cobalt in batteries. One such alternative is nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) batteries, which have a higher energy density than traditional lithium-ion batteries and are cobalt-free. Another option is lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries, which are more environmentally friendly and safer than their cobalt-based counterparts.
While these alternatives show promise, they are not yet widely available or proven to be as efficient as cobalt-based batteries. Hence, it’s unlikely that cobalt will be completely eliminated from batteries anytime soon. However, with continuous innovation, the future of cobalt in electric car batteries may look different than what we imagine it to be currently.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
As the push towards more sustainable and ethical sourcing continues, the future of cobalt in electric car batteries remains uncertain. Cobalt is a vital material used in rechargeable batteries, including those found in electric vehicles. However, the mining of cobalt has been linked to human rights violations and environmental damage, making it a controversial material.
The production of cobalt is largely concentrated in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where concerns about child labor, corruption, and other issues persist. As a result, companies are actively seeking alternatives to cobalt in their battery production, such as using different metals or improving battery designs to reduce dependence on the material. While the shift away from cobalt may take time, the push towards sustainability and ethical sourcing in the auto industry is likely to impact its future use.
Conclusion
In the world of electric vehicles, cobalt is like the secret ingredient that makes batteries powerful, efficient, and long-lasting. It’s like the superhero of the battery world, silently working behind the scenes to ensure that our cars can go the extra mile. But just like any superhero, cobalt has its limitations and limitations that need to be addressed.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what electric cars can do, we must also remember to tread lightly on the planet and find innovative solutions to minimize our use of this precious metal. After all, the future of mobility lies not only in the power of our batteries, but also in our ability to balance progress with sustainability.
FAQs
What is cobalt used for in electric car batteries?
Cobalt is a key component in the cathode of many electric car batteries, helping to improve battery performance and durability.
Is cobalt the only material used in electric car batteries?
No, electric car batteries also contain materials such as lithium, nickel, and manganese, to varying degrees depending on the specific battery design.
Is the use of cobalt in electric car batteries sustainable?
The mining and processing of cobalt has been associated with environmental and human rights concerns in some regions, leading some companies to explore alternative battery chemistries with less cobalt.
Can electric car batteries be made without cobalt?
Yes, some companies are working on developing electric car batteries that use little or no cobalt, often by increasing the proportion of nickel or other materials in the cathode.