Powering the Ride: Exploring the Various Batteries Used in Electric Cars
Electric cars have become increasingly popular over the years as people search for more environment-friendly modes of transportation. With this, there has been an increased curiosity about how they work, and specifically, what types of batteries they use. Most people might know that electric cars use batteries, but beyond that, the details might be hazy.
That’s why in this blog, we will explore the different types of batteries that electric cars use and how they differ. So, buckle up, and let’s take a deep dive into the world of electric car batteries!
Lead-Acid Batteries
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular, and as a result, more people are curious about the different types of batteries used in them. One of the most common types of batteries is lead-acid batteries. Despite being the oldest type of rechargeable battery, they are still widely used in electric cars due to their low cost and reliability.
Lead-acid batteries consist of lead plates submerged in an electrolyte solution of water and sulfuric acid. These batteries can be recharged and discharged many times, making them an ideal choice for electric cars. However, they do have some downsides, including their relatively short lifespan compared to other types of batteries.
Nonetheless, lead-acid batteries continue to be a popular choice for electric cars due to their affordability and proven performance.
Heavy and not as efficient
Lead-acid batteries may be commonly used, but they have some drawbacks that make them not as efficient as newer technologies. One of the main issues with lead-acid batteries is their weight. These batteries are heavy and can add a significant amount of weight to whatever they are powering.
This can make them less practical for certain applications, such as electric vehicles, where weight is a crucial factor in maximizing performance and efficiency. Additionally, lead-acid batteries are not as efficient as some other battery technologies on the market. They tend to lose charge faster and can take longer to recharge.
This can lead to longer downtimes and less productivity overall. While lead-acid batteries have been around for a long time and are still used in many applications today, newer and more efficient battery technologies are becoming increasingly popular and offer some significant advantages over lead-acid batteries.

Still used in some hybrid cars
Lead-acid batteries have been around for over a century and continue to be used in some hybrid cars. While newer technologies like lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride batteries have become more popular due to their higher energy density, lead-acid batteries still have their advantages. They are significantly cheaper and easier to manufacture than other types of batteries, making them a cost-effective solution for vehicles that don’t require as much power.
Additionally, they are easily recyclable, with up to 99% of the materials being able to be reused. Despite their lower energy density and heavier weight, lead-acid batteries have proven to be a reliable and efficient source of power for hybrid vehicles.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
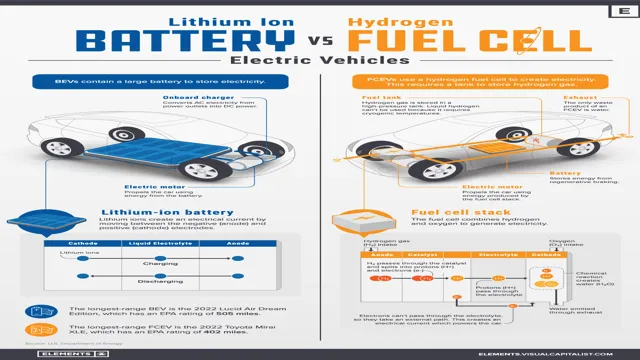
When it comes to powering electric cars, there are different types of batteries available to choose from. One of the most popular forms of battery technology used in electric cars is Lithium-Ion. The Lithium-Ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions to store and release energy.
These batteries are known for their high energy density, which means they can store more energy in the same amount of space than other types of batteries. Lithium-Ion batteries are also lighter and less bulky than other batteries, making them an ideal choice for electric cars. While they do have a higher upfront cost compared to other battery options, they are known for their long lifespan and excellent performance, which ultimately makes them a smart investment for EV owners.
Lighter and more energy-dense
Lithium-Ion Batteries are known for being lighter and more energy-dense compared to traditional batteries. This is due to the use of lithium cobalt oxide or lithium manganese oxide as the cathode material which enables the battery to hold more energy. The popularity of these batteries in recent years is due to their ability to power various devices including smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, among others.
What’s impressive about Lithium-Ion Batteries is that they have a longer lifespan, can be charged quickly, and are easy to maintain. As technology advances, researchers continue to refine these batteries to make them even lighter and more efficient. The future of Lithium-Ion Batteries is promising, with the potential to be used in a wider range of applications, such as in renewable energy storage systems.
Overall, Lithium-Ion Batteries have proved to be a game-changer in the field of energy storage.
Most commonly used in electric cars
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used batteries in electric cars. These batteries are lightweight and have a high energy density, making them the perfect choice for electric car manufacturers. The lithium-ion batteries work by storing electrical energy, which can be used to power the car’s motor.
They are renowned for their fast-charging capabilities, allowing drivers to get back on the road quickly after charging their car. Another great advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their longevity. These batteries can last for years before they need to be replaced, making them a cost-effective option for electric car owners.
Although there are alternative types of batteries available for electric cars, lithium-ion batteries remain the most popular choice, and there’s no surprise as to why. They offer efficiency, reliability, and an enhanced driving experience that drivers can truly enjoy.
Nickel-metal Hydride Batteries
One of the different types of batteries commonly used in electric cars is the nickel-metal hydride battery. These batteries have been used in electric vehicles for many years and are known for their efficiency and reliability. They are also relatively cheap compared to other battery options, making them an attractive choice for some manufacturers.
However, they do have their limitations. Nickel-metal hydride batteries can be heavier and less energy-dense than other options, meaning they may not offer as much range as some drivers would like. Additionally, they can degrade over time and may not be as durable as other types of batteries.
Despite their drawbacks, nickel-metal hydride batteries remain a popular choice for many electric car manufacturers, especially those looking for a more cost-effective option.
Higher energy density than lead-acid
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are an excellent alternative if you’re looking for a high-energy density battery that is superior to lead-acid batteries. They work by using a metal hydride, which is a compound of hydrogen and a metal, as the negative electrode, and nickel oxyhydroxide as the positive electrode. These materials are more energy-dense than the lead-acid batteries, making them a popular choice for hybrid and electric cars.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries can store more energy in a smaller space, enabling them to last longer in between charges than lead-acid batteries. Furthermore, they are more environmentally friendly than their counterparts, as they do not contain toxic substances or heavy metals that could be hazardous to the environment. The development of nickel-metal hydride batteries has been a significant milestone in advancing the technology behind energy storage, and they continue to be an essential part of the transition to renewable energy sources.
Less common in modern electric cars
While most modern electric cars are equipped with lithium-ion batteries, some older models may still use nickel-metal hydride batteries. These older batteries were once popular due to their lower cost and relative reliability, but they’ve largely been replaced by lithium-ion due to their lower energy density and larger size. However, nickel-metal hydride batteries still have some advantages over lithium-ion.
For example, they are less prone to overheating and can withstand a wider range of temperatures, making them better suited for extreme weather conditions. Additionally, they are less likely to experience “thermal runaway,” a dangerous condition in which overheating can cause the battery to explode or catch fire. Despite these advantages, however, nickel-metal hydride batteries are less efficient than lithium-ion and have a shorter lifespan, making them less cost-effective in the long run.
Solid-State Batteries
Electric vehicles rely on various battery technologies to store and supply energy to the drivetrain. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of battery used in electric cars due to their high energy density, relatively low cost, and durability. However, solid-state battery technology is becoming increasingly popular due to its unique advantages.
Solid-state batteries are safer, more efficient, and have a longer lifespan. They also have the potential to reduce the cost of electric vehicles by requiring fewer cells. Toyota, BMW, and Volkswagen are all investing in solid-state battery technology, and some analysts predict that they will start to be used in electric cars by the mid-2020s.
As the electric vehicle market continues to grow, it’s essential to understand the different types of batteries used and their benefits and drawbacks.
New technology with potential for higher energy density and safety
Solid-state batteries are a new technology that could potentially revolutionize the current battery market. These batteries utilize a solid electrolyte instead of the traditional liquid one, which offers several advantages such as higher energy density and increased safety. One of the main limitations of current lithium-ion batteries is their tendency to catch fire or explode, a risk that solid-state batteries overcome due to their stable, non-flammable nature.
Additionally, solid-state batteries have the potential to store more energy in a smaller space, making them particularly useful for electric vehicles and other energy-intensive applications. While the technology is still in its infancy, researchers are optimistic about its potential and are working to refine the manufacturing process to make solid-state batteries a commercially viable option in the near future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the different types of batteries used in electric cars may seem overwhelming, but they all have their unique strengths and weaknesses. From the efficient and lightweight lithium-ion batteries to the reliable and affordable lead-acid batteries, each type has its place in the world of electric vehicles. Much like selecting the right tool for a job, choosing the right battery for an electric car is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
So, whether you’re looking for speed, range, or cost-effectiveness, there’s a battery out there that’s just right for you. Just remember, in the world of batteries and electric cars, it’s all about finding the perfect balance between power and practicality!”
FAQs
What are the different types of batteries used in electric cars?
Lithium-ion batteries, Lead-acid batteries, Nickel-metal hydride batteries, and Solid-state batteries are some of the commonly used batteries in electric cars.
What is the lifespan of batteries used in electric cars?
The lifespan of batteries used in electric cars varies depending on the type of battery. Lithium-ion batteries have a longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries and can last up to 10 years.
Can the batteries in electric cars be recycled?
Yes, most of the batteries used in electric cars are recyclable, and the materials can be used to produce new batteries.
What happens to the batteries when they are no longer usable in electric cars?
When the batteries in electric cars are no longer usable, they can be repurposed for other applications such as home energy storage or recycled for their materials.