Revolutionizing the Future: Exploring the Role of Lithium in Electric Car Batteries
As we look towards a greener future, electric cars have risen in popularity due to their promising potential to reduce carbon emissions. However, with this surge in demand arises the question of how to power these vehicles. This is where electric car batteries come into play.
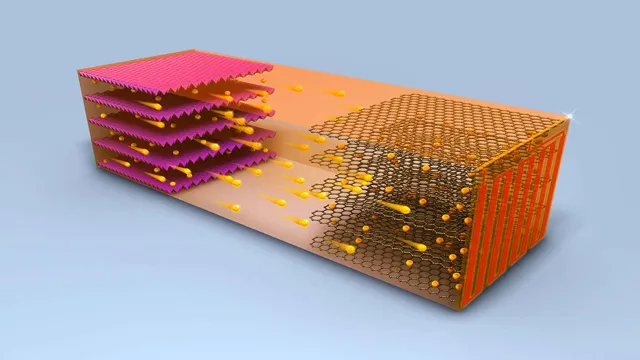
Electric car batteries, particularly lithium-ion ones, are becoming more common in the automotive industry due to their high energy density and longer lifespan. Lithium-ion batteries are composed of a cathode, an anode, and a lithium salt electrolyte, with the lithium ions transferring between the two electrodes during charging and discharging. While the use of lithium-ion batteries in electric cars has been met with some concerns, including the potential for resource depletion and environmental impacts, they remain a widely used and researched option for powering electric vehicles.
Despite their benefits, electric car batteries still have room for improvement in terms of energy efficiency and sustainability. As we continue to develop and refine these batteries, we must also consider the impact of production and disposal on the environment. Overall, electric car batteries serve as a crucial component in the shift towards more sustainable transportation methods.
Improving their performance and sustainability will continue to be an important focus for the automotive industry and researchers alike.
What are Electric Car Batteries?
Yes, electric car batteries often use lithium ion technology. Lithium is a lightweight metal that can store a great deal of energy, making it ideal for use in car batteries. Lithium ion batteries work by moving lithium ions between a positive electrode and a negative electrode, which creates an electrical current.
These batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles because they are able to provide a long range and efficient energy storage. However, it’s worth noting that some electric vehicles use other types of batteries, such as nickel-cadmium or lead-acid batteries. Ultimately the type of battery used in an electric vehicle depends on a variety of factors including cost, performance, and environmental impact.
But the use of lithium ion batteries has been gaining traction in recent years as they offer a good balance of these factors.
Description and Function
Electric car batteries are rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that power electric cars. They are the most critical component of an electric vehicle as they store the energy required to power the car’s motor and other electrical systems. Unlike traditional fuels, they are not burned to power the vehicle.
Instead, electric cars use electricity stored in the battery to power an electric motor, which then drives the wheels of the vehicle. The batteries need to be charged regularly and can be recharged using a home charging station or a public charging station. Electric car batteries are becoming more efficient and affordable, making electric cars an increasingly popular choice for environmentally conscious individuals.
Additionally, they are also helping to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and decrease our overall carbon footprint. With continued innovation in battery technology, electric vehicles will only continue to improve and become more prevalent on our roads.
Popular Electric Car Models
Electric Car Batteries One of the most crucial components of an electric car is its battery. Unlike traditional vehicles that rely on gasoline or diesel, electric cars run on electricity, and the battery is what stores that power. The type of battery used in electric cars is called a lithium-ion battery, and it is similar to the ones used in smartphones and laptops.
These batteries are lightweight, efficient, and can store a lot of energy in a small space. The batteries are made up of several smaller cells, each of which contains a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and a separator. When you charge an electric car, the battery’s cells use electricity to move lithium ions from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, creating a flow of electrical energy.
When you use the car, the process is reversed, with the lithium ions moving back to the positive electrode, powering the electric motor. While electric car batteries have come a long way in recent years, they still have some limitations, such as limited range and long charging times. However, advancements in technology are making electric cars more practical than ever before.
What is Lithium?
Yes, electric car batteries typically use lithium. Lithium is a lightweight metal that is highly reactive and has a low atomic number. It’s an ideal material for use in batteries because it has a high energy density, meaning it can store a lot of energy in a relatively small space.
Plus, lithium batteries are rechargeable, making them perfect for use in electric cars. The batteries are designed to store energy from the car’s regenerative braking system, which converts the car’s kinetic energy into electrical energy and stores it in the battery. When the driver needs to accelerate, the battery releases the stored energy, providing the power needed to propel the car forward.
Overall, lithium batteries are highly efficient and provide a reliable source of energy for electric vehicles.
Properties and Uses
Lithium is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number It is the lightest metal and belongs to the alkali metals group. Lithium is widely used in batteries for electronic devices such as laptops and smartphones.
It is also used in electric cars and renewable energy systems due to its high energy density and low weight. Lithium is also used as a medication for treating bipolar disorder and depression. The metal is highly reactive and can easily ignite when exposed to air or water.
Moreover, Lithium is found in salt flats, also known as salars, mainly in South America. The largest producers of lithium in the world are Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia. Its unique chemical properties and versatile applications make it a valuable resource in modern technology and medicine.
Lithium and Energy Storage
Lithium is a chemical element known for its highly reactive properties and its use in various industries. In recent years, Lithium has gained immense popularity due to its role in energy storage. Lithium-ion batteries, which power most electronic devices, rely heavily on Lithium for their functionality.
Additionally, Lithium plays a paramount role in the emerging field of renewable energy storage. Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in solar and wind energy storage systems due to their high energy density, long lifecycle, and low maintenance costs. As a result, Lithium has become an essential component in the shift towards more sustainable and cleaner energy sources.
With the increasing demand for renewable energy sources, the demand for Lithium is also expected to increase, making it a valuable resource in the years to come.
Do Electric Car Batteries Use Lithium?
Yes, electric car batteries do use lithium as their primary component. Lithium-ion batteries have become the standard power source for electric vehicles due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and relatively low weight compared to other battery technologies. Lithium is especially suitable for this application because it is the lightest metal, allowing for the creation of more energy-dense batteries that can store more energy in a smaller space.
The use of lithium in electric car batteries has also helped to reduce the cost of electric vehicles by providing a more efficient and cost-effective way to store energy. Overall, the shift towards lithium-ion batteries has been a major factor in the growth of the electric vehicle industry and will continue to play a crucial role as the industry moves towards a more sustainable future.
Yes, and Why
Yes, electric car batteries do use lithium. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of rechargeable battery used in electric vehicles (EVs). These batteries are lightweight, high-energy-density, and long-lasting, making them ideal for electric cars.
Lithium-ion batteries also have a high power-to-weight ratio, which means they are capable of storing more energy than other types of batteries. Additionally, lithium is a widely available element, making it relatively easy to source for battery production. However, the production of the lithium-ion batteries can have environmental impacts, such as carbon emissions during production and the disposal of used batteries.
Nevertheless, efforts are underway to improve the sustainability of the lithium-ion battery production process. Overall, while there are some challenges associated with the use of lithium-ion batteries, they are a crucial component of EVs and play a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Lithium Ion Battery Technology
Yes, electric car batteries use lithium-ion technology. These batteries have become the dominant energy storage solution for electric cars, thanks to their high energy density, long lifespan, and performance efficiencies. Lithium-ion batteries work by moving lithium ions between the electrodes and the electrolyte, creating a flow of energy.
Electric car batteries use large numbers of these cells, which are arranged in modules to create a battery pack. Depending on the size of the vehicle’s battery, the pack can contain hundreds or even thousands of these cells. Using lithium-ion technology allows electric cars to achieve long ranges, fast charging times, and high speeds, making them practical and appealing to a wider audience.
Overall, electric car batteries are evolving rapidly, and we can expect to see more advancements in lithium-ion technology and other types of batteries in the coming years.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Lithium in Electric Car Batteries
Yes, electric car batteries do use lithium as a key component in their production. Lithium batteries provide high energy density and longer battery life which makes them ideal for electric vehicles. Lithium batteries can last over five years and provide a high number of charging cycles before they start to degrade.
This makes them an attractive option for owners of electric cars who want to save money in the long run. Additionally, lithium batteries are environmentally friendly as they do not release harmful chemicals in the disposal process. However, there are some drawbacks to using lithium batteries in electric vehicles.
One of them is that lithium is a rare resource, and mining for it can lead to environmental degradation. Furthermore, the production of lithium batteries can be costly, and recycling them can be complex. Nevertheless, with advancements in technology, solutions have emerged to make the extraction and recycling of lithium less harmful to the environment.
Overall, the benefits of using lithium in electric car batteries outweigh the drawbacks, making it a primary choice for modern electric car manufacturers.
Energy Density and Efficiency
Lithium is becoming increasingly popular in electric car batteries due to its high energy density and efficiency. Benefits of lithium-ion batteries include higher energy output and longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. Moreover, lithium is lighter and takes up less space, making it an ideal fit for electric cars.
The drawback, however, is that lithium is both expensive and potentially dangerous if not handled correctly. Additionally, the extraction and disposal of lithium can have significant environmental impacts. So while lithium-ion batteries offer many benefits for electric cars, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks as well.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
When it comes to electric vehicles, one of the most significant components is the battery, which provides the power needed to run the vehicle. Lithium, a chemical element, has become a popular choice for EV batteries due to its ability to store a significant amount of energy. However, there are both benefits and drawbacks to using lithium in EV batteries.
From an environmental perspective, the production of lithium can have negative impacts such as contaminating water sources and damaging ecosystems. In terms of cost, lithium batteries tend to be more expensive than other types of batteries. On the other hand, lithium batteries have a longer lifespan and are more efficient, making them a more cost-effective option in the long run.
Additionally, the lowered emissions from using electric vehicles can help offset the environmental concerns related to the production of lithium batteries. It’s important to weigh these benefits and drawbacks when considering the use of lithium in electric car batteries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric car batteries do use lithium. Why? Well, lithium offers a winning combination of high energy density, low weight, and long lifespan – making it the perfect candidate for powering electric vehicles. It’s like the MVP of battery components – always reliable, efficient, and capable of delivering impressive performance.
So, if you’re looking for a car that’s eco-friendly, cost-effective, and fueled by one of the most badass elements in the periodic table, look no further than the lithium-powered electric car!”
FAQs
What type of batteries do electric cars typically use?
Most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries for energy storage.
Are there any alternative types of batteries used in electric cars?
While lithium-ion batteries are most common, some electric cars use other types of batteries such as nickel-metal hydride or solid-state batteries.
How long do electric car batteries typically last before needing to be replaced?
The lifespan of an electric car battery can vary depending on a variety of factors, but most modern lithium-ion batteries are designed to last up to 8-10 years.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, most electric car batteries can be recycled to recover the valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel for reuse in new batteries or other products.