Cobalt-free Future: Exploring the Reality of Electric Cars Without Cobalt Batteries
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as people look for alternatives to fossil fuel-based vehicles. However, there’s a catch to their green image – the batteries needed to power electric vehicles contain a metal called cobalt that is often mined under unfavorable conditions. Cobalt mining is a hazardous and environmentally damaging process that puts the lives of miners at risk and can harm nearby ecosystems.
But why is cobalt essential for electric vehicle batteries, and what are the long-term implications of this mineral’s continued use? This blog will delve into the world of electric cars and cobalt batteries, exploring the benefits and consequences of this innovative technology for both individuals and the environment.
What are Cobalt Batteries?
Electric cars use various types of batteries, one of which is cobalt batteries. Cobalt is an essential component in the production of rechargeable batteries, and it helps increase the battery’s energy density and lifespan. However, it has raised concerns regarding sustainability because Cobalt mining can have an environmental impact and ethical issues, including child labor, where most of the cobalt production occurs.
Many car companies, though, are now moving towards using alternatives to cobalt to address this issue. Despite the concerns, cobalt batteries remain a viable option for electric cars as they still offer excellent performance, high energy storage, and long battery lives.
Definition and Composition
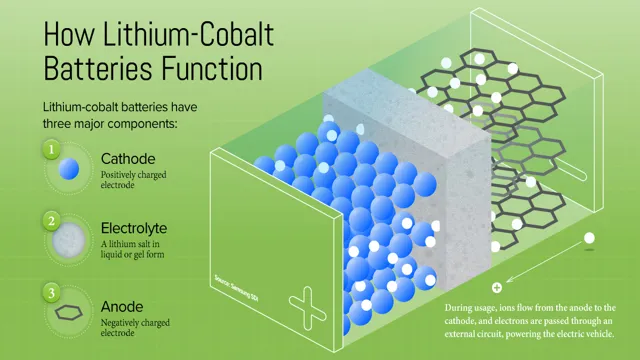
Cobalt batteries, also known as cobalt-based lithium-ion batteries, are a type of rechargeable battery that uses cobalt as a cathode material. These batteries have a high energy density and are commonly used in electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and cameras. The composition of cobalt batteries includes a cathode made of cobalt oxide, an anode made of graphite, and an electrolyte made of lithium salt in an organic solvent.
The cobalt content in these batteries can range from 5% to 80%, and the more cobalt a battery has, the higher its energy density. However, cobalt is a rare and expensive metal, which is why researchers are exploring alternative cathode materials that are cheaper and more sustainable. Despite their high energy density, cobalt batteries have received scrutiny for their environmental and ethical impact due to the mining of cobalt in conflict zones and poor working conditions for miners.
Electric Cars and Battery Types
Many electric cars use batteries that contain cobalt, but it’s not the only material used in these battteries. Cobalt is a key component of lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly found in electric vehicles (EVs). However, there are other battery types available that do not use cobalt.
For instance, some EVs use nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) batteries and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which have lower cobalt content or no cobalt at all. Cobalt has come under scrutiny due to its potential environmental and ethical impacts, but scientists and researchers are working to develop alternatives to cobalt to make EV batteries more sustainable in the future. So, while cobalt is currently used in many electric car batteries, it’s not the only option, and we can expect to see other battery types become more prevalent in the coming years.
Different Battery Types Used in Electric Cars
Electric cars are rapidly becoming popular as people’s awareness about the environment and fuel efficiency increases. However, before buying an electric car, one must consider the different types of batteries used in them. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type used in electric vehicles due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are another type used, but they are less efficient and have a shorter lifespan than lithium-ion batteries. There are also lead-acid batteries, which are the least expensive but have a significantly shorter lifespan and are environmentally damaging. Some electric cars also use solid-state batteries, which are more efficient than lithium-ion batteries and have a longer lifespan, but they are still in the early stages of development and are not yet widely available.
Knowing the different types of batteries and their pros and cons will help you make an informed decision when purchasing an electric car.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cobalt Batteries
Electric cars have become increasingly popular in recent years as more people seek eco-friendly alternatives to conventional gas vehicles. Electric cars are powered by electric batteries, which come in various forms. One of the most popular battery types is cobalt batteries.
These batteries offer a high energy density, meaning they can hold more energy per unit volume than other batteries. This makes them ideal for applications that require high power output, such as electric cars. However, they also have several disadvantages.
Cobalt batteries have a shorter lifespan than other types of batteries, which means they need to be replaced more frequently. Additionally, cobalt is a rare earth mineral that is expensive and could lead to supply chain issues in the future. Overall, cobalt batteries are an excellent choice for powering electric vehicles, but they do come with some drawbacks.
It’s up to individuals to weigh the pros and cons and decide which battery type is best suited for their needs.
Cobalt Mining Controversies
Yes, electric cars do use batteries that contain cobalt. Cobalt is a vital component for the production of lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in electric vehicles. However, there have been controversies surrounding cobalt mining due to the unethical practices, including the use of child labor, environmental destruction, and unsafe working conditions.
The majority of the world’s cobalt comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where these issues are prevalent. It is crucial for electric car manufacturers to ensure that their cobalt supply chain is ethical and sustainable. Some companies have committed to sourcing cobalt responsibly and have implemented measures to trace the cobalt from the mine to the end user.
However, this is still an ongoing issue that needs to be addressed to ensure the responsible and ethical production of electric vehicles.
Child Labour and Environmental Concerns
One of the major issues with cobalt mining is the involvement of child labour. Most of the cobalt extraction takes place in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where children as young as seven years old are forced to work long hours in hazardous conditions. These children are often separated from their families and denied access to education.
Not only does this violate their basic human rights, but it also puts them in danger of serious injuries and health problems. In addition to the ethical concerns surrounding child labour, there are also environmental issues associated with cobalt mining. Cobalt is an important component in the manufacture of batteries for electric vehicles and other electronics, but the mining process involves heavy use of chemicals that can pollute the soil and water sources in nearby areas.
The vast amount of waste produced during mining activities can also contribute to deforestation and the destruction of habitats for wildlife. It is crucial that companies and governments work together to ensure that cobalt is sourced in a responsible and sustainable way, without exploiting children or harming the environment.
Alternatives to Cobalt Batteries
Yes, electric cars commonly use cobalt batteries, but there are alternatives to reduce the reliance on this mineral. One option is to use batteries that contain little or no cobalt, such as iron phosphate or nickel-based batteries. These alternatives tend to have a lower energy density, which means they may not be as efficient as cobalt batteries.
Another solution is to source cobalt responsibly, such as from mines that adhere to ethical practices and do not involve child labor. Companies like Tesla have made commitments to sourcing ethical cobalt and reducing the overall amount used in their batteries. Additionally, researchers are constantly looking for ways to improve battery technology and find new materials to replace cobalt altogether.
As technology improves and the demand for electric vehicles grows, it’s essential that we continue to explore and invest in sustainable and ethical solutions for battery production.
LFP and NMC Batteries
LFP and NMC batteries are alternatives to cobalt batteries that are gaining popularity in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. Cobalt, an expensive and scarce resource, is commonly used in lithium-ion batteries, which power most EVs. However, LFP and NMC batteries are now being considered as more sustainable and cost-effective alternatives.
LFP batteries use lithium iron phosphate, which is cheaper and more abundant than cobalt. Meanwhile, NMC batteries use nickel, manganese, and cobalt, but in lower percentages than traditional lithium-ion batteries. This results in a reduced cost and environmental impact.
Although these alternatives are still being developed, they show promising results and may soon become a mainstream option for EVs. By using these alternatives, we can promote sustainable and eco-friendly mobility solutions while reducing our dependence on scarce resources and harmful environmental practices.
Comparing LFP and NMC Batteries
LFP and NMC batteries are two alternatives to traditional cobalt batteries that have gained significant attention in recent years. LFP (lithium iron phosphate) batteries are known for their safety and long lifespan, making them a popular choice for electric vehicles and large-scale storage applications. On the other hand, NMC (nickel-manganese-cobalt) batteries are capable of higher energy density, allowing them to provide more power in a smaller package.
Although they are not as safe as LFP batteries, NMC batteries are still considered a viable option for many applications. When choosing between these two alternatives, it’s important to consider factors such as safety, lifespan, energy density, and cost to determine which battery technology is best suited for your specific needs. Ultimately, the decision will come down to a balance between these factors, as well as the unique requirements of your application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, yes, electric cars use cobalt batteries. However, the real question is whether or not we can truly call them electric. After all, without the mining and refining industries that provide the cobalt necessary for these batteries, these vehicles would not be possible.
So while we may consider ourselves eco-conscious for driving electric cars, let’s not forget the impact of our beloved cobalt on the environment and human rights.”
FAQs
What type of batteries do electric cars use?
Electric cars typically use lithium-ion batteries, which may or may not contain cobalt.
What is the role of cobalt in electric car batteries?
Cobalt can be used in the cathode of lithium-ion batteries, which helps to increase the energy density and overall performance of the battery.
Are there any concerns regarding the use of cobalt in electric car batteries?
Yes, there are concerns related to the ethical and environmental implications of mining cobalt, as well as the potential for cobalt to cause health issues in battery factory workers.
Are there any alternatives to using cobalt in electric car batteries?
Yes, some companies are experimenting with cobalt-free lithium-ion batteries, as well as other types of battery technologies such as solid-state batteries.