Revolutionizing the Road: The Fascinating History of Early Electric Car Batteries
Electric cars have quickly become a popular choice for people who are concerned about the environment and want to reduce their carbon footprint. But, did you know that early electric cars were powered by batteries that were vastly different from the lithium-ion batteries used today? These early batteries were bulky, heavy, and had limited range, making them impractical for everyday use. However, they paved the way for the advanced batteries that power modern electric vehicles.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the history of early electric car batteries and how they evolved over time. So, buckle up, and let’s dive in!
The Beginning of Electric Cars
The early days of electric cars were powered by batteries that were bulky, heavy, and didn’t last very long. These batteries were made from lead-acid and had limited power output, which meant electric cars could only travel short distances before needing a recharge. Despite these limitations, electric cars still managed to gain some popularity in the early 1900s, especially for city driving.
However, with the discovery of oil in the United States and the rapid growth of the petroleum industry, gasoline-powered cars soon became the preferred choice for many Americans. Electric cars were eventually phased out and it wasn’t until the early 2000s when they made a comeback with the introduction of more advanced and efficient batteries like lithium-ion. The early electric car batteries may have been limited in their capabilities, but they paved the way for the development of the technology we see today.
Innovative Battery Design
The beginning of electric cars can be traced back to the 1830s when rechargeable batteries were invented. However, it was not until the late 1800s that electric cars gained popularity due to the development of innovative battery design. One of the most significant advancements during this time was the creation of the lead-acid battery, which led to the production of electric cars that were capable of traveling long distances.
This groundbreaking technology was embraced by automakers and electric cars became a common sight on American roads in the early 1900s. However, the rise of gasoline-powered cars and the discovery of cheap oil made electric cars less attractive, and they virtually disappeared from the market for many years. Today, we are witnessing a resurgence of electric cars due to a renewed interest in sustainable transportation and the development of even more innovative battery designs.
Lithium-ion batteries, for instance, have revolutionized the electric car industry by providing longer driving ranges and faster charging times. With continued advancements in battery technology, experts predict that electric cars will become even more efficient and affordable, ultimately replacing gasoline-powered cars as the primary mode of transportation in the future.
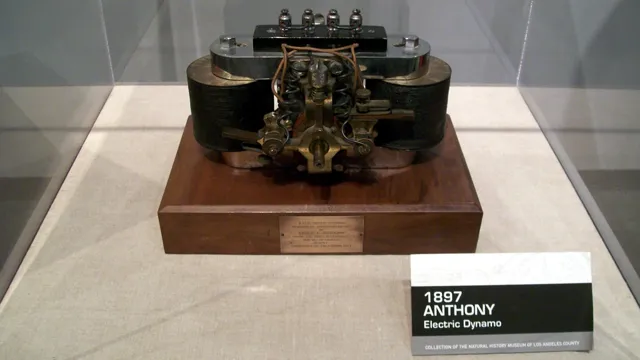
Early Storage Batteries Used
Early storage batteries played a crucial role in the development of electric cars. The first practical battery was invented by Alessandro Volta, an Italian physicist, in 1800. However, it wasn’t until the late 19th century that rechargeable batteries became feasible.
One of the pioneers in this field was the French scientist Gaston Planté, who invented the lead-acid battery in 185 This type of battery was used in the first electric cars, which appeared in the early 20th century. The lead-acid battery was large and heavy, and had limited range, but it was the best option available at the time.
Even today, lead-acid batteries are still used in some electric vehicles, although they have been largely replaced by more advanced technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries. Despite their limitations, early storage batteries paved the way for the electric cars of today, and their development and improvement continue to shape the future of transportation.
Lead Acid Batteries
Early electric car batteries were predominantly lead-acid batteries, which are still in use today for a variety of applications. These batteries were first developed in the mid-19th century and became the primary technology for electric vehicle batteries in the early 20th century. They were favored due to their high energy density and low cost of production, making them a practical option for mass production.
However, their weight and limited lifespan made them less desirable for use in vehicles, leading to the development of alternative battery technologies. Despite this, lead-acid batteries are still widely used for backup power and other applications where cost-effectiveness is key. Improvements in battery technology have made them more efficient, but there is still room for innovation to increase their performance and lifespan.
The First Mass-Produced Battery
Lead Acid Batteries Lead acid batteries are the first mass-produced battery type and are still widely used today. They are popular in applications that require a large amount of power such as automotive, marine, and backup power systems. The lead acid battery uses an electrochemical reaction to create electrical energy.
They are made up of lead and lead oxide plates that are submerged in sulfuric acid electrolyte. When a load is connected to the battery, a chemical reaction occurs, creating an electrical current. These batteries are rechargeable and have a low internal resistance, making them ideal for high current applications.
However, they are heavy and have a relatively short lifespan compared to other battery types. Despite this, lead acid batteries continue to be a popular choice due to their low cost and reliability.
Advantages and Challenges of Lead Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries are one of the oldest and most commonly used types of batteries. They are known for being reliable, cost-effective, and durable. One of their advantages is that they can deliver high surge currents, making them ideal for applications that require a lot of power in a short amount of time, like starting a car.
They are also relatively cheap, making them a popular choice for backup power systems. However, lead acid batteries have their challenges as well. They are heavy and bulky, making them unsuitable for some applications where the weight and size of the battery are a concern.
They also require regular maintenance, including adding distilled water and ensuring that they’re charged properly. Lead acid batteries also have a limited lifespan and cannot be fully discharged without damaging the battery. So while lead acid batteries have their advantages, they also have their limitations that need to be considered when deciding which type of battery to use.
Impact on the Electric Car Industry
Lead acid batteries have been a staple in the electric car industry for many years due to their affordability and reliability. However, their impact on the industry has been a mixed bag. On the one hand, they have allowed for more affordable electric car models to be produced.
On the other hand, they have limited the range and performance of these cars due to their weight and low energy density. As technology advances and more efficient battery options become available, it’s likely that lead acid batteries will become less common in the electric car market. Nevertheless, they have played an important role in the development and accessibility of electric vehicles, and their legacy will continue to be felt for years to come.
Nickel-Iron Batteries
Early electric car batteries were predominantly nickel-iron batteries, also known as Edison batteries, named after the famous inventor Thomas Edison who improved the technology. These batteries were widely used in the early 20th century and were notorious for their durability and longevity. Edison batteries were perfect for electric cars because of their low cost, long life, and low maintenance.
However, they had their fair share of downsides, including their low energy density and heavy weight. The nickel-iron batteries were bulky, and a single battery unit weighed around 60 pounds! Despite this, they still powered some of the earliest electric cars and remain a critical historical element in the evolution of electric car technology. Today, modern batteries have significantly improved in terms of energy density, capacity, safety, and price.
Nonetheless, some enthusiasts still prefer nickel-iron batteries retrofitted into vintage electric cars, to maintain the authenticity of the early electric cars of the past.
Development and Characteristics
Nickel-iron batteries have a long and interesting history, having been first developed over a century ago by Thomas Edison. Also known as Edison batteries, these batteries are distinguished by their unique chemistry: a nickel oxide-hydroxide cathode, an iron anode, and an alkaline (potassium hydroxide) electrolyte. One of the key advantages of nickel-iron batteries is their durability, with a typical lifespan of 20 to 30 years.
This makes them ideal for applications where frequent battery replacement is impractical or impossible. Another notable feature of nickel-iron batteries is their ability to tolerate overcharging and deep discharge without damage, resulting in a higher degree of safety and reliability. However, this durability comes at a cost, as nickel-iron batteries have a lower energy density compared to other battery chemistries, making them less well-suited for high-energy applications.
Despite this limitation, nickel-iron batteries continue to be used in a variety of applications where their unique set of characteristics make them an ideal choice.
Comparison to Lead Acid Batteries
Nickel-Iron Batteries When it comes to comparing Nickel-Iron batteries to lead-acid batteries, there are a few key differences to take into consideration. First and foremost, Nickel-Iron batteries have a much longer lifespan than their lead-acid counterparts, with an average lifespan of over 20 years compared to just 5-7 years for lead-acid batteries. Additionally, Nickel-Iron batteries have a much deeper cycle capability, meaning they can be discharged further without any damage to the battery or reduction in lifespan.
Another major advantage of Nickel-Iron batteries is their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, without any negative impacts on their performance. This makes them ideal for use in off-grid and remote locations where temperature extremes are common. Finally, Nickel-Iron batteries are also more environmentally friendly than lead-acid batteries, as they do not contain any toxic materials and can be easily recycled.
Despite all these advantages, there are some drawbacks to Nickel-Iron batteries that must be taken into consideration. Firstly, they are much more expensive than lead-acid batteries, making them less accessible to some users. They are also less efficient than other battery types, meaning that they require more charging time and energy.
Despite these limitations, however, the many benefits of Nickel-Iron batteries make them an excellent choice for many off-grid energy applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, early electric car batteries were a bit like trying to power a car with a crank-operated flashlight. They were bulky, heavy, and had limited range. And let’s not forget the whole exploding acid issue.
But hey, at least they were trying! We’ve come a long way since then with modern lithium-ion batteries. So the next time you’re quietly cruising down the highway in your electric vehicle, take a moment to appreciate the technological advancement that made it all possible. And be thankful you’re not lugging around a 1,200 lb battery pack on your road trip.
“
FAQs
What types of batteries were commonly used in early electric cars?
Early electric cars commonly used lead-acid batteries, which were heavy and had limited range.
Were there any other types of batteries used in early electric cars besides lead-acid?
Yes, nickel-iron and nickel-cadmium batteries were also used in some early electric cars, but they were more expensive and less efficient than lead-acid.
Why did early electric car batteries have such limited range?
Early electric car batteries had limited range due to their low energy density and overall inefficiency compared to modern lithium-ion batteries.
How long did early electric car batteries typically last before needing to be replaced?
Early electric car batteries typically lasted between 2 and 3 years before needing to be replaced, but this varied depending on usage and maintenance.






