Unmasking the Truth of Electric Car Batteries: Why Green Lithium Batteries May Not Be So Green
When it comes to the debate between electric car batteries and lithium batteries, there’s been a lot of talk about which is truly green. On one hand, electric car batteries are seen as a more eco-friendly option, since they don’t emit harmful pollutants. However, lithium batteries have been touted as the superior choice due to their higher energy density and longer lifespan.
So, which one is really the greener choice? Well, the answer isn’t quite so cut and dry. It really depends on how you define “green.” If your goal is to reduce emissions and promote a cleaner environment, then electric car batteries are definitely the way to go.
These batteries rely on renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, which means they leave a much lighter carbon footprint than traditional fossil fuels. On the other hand, if your focus is on reducing waste and promoting sustainability, then lithium batteries might make more sense. These batteries have a longer lifespan than electric car batteries and can be recycled more easily, which means they won’t end up in landfills as often.
Plus, the fact that they have a higher energy density means that they require fewer resources overall, which is always a good thing for our planet. Ultimately, the choice between electric car batteries and lithium batteries comes down to your specific needs and priorities. Both options have their own unique benefits and drawbacks, and it’s up to you to decide which one fits with your individual goals and values.
Whether you’re looking for a more eco-friendly car or simply trying to reduce waste and promote sustainability in your daily life, there are plenty of options out there to help you make a positive impact on the world around us.
Introduction
While electric cars are often touted as the solution to reducing our carbon footprint, the truth is that their lithium-ion batteries are not as environmentally friendly as we may think. The production of these batteries requires a significant amount of energy and resources, including the mining and refining of lithium, cobalt, and other metals. Furthermore, the disposal of these batteries can lead to toxic waste and environmental damage if not properly handled.
Despite these concerns, there are alternatives being developed that may prove to be greener options. For instance, solid-state batteries and hydrogen fuel cells are being explored as potential alternatives to traditional lithium-ion batteries. While it may take some time for these technologies to become mainstream, it is vital that we continue to invest in and support their research to create a more sustainable future for our planet.
Explaining the importance of sustainability in car batteries
In recent years, sustainability has become an increasingly important topic when it comes to car batteries. With the growing number of electric vehicles on the road, it’s crucial that we consider the environmental impact of our energy sources. When it comes to car batteries, this means finding ways to reduce waste and dependence on non-renewable resources.
By harnessing renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, we can reduce the carbon footprint of the battery production process. Additionally, recycling and reusing materials in car batteries can help to reduce waste and preserve valuable resources. Ultimately, making sustainable choices in the manufacture and disposal of car batteries is not only important for the environment, but it also ensures that we can continue to rely on this technology for years to come.
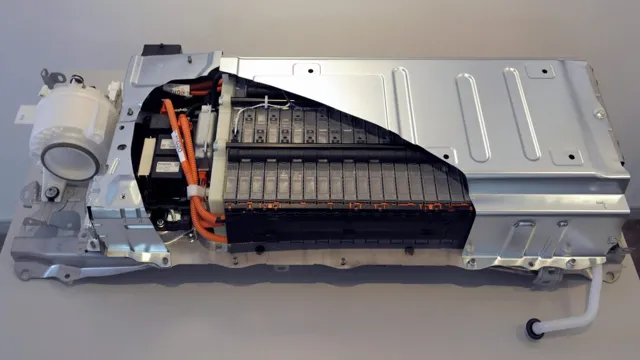
Overview of the different types of electric car batteries
Electric car batteries come in different types, each with its own advantages and limitations. As electric vehicles gain popularity, the demand for high-performance, reliable, and long-lasting batteries has become increasingly important. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of electric car battery, known for their energy density, long lifespan, and fast charging capabilities.
They are widely used in electric cars, from Tesla to Nissan Leaf. However, solid-state batteries are also gaining attention due to their higher energy density, lower risk of fire, and improved safety. Additionally, there are nickel-metal hydride batteries and lead-acid batteries, but these are mostly used in older or lower-end electric cars due to their lower range and performance.
In conclusion, the type of battery used in electric cars depends on the car’s range, performance, and cost, and as technology advances, we can expect to see even more advanced and efficient batteries in the future.
The Problem with Lithium Batteries
When it comes to electric cars and batteries, many people assume that they are a green and sustainable solution for the environment. However, the reality is that the lithium batteries used in most electric cars are far from eco-friendly. The mining of lithium is a highly resource-intensive process that can lead to significant environmental damage, including soil and water pollution and harm to wildlife.
In addition, lithium batteries have a limited lifespan and must be replaced every few years, creating an additional waste problem. While electric cars are certainly a step in the right direction towards a more sustainable future, we must acknowledge the challenges associated with their batteries and explore alternative solutions that are truly green and sustainable.
Environmental impact of mining lithium
As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the demand for electric vehicles has increased. However, a significant challenge to this transition is the environmental impact of mining lithium, which is a key component of rechargeable batteries. The extraction of lithium leads to water scarcity and soil pollution, severely affecting the natural ecosystem.
In addition, the process of obtaining lithium often involves significant amounts of energy consumption, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. While lithium batteries provide an impressive energy storage capacity, the process of obtaining this mineral comes at a cost to the environment. As we seek to reduce our carbon footprint, it is crucial to develop eco-friendly methods for obtaining lithium that do not harm the environment.
Limited supply and geopolitical issues
One of the biggest problems with lithium batteries is their limited supply and geopolitical issues surrounding their production. Despite being an important component in electric vehicles, laptops, and smartphones, there are only a few countries with significant lithium reserves, which means the supply chain is vulnerable to disruption. Additionally, some of these countries are politically unstable, which can further complicate the supply chain.
The rising demand for lithium-ion batteries is also putting a strain on the industry, as companies scramble to ramp up production and secure their supply of raw materials. As a result, the cost of lithium has increased significantly over the years. However, there are efforts underway to increase recycling and find alternative sources of lithium, such as seawater.
The quest for a sustainable and secure supply of lithium is ongoing, but it is clear that this is a vital issue that needs to be addressed urgently to keep pace with the growing demand for lithium-ion batteries.
Disposal and recycling challenges
The problem with lithium batteries is that they pose a significant challenge when it comes to disposal and recycling. These batteries contain hazardous materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can pose a threat to the environment if not disposed of properly. Additionally, these batteries can explode if they are not handled with care during the recycling process.
The process of recycling lithium batteries can also be complicated, as the materials inside must be separated and processed in a specific way to avoid contamination. This can be expensive and time-consuming, which may deter some companies from properly recycling their batteries. Ultimately, it is important to find a solution to these challenges to ensure that lithium batteries do not harm the environment or public safety.
Alternative Green Electric Car Batteries
While lithium-ion batteries have become popular in electric cars due to their high energy density, they still pose environmental concerns. Fortunately, there are alternative green electric car batteries available. One option is nickel-metal hydride batteries, which are recyclable and safer than lithium-ion batteries.
Another option is solid-state batteries, which eliminate the need for flammable liquid electrolytes and have a longer lifespan. Hydrogen fuel cells are also a promising technology that use hydrogen gas to create electricity, leaving water as the only emission. While these alternative batteries may not have the same level of energy density as lithium-ion batteries, they offer a greener and safer option for electric car owners.
Solid-state battery technology
Solid-state batteries are a promising new technology that could revolutionize the electric vehicle industry. These batteries use solid materials instead of the liquid electrolyte found in traditional lithium-ion batteries, which makes them safer, more reliable, and more energy-dense. Solid-state batteries offer many advantages, like higher energy density, faster charging times, longer lifetime, and improved safety.
Some experts predict that solid-state batteries could eventually replace lithium-ion batteries because of their superior performance. Using solid-state batteries in electric cars means that drivers could travel farther on a single charge and spend less time waiting for their car to charge. Additionally, solid-state batteries have a longer lifespan, which means they will need to be replaced less often, making them a more eco-friendly option.
With the development of solid-state battery technology, we could be one step closer to a sustainable future with cleaner air and less dependency on fossil fuels.
Flow batteries
Flow batteries are a promising alternative for green electric car batteries. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries use liquid electrolytes to store and release energy, which can be continually replenished. This means that flow batteries can provide longer driving ranges and easier maintenance for electric vehicles.
Additionally, flow batteries are more environmentally friendly as they contain non-toxic materials and can be easily recycled. While flow batteries are still in the developmental stages, they offer a potentially game-changing solution for the future of eco-friendly transportation.
Zinc-air batteries
Zinc-air batteries are a promising alternative to traditional electric car batteries because they offer higher energy density and lower cost. While lithium-ion batteries have dominated the marketplace, they have some serious drawbacks including high cost, limited range, and safety concerns. Zinc-air batteries, on the other hand, are cheaper and more efficient due to their simple design and the abundance of zinc.
They work by using oxygen from the air to help generate electricity, which means they don’t require heavy metals or rare earth materials. This makes them a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly choice for electric vehicles. While they are still in the testing phase, many experts believe that zinc-air batteries have the potential to revolutionize the electric car industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the idea that electric car batteries are inherently green due to their lack of emissions is not the entire truth. While they may not emit harmful gases on the road, the lithium batteries that power them have their own environmental impact. From the mining of the necessary materials to the disposal of the batteries at the end of their life, there are a multitude of challenges to overcome in order to make electric car batteries truly green.
So, while they may be a step in the right direction, let’s not put all of our green eggs in the lithium battery basket just yet. Perhaps we should keep looking for a truly eco-friendly alternative. Unless, that is, we want to end up with a green conscience and a toxic landfill.
#AlternateBatteryOptionsPlease”
A summary of the sustainability issues with lithium batteries
Lithium batteries have long been touted as the solution to the world’s energy problems, particularly in the electric vehicle industry. However, in recent years, concerns have been raised about the sustainability issues with lithium batteries. For one, the mining of lithium is a controversial activity, with environmental groups raising concerns about the impact on wildlife and water resources.
Additionally, the disposal of these batteries at the end of their useful life is a challenge, as they contain toxic materials that can harm the environment if not properly disposed of. Fortunately, there are already alternative green electric car batteries available. One example is the use of hydrogen fuel cells.
These cells have the potential to offer a more sustainable and efficient energy solution, as they produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, with water as the only by-product. This makes them a great option for the future of electric cars, where sustainability is a significant priority.
The potential of greener alternatives
As the world shifts towards a greener future, one of the biggest hurdles that we face is finding energy-efficient and sustainable alternatives to traditional car batteries. Fortunately, there are some promising innovations in the field of alternative green electric car batteries that hold the potential to revolutionize the industry. One such innovation involves replacing the lithium-ion batteries commonly used in modern electric cars with sodium-ion batteries.
These batteries offer a more sustainable and cost-effective solution, as they are made using abundant elements found in seawater and do not rely on rare earth metals. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of solid-state batteries, which are safer and more efficient than their liquid-state counterparts. By investing in these greener alternatives, we can not only reduce our impact on the environment but also help to build a more sustainable future for generations to come.
FAQs
Are electric car batteries really not environmentally friendly?
It depends on the type of battery. While traditional lithium-ion batteries do have environmental concerns, newer types of batteries such as solid-state and zinc-air batteries are much more eco-friendly.
What are the environmental concerns with traditional lithium-ion batteries?
The production process for traditional lithium-ion batteries releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases. Additionally, the disposal of these batteries can lead to toxic pollution if not properly managed.
How do solid-state batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries in terms of environmental impact?
Solid-state batteries have a significantly lower carbon footprint than lithium-ion batteries. They are also more efficient and have a longer lifespan.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, most electric car batteries can be recycled. Lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are commonly used in electric car batteries, can be extracted and reused in the production of new batteries. Proper recycling practices can significantly reduce the environmental impact of electric car batteries.