The Shocking Truth About Electric Car Batteries: Why Rare Earth Metals Are Key to Sustainability and Performance
Have you ever wondered how electric cars work and what’s behind the iconic quiet and smooth ride? Well, the answer is found in the batteries that power them. Electric vehicles rely on a specific type of battery known as a Lithium-Ion battery, which is rich in rare earth metals. These metals play a crucial role in powering the car and ensuring that we have a sustainable future.
The mining and processing of these rare earth metals are expensive and often environmentally destructive. While the demand for electric vehicles is growing across the globe, it’s imperative to find ways to optimize the use of these rare earth metals to keep costs low and reduce environmental damage. In this blog, we will delve into how electric car batteries work and how rare earth metals play an integral part in propelling electric vehicles.
We will also explore the challenges associated with mining these metals and how they can be acquired effectively and sustainably. So sit tight and let us take you on a journey into the world of electric cars and rare earth metals. You will get to learn about the nitty-gritty details of this delicate eco-friendly balance and why it’s vital for our future.
The Role of Rare Earth Metals
Electric car batteries rely heavily on rare earth metals. These materials, including neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, are crucial in the manufacturing process of the magnets that drive many electric motors. However, despite their importance, access to these metals is limited due to their scarcity, as well as geopolitical tensions surrounding their distribution.
As the demand for electric cars grows, so does the need for secure and sustainable sources of these essential materials. Many researchers are now exploring alternative methods for producing electric motor magnets without relying on rare earth metals, while others are investigating new ways to extract and recycle these materials. Ultimately, addressing the issue of rare earth metals is crucial for the development and proliferation of electric cars, and may even impact the future of sustainable transportation as a whole.
What Are Rare Earth Metals?
Rare earth metals are a group of 17 elements with unique properties that make them essential in a wide range of technological applications. From smartphones and laptops to wind turbines and electric cars, rare earth metals play a critical role in the development and functioning of many modern-day devices. Despite their name, rare earth metals are not actually rare.
They can be found in small quantities in various minerals all over the world. However, extracting them can be a complicated and expensive process that requires advanced technology and expertise. Overall, while rare earth metals may not be used in large quantities, they are vital for the development and growth of many industries, and their future availability will likely be a key aspect of global technological advancement.

How Are They Used in Electric Car Batteries?
Rare earth metals play a significant role in electric car batteries. These metals are essential components of permanent magnets and are commonly used in electric motors. Some of the commonly used rare earth metals in electric car batteries include neodymium and dysprosium, which are essential in making high-performance electric motors.
Rare earth metals are also used in the production of nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries and lithium-ion batteries. In NiMH batteries, lanthanum is used to improve their performance, while cerium and praseodymium are used in the production of the electrodes. In lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, a small amount of rare earth metals such as yttrium, cerium, and lanthanum are used in the cathodes.
These metals improve the performance and durability of the batteries. In summary, rare earth metals play a crucial role in the production of electric car batteries and are essential in achieving high performance, energy efficiency, and durability.
Supply and Demand
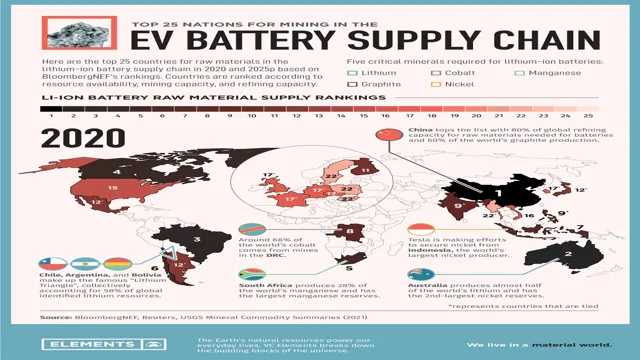
With the rise in demand for electric cars, the need for electric car batteries has also surged. These batteries require metals such as nickel, cobalt, and rare earth metals like neodymium and praseodymium. However, the supply of these metals is limited and their extraction can be extremely harmful to the environment.
This has led to a higher cost in producing electric cars and the need for alternative sources of these metals. Additionally, the current global supply chain for these metals is largely controlled by China, leaving many countries vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. While efforts are being made to increase the supply and find alternatives, it is important to consider the complexity of the situation and the potential consequences of our increasing demand for these metals.
Why Are Rare Earth Metals Considered Rare?
Rare earth metals are not actually rare in abundance, but rather difficult and expensive to extract. The reason for this is due to the supply and demand dynamics of the industry. Supply is limited due to the fact that these metals are found in very small concentrations within the earth’s crust, making them difficult to extract.
In addition, most rare earth metals are found in China, leading to concerns about monopolies and geopolitical tensions. As demand for rare earth metals increases due to their use in high-tech products such as smartphones and electric cars, the price for extraction and processing also increases. This creates a cycle where these metals become more expensive, and their extraction becomes increasingly difficult, leading to their classification as “rare.
” It is important to explore alternative ways to extract rare earth metals and diversify the supply chain in order to mitigate the challenges and risks associated with this industry.
Which Countries Have the Largest Reserves?
When it comes to the supply and demand of natural resources, the countries with the largest reserves hold significant leverage in the global market. Oil, gold, and uranium are just a few examples of resources that have the potential to greatly impact a country’s economy. Saudi Arabia currently holds the largest oil reserves, followed by Venezuela and Canada.
In terms of gold, the United States has the largest reserves, followed by Germany and Italy. Kazakhstan holds the largest uranium reserves, followed by Canada and Australia. It’s important to note that having the largest reserves doesn’t always translate to being the largest producer or exporter, as economic and political factors can play a crucial role.
Nonetheless, these reserves remain essential for each country’s economic future.
What Impacts Availability of Rare Earth Metals?
Rare Earth Metals The availability of rare earth metals is impacted by the forces of supply and demand. These metals are used in various technologies, including smartphones and electric vehicles, and as a result, the demand for them has increased significantly. However, the supply of rare earth metals is limited, and their extraction and processing are costly and complex.
Additionally, the mining of these metals can have adverse environmental effects, making it challenging to increase the supply. Furthermore, current geopolitical tensions and trade policies can also impact the availability of rare earth metals. Thus, the scarcity of these metals has led to high prices and concerns about their sustainability.
In conclusion, the balance between the supply and demand of rare earth metals is a delicate one, and careful management is required to maintain their availability in the future.
Alternatives to Rare Earth Metals
Electric car batteries typically use rare earth metals in their construction, but there are alternatives available which can be used instead. One such option is nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which are commonly used in hybrid cars. These batteries are less expensive than rare earth batteries and are easier to recycle, making them an attractive option for manufacturers looking to reduce their environmental impact.
Another alternative is lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, which are more stable and safer to use than traditional lithium-ion batteries. While these batteries are more expensive, they have a longer lifespan and are more efficient at storing energy, making them a good choice for electric cars. Ultimately, replacing rare earth metals in electric car batteries is a necessary step towards creating a more sustainable, environmentally-friendly future, and these alternatives offer a promising solution.
What Are the Alternatives to Rare Earth Metals?
Rare Earth Metals While rare earth metals have unique properties that make them valuable for technology, their mining and processing pose many environmental challenges. Luckily, there are viable alternatives available. Among the alternatives to rare earth metals include aluminum, titanium, and copper.
These metals, though not as rare as their counterparts, are excellent conductors of heat and electricity and can be used to make high-tech products such as smartphones, satellites, and electric cars. Silicon is another alternative widely used in electronics. More research is also being conducted in the use of graphene, a lightweight and durable material that can replace rare earth metals in solar panels, batteries, and other technological applications.
With these alternatives, industries have more options to avoid environmental constraints while still delivering high-performing electronic products to the market.
How Effective Are These Alternatives?
Rare Earth Metals There are several alternatives to rare earth metals that are being explored due to their scarcity and environmental impact. These alternatives range from using recycled materials to utilizing other types of elements in the manufacturing process. One promising alternative is the use of magnetocaloric materials, which can replace rare earth metals in certain applications.
These materials have the ability to change temperature when subjected to a magnetic field, which makes them ideal for use in refrigeration and cooling systems. Another option is the use of gallium nitride, which has similar properties to rare earth metals when it comes to electronic devices. Gallium nitride has the added benefit of being more efficient and durable than traditional rare earth metals.
Overall, these alternatives show promise in reducing our reliance on rare earth metals and mitigating their negative impact on the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric car batteries are powered by rare earth metals, which are not actually as rare as the name suggests. However, their mining and extraction can have significant environmental impacts, making it important for automakers to continue exploring alternative materials and sustainable sourcing methods. So, the next time you’re cruising down the road in your electric car, remember that behind the scenes, there’s a complex (and hopefully eco-friendly) process that makes it all possible.
Let’s keep pushing the boundaries of innovation and sustainability, and drive towards a greener future.”
FAQs
What are rare earth metals and how do they relate to electric car batteries?
Rare earth metals are a group of 17 elements that are crucial components in electric car batteries due to their ability to improve the battery’s performance and energy storage capacity.
Why are rare earth metals considered vital for electric car batteries?
Rare earth metals are considered vital for electric car batteries because they help to increase energy storage capacity and improve the overall performance of the battery.
What are some of the challenges associated with using rare earth metals in electric car batteries?
Some of the challenges associated with using rare earth metals in electric car batteries include high cost, limited supply, and environmental concerns related to the mining and processing of these metals.
Can electric car batteries be made without rare earth metals?
Yes, electric car batteries can be made without rare earth metals, but they may not be as efficient or effective in terms of energy storage and performance. Researchers are exploring alternative materials to rare earth metals for use in electric car batteries.