The Future of Driving: Exploring the Revolutionary Electric Car Battery Technology
Electric car batteries have come a long way since their inception. As humans continue to push the boundaries of science and technology, there are now electric car batteries that are unlike anything we’ve seen before. These batteries have the potential to revolutionize the entire automotive industry by making electric cars more accessible and efficient.
The future of electric car batteries is bright, and it looks like we are on the cusp of a monumental shift towards a greener and more sustainable world. The world is changing rapidly, and we’re all clamoring for a more sustainable future. One of the most critical pieces of the puzzle is the electric car battery.
As more and more people adopt electric vehicles, the demand for more efficient and effective batteries is growing. With traditional lithium-ion batteries approaching their limits in terms of capacity and efficiency, it’s time for something new. Luckily, the future of electric car batteries looks very promising, thanks to revolutionary technology.
Some of the industry’s brightest minds have been working on innovations such as solid-state batteries, which promise improved performance, safety, and longevity. And, like most breakthroughs, these innovations come with the promise of cost reduction, making electric cars more affordable to the average consumer. Solid-state technology is just one of many advancements on the horizon, making it an exciting time for electric cars.
But how do these batteries work, and what makes them so groundbreaking? And, more importantly, how will they impact you as a consumer? This article will answer all of these questions and more, giving you an inside look at the future of electric car batteries.
Types of Electric Car Batteries
Electric car batteries technology has come a long way since their inception. There are three main types of electric car batteries available nowadays: Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH), Lithium-Ion (Li-ion), and Solid-State Batteries. NiMH batteries used to be the go-to choice due to their low cost and environmental sustainability.
Li-ion batteries, on the other hand, have become the most popular option due to their higher energy density and longer lifespan. Solid-state batteries are the newest type of electric car battery, and they are still in the experimental stage. They offer better performance and safety compared to Li-ion batteries, but they are currently more expensive.
It’s important to note that the choice of battery type depends on the specific needs and preferences of the driver. Factors such as range, cost, and environmental impact should all be considered when selecting the right electric car battery.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Powering Most Electric Cars Today
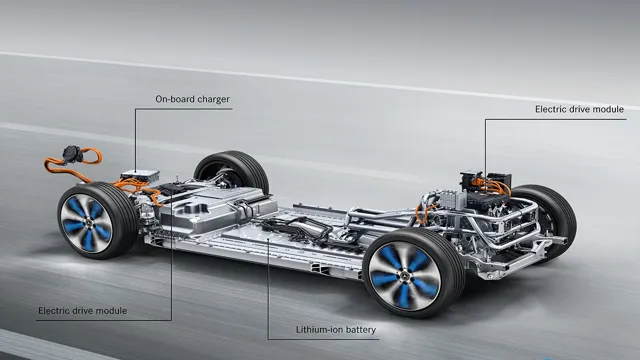
When it comes to electric cars, lithium-ion batteries are currently the most common type used to power them. These batteries are made up of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte in between them. The anode is typically made of graphite, while the cathode can be made from a variety of materials, such as lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate.
Lithium-ion batteries are popular for electric cars because they offer a high energy density, meaning they can store a lot of energy in a small space. This allows electric cars to have a longer range. Additionally, lithium-ion batteries can recharge quickly, making them convenient for busy drivers.
While there are other types of batteries that can power electric cars, such as nickel-metal hydride batteries, lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used due to their performance and availability.

Solid-State Batteries: The Up-and-Coming Game Changer
Electric car batteries are a crucial component of electric vehicles that determine its range, performance, and price. The common types of electric car batteries include Lithium-ion, Nickel-Cadmium, and Lead-Acid batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular and widely used type of electric car battery.
They offer high energy density, low self-discharge rate, and longer lifespans, making them ideal for electric vehicles. However, they are prone to thermal runaway, which can lead to explosion or fire in extreme conditions. On the other hand, Nickel-Cadmium and Lead-Acid batteries are less expensive but have lower energy density and shorter lifespans than Lithium-ion batteries.
Despite this, they can be a good option for low-cost electric cars or backup power solutions. Recently, Solid-state batteries have emerged as the up-and-coming game-changer in electric car batteries. They offer higher energy density, faster charging, longer lifespans, and improved safety than Lithium-ion batteries.
However, they are still in the early stages of development and yet to be commercially available.
Graphene Batteries: The Ultra-Fast-Charging Option
When it comes to electric car batteries, there are several types to consider. One of the most promising options is the graphene battery. Graphene batteries have the potential to revolutionize the electric car industry, thanks to their ultra-fast charging capabilities.
Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, which can take several hours to charge, graphene batteries can be charged in just a few minutes. This is a major advantage for drivers who don’t want to waste time sitting around waiting for their car to charge. Additionally, graphene batteries are more durable than traditional batteries, meaning they are less likely to degrade over time.
While there are still some challenges to overcome before graphene batteries become mainstream, they are certainly a technology to watch in the coming years.
The Impact of Battery Technology on Electric Cars
Electric car batteries technology has revolutionized the automotive industry in recent years. Advancements in this technology have allowed electric vehicles (EVs) to travel longer distances, reducing the range anxiety that had previously been a major barrier to their adoption. Lithium-ion batteries, which are used in most EVs, have become cheaper and more efficient, making EVs a more viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
The deployment of fast-charging networks has also made it easier for drivers to recharge their vehicles on the go, further boosting the appeal of EVs. Despite these developments, challenges such as the limited availability of raw materials needed to make batteries, the high initial cost of purchasing an EV, and the slow pace of infrastructure development remain. However, as battery technology continues to improve, the future looks bright for this game-changing mode of transportation.
Range: How Far Electric Cars Can Go
Battery technology is a key factor in determining how far electric cars can go, or their “range”. With advancements in battery technology, electric cars are now able to travel further on a single charge than they were just a few years ago. The lithium-ion battery is currently the most commonly used type of battery in electric cars.
However, newer battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, are being developed that could offer even greater range and faster charging times. In addition to battery technology, other factors such as driving style, temperature, and terrain can also affect the range of an electric car. While there is still room for improvement in battery technology, electric cars are becoming increasingly practical for everyday use as their ranges continue to increase.
Charging Time: How Long It Takes to Charge an Electric Car
When it comes to charging an electric car, one of the most pressing questions on people’s minds is how long it takes for the battery to fully charge. The answer to this question depends largely on the type of battery technology that’s being used. In recent years, there have been significant advances in the development of electric car batteries, resulting in longer ranges and shorter charging times.
For example, the latest lithium-ion batteries can charge to 80% in as little as 30 minutes. This is a vast improvement over older battery technologies, which could take several hours to reach full charge. The improved charging times have made electric cars more practical for everyday use, as drivers can recharge their vehicles quickly and easily when they need to.
As battery technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more impressive charging times in the future, making electric cars an even more viable alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles.
Cost: The Effect on Electric Car Affordability
Battery technology has a significant impact on the affordability of electric cars. As battery technology continues to improve, making batteries more efficient and longer lasting, the cost of electric cars will become more affordable. The main reason why electric cars are currently more expensive than traditional gasoline-powered cars is due to the cost of the battery.
However, as battery technology continues to advance, the cost of the battery is expected to decrease significantly over the next few years. This will make electric cars more accessible to the general public and will ultimately make them a more viable option for anyone in the market for a new car. In fact, it’s estimated that the cost of batteries for electric cars has dropped by as much as 80% over the last decade.
As the cost of batteries decreases, electric cars will become more and more affordable for the average consumer.
The Future of Electric Car Batteries
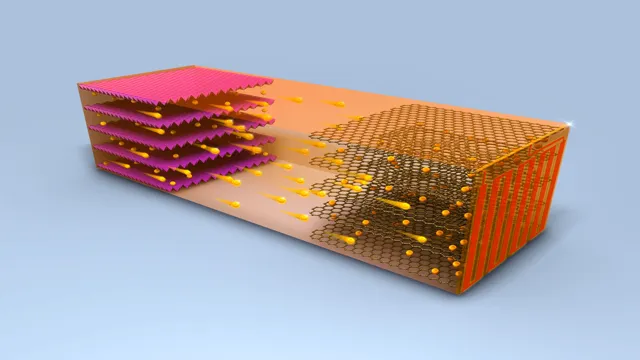
Electric car batteries technology is advancing at a rapid pace, and the future looks bright for electric vehicles. One of the most promising developments is the use of solid-state batteries. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries, which use a liquid electrolyte, solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte that offers several benefits, such as improved safety and increased energy density.
Companies like Toyota and BMW are already investing heavily in this technology, and we can expect to see solid-state batteries in commercial electric vehicles by the mid-2020s. Other advancements include the use of silicon anodes, which have the potential to increase energy capacity by up to 10 times, and new electrode materials that can improve efficiency and reduce costs. The future of electric car batteries is bright, and as technology continues to improve, we can expect longer driving ranges, shorter charging times, and more affordable electric vehicles for all.
Improved Energy Density: More Power in Smaller Batteries
The future of electric car batteries is bright with the possibility of improved energy density that packs more power into smaller batteries. With advancements in technology and materials, researchers are making strides in creating batteries with higher energy densities that allow for longer driving ranges and faster charging times. Imagine being able to travel farther without needing to stop for a charge or having a smaller, lighter battery that can still deliver the same amount of power as the larger, heavier ones currently used in electric cars.
This is the kind of future that improved energy density could offer. It’s like going from a suitcase that can only hold a few items to a backpack that can store everything you need for your trip. And with more power in smaller batteries, electric cars could become even more practical and efficient for everyday use.
So, while the technology is still in development, the promise of better energy density is an exciting development for the electric car industry.
Wireless Charging: Convenient and Effortless Charging
Wireless Charging Electric cars are becoming more popular as people strive to reduce their carbon footprint. With this increase in demand, researchers have been focusing on improving the electric car batteries to make them more efficient and convenient. One of the emerging technologies in battery charging is wireless charging.
This technology eliminates the need to plug in your car as the energy is transferred wirelessly through electromagnetic fields. It’s convenient, effortless, and with the growing number of wireless charging stations, you can charge your electric car just about anywhere. Imagine driving your car into a parking lot, and it begins to charge without requiring you to step out of the vehicle.
It’s like the future is already here. This wireless charging technology is still in its early phase, but it holds significant promise to drive the electric car industry forward.
Conclusion: The Revolution Continues
In conclusion, the advancements in electric car battery technology have revolutionized the way we think about transportation and sustainability. From nickel-cadmium to lithium-ion, we’ve come a long way in terms of battery chemistry and efficiency. With longer driving ranges and faster charging times, electric cars are no longer seen as a niche market, but as a viable option for everyday commuters.
And who knows, soon we may even be able to charge our cars as quickly and easily as we charge our phones. So, let’s raise a toast to the electrifying future of transportation!”
FAQs
How do electric car batteries work?
Electric car batteries work by converting stored chemical energy into electrical energy, which can then be used to power an electric motor. The battery is charged by plugging the car into an external source of electricity.
How long do electric car batteries typically last?
The lifespan of an electric car battery depends on many factors, such as the type of battery and how it is used and maintained. Most electric car batteries last at least 8-10 years or 100,000 miles before they need to be replaced.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, electric car batteries can be recycled. The process involves breaking down the battery into its component parts and then separating and reusing materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
What are the latest advancements in electric car battery technology?
The latest advancements in electric car battery technology include solid-state batteries, which offer higher energy density and longer lifespan, and lithium-sulfur batteries, which are lighter and more affordable. Other promising technologies include flow batteries and sodium-ion batteries.