The Anatomy of Electric Car Batteries: Delving into their Composition and Components
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as people look for more environmentally friendly ways to travel. One of the key components of an electric car is its battery, but you may be wondering what electric car batteries are made of. Unlike conventional cars that use fuel to power their engines, electric cars use large lithium-ion batteries to power an electric motor.
These batteries are made up of several layers, including the anode, cathode, and electrolyte, which work together to store and release energy. The anode and cathode are made from a combination of metals and compounds like graphite and lithium cobalt oxide, while the electrolyte helps facilitate the movement of ions between the two layers. The components are carefully designed and engineered to ensure that they work together efficiently to provide the power needed to propel the car forward.
Electric car batteries are also recyclable, which makes them an even more environmentally friendly option. When the battery reaches the end of its life, it can often be recycled to create new batteries or used in other industries to create new products. In summary, the batteries used in electric cars are made up of several layers of metals and compounds that work together to store and release energy.
These carefully engineered batteries offer a more eco-friendly option for powering cars, and are also recyclable, making them a sustainable choice for the future.
Introduction
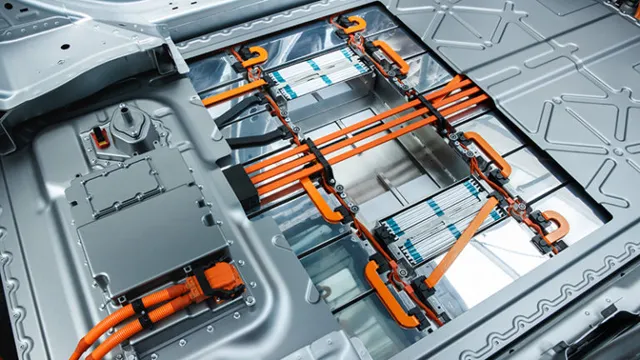
Electric car batteries are an essential component of an electric car, serving as the vehicle’s energy source. These high-tech batteries are made up of several small cells, which rely on lithium-ion technology to store and discharge electrical energy. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of battery used in electric vehicles due to their high efficiency and energy density.
They have a unique structure composed of a positive electrode made up of metal oxide, a negative electrode made up of graphite, and an electrolyte that connects the two electrodes. The metallic casing encloses all of these components to provide insulation and protection. The battery management system controls all functionality of the battery, ensuring its safety and optimal performance.
The battery pack’s size and capacity can vary depending on the specifications of the vehicle, ranging from 40 kWh to 100 kWh. A larger battery pack means greater driving range for the electric car. Given that range anxiety is the biggest concern for EV buyers, battery technology is constantly evolving to improve energy storage capability, durability, and efficiency.
With advancements in battery technology, electric cars will likely become more accessible and widespread in the future.
The Importance of Car Batteries
Car batteries are an essential component of a vehicle, providing the necessary electrical power needed to start the engine and run the car’s electrical systems. Without a functioning battery, your vehicle won’t start and will be rendered useless. It’s crucial, therefore, to ensure that your car battery is in proper working condition.
But why is it so important? Well, think of it this way: Your car battery is like the heart of your vehicle; just as the heart pumps blood to ensure the body’s proper functioning, the battery provides electrical power to keep your car running smoothly. A dead battery can cause not only inconvenience but also safety concerns when you’re stranded on the side of the road. It’s recommended that you have your car battery checked regularly by a professional and replaced every three to five years, depending on the make and model of your vehicle.
By taking care of your car battery, you’re ensuring your vehicle’s health and longevity on the road.

The Rise of Electric Cars
Electric cars have captured the public’s imagination in ways that few other inventions have managed to do. Over the past few decades, these vehicles powered by rechargeable batteries have evolved from being niche curiosities to become mainstream alternatives to traditional gasoline cars. And it’s no surprise that the rise of electric cars has coincided with a growing awareness of environmental concerns, as people look for greener and more sustainable ways to get around.
Today, major car manufacturers such as Tesla, Nissan, and Ford are investing billions of dollars to develop electric cars with longer ranges, faster charging times, and enhanced technology. With the electric car revolution showing no signs of slowing down, it’s no wonder that companies like these are betting big on this futuristic mode of transportation.
Electric Car Battery Composition
Electric car batteries are typically made up of a combination of several types of metal, including cobalt, nickel, and lithium. These metals are carefully selected for their chemical properties, allowing for the creation of a high-capacity battery that can store a significant amount of energy. Cobalt is an essential component due to its ability to stabilize the lithium-ion cells and prevent overheating.
Nickel, on the other hand, provides significant power density, which allows for extended driving ranges. Finally, lithium itself is the key ingredient that allows for the movement of charged particles, creating the flow of electricity that powers the vehicle. Additionally, the casing of the battery is made from materials like aluminum and copper, which are highly conductive and can withstand the intense heat generated during charging and discharging.
By utilizing these specific metals and materials, manufacturers can create high-quality electric car batteries that have the potential to power vehicles for hundreds of miles.
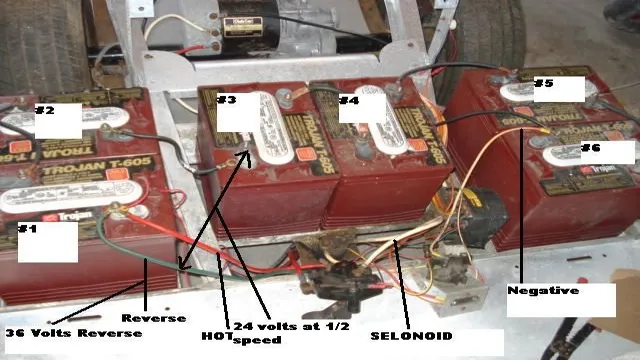
Components of Lithium-ion Batteries
When it comes to electric cars, the battery that powers the car is the most critical component. Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular choice for electric vehicles. These batteries contain two electrodes, a positively charged cathode, and a negatively charged anode.
The cathode is typically made of lithium cobalt oxide, while the anode is made of graphite. The two electrodes are separated by an electrolyte, which is a liquid or a gel containing lithium salt. A separator also protects these electrodes from touching each other while allowing free flow of ions.
Lithium-ion batteries are lightweight, durable, and have a high energy density, making them perfect for electric cars. The battery’s capacity depends on the number of cells connected, which determines how far your car can travel on a single charge. The battery management system monitors the battery’s state of charge, temperature, and voltage, ensuring optimal performance and a longer lifespan for your vehicle’s battery pack.
In conclusion, while electric cars are gaining popularity, the lithium-ion battery is a crucial part of the vehicle that allows for sustainable transportation.
Other Battery Materials
Electric car battery composition has come a long way, with researchers exploring different battery materials to increase performance and reduce costs. Aside from lithium-ion batteries, other promising materials include solid-state batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and flow batteries. Solid-state batteries are a potential replacement for traditional lithium-ion batteries, which use liquid electrolytes that can overheat and pose a safety risk.
Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte, making them safer and potentially longer-lasting. Sodium-ion batteries are still in the early stages of development, but they have the potential to be more environmentally friendly by using sodium, an abundant and low-cost material, compared to lithium. Finally, flow batteries work by storing energy in large tanks of liquid and pumping it into the battery when needed.
This technology is still relatively new and is currently being used for grid-scale energy storage, but it has potential applications for electric cars in the future. Overall, while lithium-ion batteries remain the dominant battery composition for electric cars, researchers are continuously exploring other options to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Comparison to Traditional Car Batteries
When comparing electric car batteries to traditional car batteries, there are a few significant differences to note. Firstly, the composition of an electric car battery is different from a traditional battery. While traditional car batteries are typically lead-acid batteries, electric car batteries are lithium-ion batteries.
These batteries are made up of several cells that work together to create energy to power the car. Another significant difference between the two types of batteries is the amount of energy they can store. Electric car batteries can store significantly more energy than traditional car batteries, which is necessary to power the larger electric motor.
Additionally, electric car batteries tend to have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance than traditional car batteries. While the initial cost of an electric car battery may be higher than a traditional battery, the long-term benefits make it a worthwhile investment for those looking to switch to a more sustainable form of transportation.
Environmental Impact
Electric car batteries are typically made up of a few key components that work together to power the vehicle. The main component of an electric car battery is the cathode, which is typically made up of a combination of nickel, cobalt, and manganese. These metals are carefully chosen to provide the necessary conductivity and stability for the battery to function.
The anode of the battery is usually made up of graphite, which serves as an electrode that can store energy for use later. Additionally, the electrolyte solution used in electric car batteries is typically made up of a salt or acid that allows for the flow of electrons between the anode and cathode. While these materials are all carefully chosen to provide the best possible performance for the battery, there are also environmental concerns to consider.
The mining and extraction of the metals used in electric car batteries can have significant impacts on local ecosystems and may contribute to climate change. As electric cars become more popular, it will be important for manufacturers to find more sustainable and environmentally friendly ways to source the materials needed for these batteries.
Production and Disposal
Production and disposal have a significant impact on the environment. The production of goods and products requires the use of resources such as water, energy, and raw materials, which can contribute to the depletion of natural resources and pollution. Additionally, the disposal of waste generated from the production and consumption of goods can have long-lasting effects on the environment, such as landfills and ocean pollution.
Therefore, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact of our actions. One thing we can do is to reduce our consumption and waste. We can buy thoughtfully, purchase products that have minimal packaging, and recycle whenever possible.
Recycling helps conserve resources and decreases the amount of waste sent to landfills. Moreover, we should support companies that prioritize sustainability and eco-friendliness in their production methods. Being conscious of the environmental impact of our actions can lead to a cleaner and healthier planet.
Let’s work together to make a positive difference for the environment.
Efficiency and Sustainability
Efficiency and Sustainability are important elements of any business today, and environmental impact is a major factor that must be considered. The carbon footprint of a company’s activities can have a significant effect on the environment. This includes the emissions produced by transportation, energy usage, and resource depletion.
To reduce this impact, companies must adopt sustainable practices such as using renewable energy sources and maximizing the use of resources. They can also implement more efficient processes and technologies to minimize waste and reduce their overall carbon footprint. Through these efforts, businesses can make a positive contribution to the environment while also improving their bottom line.
It’s essential for companies to prioritize sustainability to protect the world we live in for future generations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric car batteries are not just your average AA or AAA power source. These high-tech batteries are made up of a complex mix of materials, including cobalt, nickel, manganese, and graphite. Without them, we wouldn’t be able to enjoy the smooth, sustainable ride of an electric vehicle.
So the next time you’re cruising in your eco-friendly ride, take a moment to appreciate the scientific marvel that is your car battery. It’s not just powering your car, it’s powering a cleaner, greener future. And that’s a pretty electrifying thought.
“
FAQs
What materials are used to make electric car batteries?
Electric car batteries are typically made of lithium-ion cells, which consist of lithium cobalt oxide, nickel cobalt aluminum oxide, or lithium iron phosphate.
How efficient are electric car batteries compared to traditional gasoline engines?
Electric car batteries are much more efficient than gasoline engines because they convert energy into motion with almost 100% efficiency, while gasoline engines waste a significant amount of fuel energy through heat.
How long do electric car batteries last and when do they need to be replaced?
The lifespan of electric car batteries can vary depending on the usage and charging habits, but they typically last between 8-12 years or around 100,000 miles. When they start to degrade and lose capacity, they may need to be replaced.
How does the cost of replacing an electric car battery compare to regular car maintenance costs?
The cost of replacing an electric car battery can vary greatly depending on the make and model, but it can be significantly higher than regular car maintenance costs. However, as the technology advances and becomes more widespread, the cost is expected to decrease.