Rev Up Your Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Car Battery Charging!
Electric cars have been rapidly increasing in popularity, thanks to their eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness. However, one of the most common concerns for people interested in purchasing an electric car is the battery charging process. Charging an electric car battery seems like a complex and confusing task for many people, but it doesn’t have to be.
In this blog post, we will break down the battery charging process for electric cars and explain the different types of charging options available, so you can make an informed decision when it comes to buying an electric car. So, fasten your seatbelt, and let’s dive into the world of electric car battery charging!
How Electric Car Charging Works
Electric car battery charging explained: The process of charging an electric car battery varies depending on the type of charger used. At home, most electric cars can be charged using a 120-volt outlet or a 240-volt Level 2 EV charger. These chargers use AC power from the grid to charge the battery pack.
When the charger is plugged in, a signal is sent to the car to start charging. The onboard charger converts the AC power from the outlet to DC power, which is used to recharge the battery pack. The rate of charging depends on the size of the battery and the capacity of the charging station.
When charging at a public station, the process is similar, but often faster. Level 3 DC fast chargers can charge a battery pack to 80% in as little as 30 minutes. As electric car technology improves, the charging process will become even faster, more convenient, and widely available.
By driving an electric vehicle, you reduce carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner environment.
AC vs. DC Charging
Electric car charging can be done using either AC or DC power. AC charging, or alternating current charging, uses a charging cable with a plug that plugs into a standard electrical outlet or a specially designed charging station. AC charging is slower than DC charging, taking anywhere from a few hours to overnight to fully charge an electric car.
DC charging, or direct current charging, uses a charging station that converts AC power to DC power and can charge an electric car much faster, taking as little as 30 minutes to reach an 80% charge. However, DC charging stations are not as widely available as AC charging stations and can be more expensive to install. It’s important for electric car owners to understand the differences between AC and DC charging and to plan their charging needs accordingly depending on the availability of charging stations and how quickly they need to charge their vehicle.
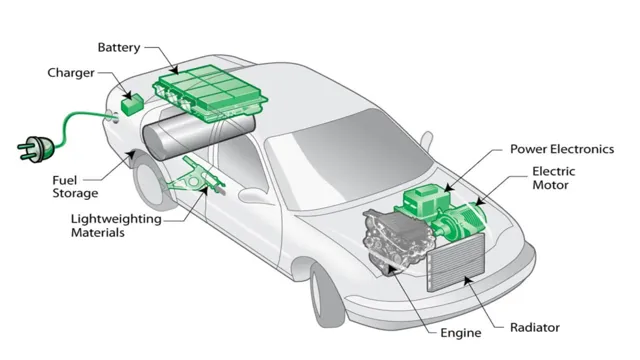
Charging Rates and Time
Electric car charging rates and time can vary depending on several factors, such as the battery capacity, the charging station used, and the car model. Generally, the charging process can be categorized into three levels: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging. Level 1 uses a standard household outlet and can charge a car battery fully in 8-12 hours, making it suitable for overnight charging.
Level 2 charging utilizes a 240-volt outlet, which cuts the time down to 4-6 hours for a full charge. DC Fast Charging, on the other hand, is the quickest option available, charging a car battery to 80% in as little as 20 to 30 minutes. However, it’s worth noting that using DC Fast Charging frequently can degrade the battery’s capacity over time.
An electric car owner needs to take into account the charging station network and availability in their area to plan their trips adequately. Additionally, battery size and car model will dictate the amount of energy required to fill the battery, which ultimately affects the charging rate and time. As a result, understanding the different charging rates and time frames will help an electric car owner make informed decisions and get the most out of their electric car.
Types of Electric Car Chargers
When it comes to electric car battery charging, there are a few types of chargers to consider. The most common is Level 1 charging, which uses a standard household outlet and takes several hours to fully charge the battery. Level 2 chargers use higher voltage and can be installed in a garage or parking spot for faster charging times, usually around 4-6 hours.
Fast chargers, or DC fast chargers, are the quickest option and can fully charge a battery in as little as 30 minutes, but are typically only found at public charging stations. It’s important to note that charging times can vary depending on the size of the battery and the charging rate of the specific vehicle. Overall, understanding the different types of chargers can help drivers plan their charging needs and utilize the most efficient charging options available.
Level 1 Chargers
Level 1 Chargers Level 1 chargers are the most basic type of electric car charger available. They are also the slowest to charge, taking around 8-12 hours to fully charge an empty battery. As a result, they are best suited for overnight charging at home or in a workplace car park.
Level 1 chargers are usually provided with the purchase of a new electric car, making them a great option for those who are new to EV ownership. They typically operate on a standard household 120-volt outlet, which means that they can be used almost anywhere. However, it’s worth noting that their slow charging speeds may not be sufficient for those who need to travel long distances regularly.
Overall, level 1 chargers are a great option for those who want to start driving an electric car without making a significant investment in charging infrastructure.
Level 2 Chargers
Level 2 chargers are one of the most popular types of electric car chargers available in the market. They are capable of charging an electric car much faster than Level 1 chargers, typically providing around 20 to 25 miles of range per hour of charging. Level 2 chargers require a 240-volt power source, which is commonly found in homes and businesses.
They come in two different types- portable and stationary. Portable Level 2 chargers can be carried around and plugged into any 240-volt power source. They are typically more expensive than stationary options.
Stationary Level 2 chargers need to be hardwired into an electrical system and cannot be moved around. They are much cheaper than portable Level 2 chargers, making them a more affordable option for those looking to install a charger at their home or business. Overall, Level 2 chargers are an excellent choice for those who want to quickly and easily charge their electric car.
DC Fast Chargers
DC fast chargers are one of the most popular types of electric car chargers available in the market today. These chargers use direct current to charge an electric vehicle’s battery quickly, allowing it to fully charge in as little as 30 minutes. There are three different types of DC fast chargers: CHAdeMO, CCS, and Tesla Supercharger.
CHAdeMO is commonly used in Japanese-made cars, while CCS is used by European and American manufacturers. Tesla’s Supercharger is unique to their brand and provides one of the fastest charging speeds available, up to 250 kW. It is important for electric vehicle owners to know which type of fast charger is compatible with their specific make and model to ensure efficient charging times and avoid any potential issues.
Overall, DC fast chargers are a convenient option for drivers who need to quickly recharge their electric vehicle on the go, offering an alternative to slower, traditional charging methods.
Factors That Affect Electric Car Charging
When it comes to electric car battery charging, there are several factors that come into play. The first factor is the type of charger being used. There are several types of chargers available, ranging from standard level 1 chargers to high-speed level 3 chargers.
The type of charger will determine how quickly the battery can be charged. Another factor to consider is the age of the battery. As batteries age, they slowly lose their ability to hold a charge, which means it may take longer to fully charge the battery.
Another factor that affects charging time is the temperature of the battery. If the battery is too cold, it may take longer to charge. Lastly, the distance being traveled also plays a role in charging time.
If the vehicle is being used for long distances, it may require more frequent charging stops, resulting in longer overall charging times. Understanding these factors can help electric vehicle owners make informed decisions about charging their cars.
Battery Capacity and Type
When it comes to charging electric cars, there are several factors that can affect the process. One of the most critical ones is the battery capacity and type. The largest battery capacity means more time to charge, which is why it’s essential to have a battery with a high capacity.
Moreover, the type of battery can play a significant role in determining charging speed. For example, lithium-ion batteries can charge faster than lead-acid batteries due to their chemical composition. It’s important to note that not all electric cars use the same battery type, so charging time can vary depending on the vehicle.
Additionally, the charging infrastructure also plays a significant role in charging speed, so it’s best to choose a charging station that is compatible with your vehicle’s battery type and capacity.
Temperature and Climate
Temperature and Climate One of the most crucial factors that affect electric car charging is the temperature. Electric car batteries tend to function optimally within a specific temperature range, and if the temperature falls outside this range, it can significantly impact the charging time and range of the vehicle. For instance, extremely low temperatures can cause the battery’s capacity to drop, reducing the vehicle’s range, whereas high temperatures can decrease the battery’s lifespan.
Additionally, the charging process generates heat, which can further affect battery temperature. Therefore, it’s essential to ensure that electric vehicles are parked in an area where the charging station is protected from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Proper temperature control can reduce the variation in charging times and preserve battery health, ensuring that electric vehicles can run efficiently and reliably.
Tips for Maximizing Electric Car Battery Life
If you own an electric car, it’s crucial to understand how electric car battery charging works to maximize its lifespan. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles, and their lifespan is affected by various factors, including temperature, charging frequency, and depth of discharge. It’s best to avoid charging your battery to 100% and discharging it to 0%, as this puts excessive stress on the battery, reducing its total lifespan.
Ideally, charging your battery to around 80-90% and discharging to around 20-30% is optimal for battery health and longevity. It’s also essential to avoid exposing your vehicle to extreme temperatures, either hot or cold, as this negatively impacts the battery’s lifespan. Additionally, it’s important to use only the manufacturer’s recommended charging equipment and avoid using third-party chargers and adapters.
By following these tips, you can ensure your electric car battery lasts longer and performs optimally, saving you money and prolonging the life of your vehicle.
Conclusion
In summary, charging your electric car’s battery may seem like a complicated process, but at its core, it’s simply a matter of plugging in and letting the electrons flow. Just like charging your phone or laptop, the key is to find the right charging solution for your needs, whether that’s at home or on the go. So go ahead and embrace the convenience and environmental benefits of electric vehicles – just remember to keep your charger close at hand!”
FAQs
How long does it take to charge an electric car battery fully?
Charging time for an electric car battery largely depends on the size of the battery and the charger’s capacity. However, the average charging time can be around 8-12 hours for a full charge at home using a Level 2 charging station.
How much does it cost to charge an electric car battery?
The cost of charging an electric car battery can vary based on the electricity rate in the area and the vehicle’s battery size. However, the average cost can be around 12-15 cents per kWh, whereas a typical electric car battery contains around 60 kWh of energy.
Can I charge an electric car battery using a regular household outlet?
Yes, you can charge an electric car battery using a regular household outlet. However, it can take significantly longer to charge the battery fully. It is recommended to use a Level 2 charging station for faster charging.
Can I charge an electric car battery when it is raining or snowing?
Yes, you can charge an electric car battery when it is raining or snowing as the charging port and cable are designed to be weatherproof. However, it is recommended to keep the charging port clean and dry for safety purposes.