Cobalt: The Key Ingredient in Boosting Electric Car Battery Performance
Electric cars have been gaining popularity in recent years as people become more conscious about the environment and the impact of traditional vehicles on it. When it comes to electric cars, their batteries are a crucial component that allows them to function. And one of the essential elements that make up these batteries is cobalt.
Cobalt is a transition metal that is used in many applications, including the production of electric car batteries. But what makes this metal so crucial, and how does it contribute to the performance and efficiency of electric cars? In this blog post, we will explore the importance of cobalt in electric car batteries and its role in shaping the future of electric cars.
What is Cobalt?
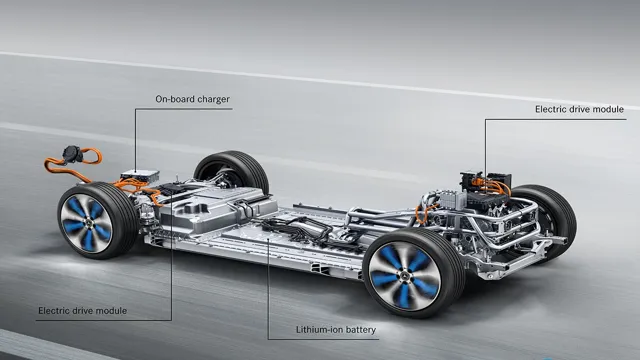
Electric car battery cobalt is a material that is essential to the manufacturing process of rechargeable batteries used in electric vehicles. Cobalt is a naturally occurring element that is mined in countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). It is known for its high energy density and thermal stability, making it an ideal component of lithium-ion batteries.
However, there are concerns about the ethical and environmental impact of cobalt mining. Many companies are working to find alternatives to cobalt or to ensure responsible sourcing, but for now, it remains a vital component in electric car batteries. As demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, the importance of cobalt in clean energy production will only increase.
A brief explanation on the composition of cobalt.
Cobalt is a metallic element that is represented by the symbol Co and the atomic number 2 It is a hard, brittle, silver-gray metal that is commonly found in the Earth’s crust. Cobalt has a close association with nickel and is often found along with it in mineral deposits.
Cobalt has a unique atomic structure that is composed of 27 protons and 32 neutrons, along with 27 electrons. Its atomic mass is approximately 593 atomic mass units.
Cobalt is a transition metal that is known for its magnetic properties and its ability to be alloyed with other metals, making it useful in various industries such as aerospace, electronics, and medicine. Furthermore, cobalt is used in rechargeable batteries and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. This versatile element has an important role in various aspects of life and plays a significant role in technological advancements.

The Role of Cobalt in Electric Car Batteries
Electric car batteries rely heavily on cobalt, a versatile metal that is commonly used as a cathode material in lithium-ion batteries. This metal is a crucial component in the production of long-lasting and efficient electric car batteries. Cobalt has the ability to retain high energy capacity, which makes it ideal for sustaining the energy levels required in electric car batteries.
However, the over-reliance on cobalt has become a growing concern, given the environmental and ethical issues associated with its mining and processing. The search for an alternative component that is sustainable and environmentally friendly is on the rise, as the world shifts towards a greener economy. Some car manufacturers, such as Tesla, have already reduced the amount of cobalt used in their batteries by substituting cobalt with nickel or manganese, both of which are cheaper and more abundant.
The role of cobalt in electric car batteries may evolve, but it remains an important element in the quest for sustainable energy solutions.
How cobalt affects the performance and durability of electric car batteries.
Cobalt plays a crucial role in the performance and durability of electric car batteries. It is an essential element in the cathode of a lithium-ion battery, which is responsible for storing and releasing energy. Although cobalt is important, too much of it can lead to increased costs and environmental concerns.
Recent advancements in battery technology have aimed to reduce the amount of cobalt used, replacing it with materials such as nickel and manganese in order to create more affordable and environmentally friendly options. However, cobalt still remains the most efficient option in terms of energy density and has a significant impact on the overall performance of electric car batteries, making it an important consideration in the development and improvement of electric vehicles.
The benefits of using cobalt in electric car batteries.
Cobalt plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of electric car batteries. The mineral is one of the main components of lithium-ion batteries, which powers electric cars. Cobalt not only improves the energy density of the battery but also enhances its durability and lifespan.
It helps to prevent overcharging and overheating, which, in turn, increases the safety of the battery. As a result, electric car batteries that use cobalt tend to have a longer range, quicker charging time, and better overall performance. However, there are concerns over the reliance on cobalt, as mining for the mineral can have adverse effects on the environment and communities in cobalt-producing countries.
Efforts are being made to reduce the amount of cobalt used in electric car batteries or find alternative materials that can perform just as well. Nonetheless, for the time being, cobalt remains an essential component in the development of sustainable electric cars.
Cobalt Mining and Production
If you’re familiar with electric cars, you’d know that their batteries are one of the most essential parts of the vehicle. One key component used to create such batteries is cobalt, a precious metal found in some parts of the world, including the Democratic Republic of Congo. As the demand for electric cars continues to skyrocket, so does the need for cobalt.
Unfortunately, cobalt mining can be environmentally damaging and has been linked to child labor. However, there are ongoing efforts to improve conditions for miners and reduce the environmental impact of cobalt mining. Additionally, alternative technologies are being explored and developed to reduce or eliminate the need for cobalt in electric car batteries.
It’s important to consider the impact of our actions and choices, as we work towards a more sustainable future.
A look into the process of cobalt mining and production.
Cobalt mining and production involve a complex process that requires a lot of energy and resources. Cobalt is mainly found in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where it is extracted from the earth using traditional methods. The mineral is then transported to processing plants where it is purified and turned into cobalt salts, oxide, or metallic cobalt.
However, the cobalt industry has been plagued by ethical concerns as child labor and human rights abuses are common. Moreover, the use of toxic chemicals during the refining process poses a significant environmental threat. Despite these challenges, cobalt remains a crucial component in many high-tech industries, including electric cars and mobile phones.
As the demand for these technologies continues to grow, it is critical to find sustainable ways of producing cobalt that do not harm the environment or exploit vulnerable communities.
Environmental impacts and ethical concerns surrounding cobalt mining.
Cobalt mining and production have become a cause for environmental concern around the world. Cobalt is an essential component of rechargeable batteries used in electric cars, smartphones, and laptops. However, the mining of cobalt has led to serious environmental degradation, including deforestation, water pollution, and the destruction of wildlife habitats.
Furthermore, the production of cobalt involves the use of toxic chemicals, leading to air and water pollution, which can harm nearby communities and workers. This issue has raised ethical concerns, as many of the countries where cobalt is mined lack adequate health and safety regulations to protect workers and their communities from the harmful effects of cobalt mining. The increasing demand for cobalt has also led to the use of child labor in some mining sites, a practice that is both unethical and illegal.
These issues highlight the need for sustainable and ethical practices in cobalt mining and production to preserve the environment and safeguard the welfare of workers and communities involved in the industry.
Cobalt Alternatives in Electric Car Batteries
When it comes to electric car batteries, cobalt has been a popular choice due to its ability to increase energy density and improve performance. However, concerns about ethical sourcing and the environmental impact of cobalt mining have led manufacturers to search for alternatives. One promising option is nickel-based batteries, which have a higher energy density and are more widely available.
Additionally, new battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries, have the potential to eliminate the need for cobalt altogether. While these alternatives are still in development and may come with their own challenges, the push towards cobalt-free batteries is an important step towards creating more sustainable and socially responsible electric vehicles.
Alternative materials being used in electric car batteries and their effectiveness.
As the demand for electric cars grows, manufacturers are looking for alternative materials to reduce costs and environmental impact. Cobalt is a commonly used material in electric car batteries, but it is expensive and acquired through unethical mining practices. One of the most promising alternatives is nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC), which reduces the amount of cobalt needed while increasing stability and energy density.
Another alternative is lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP), which removes cobalt altogether and has a longer lifespan. Both options are being tested and implemented in electric car batteries, but they have their own advantages and disadvantages. NMC batteries may have safety concerns due to the instability of nickel, while LFP batteries may not have as high of an energy density as cobalt-based batteries.
However, as technology continues to advance, it is likely that even more effective and sustainable alternative materials will be discovered and utilized.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cobalt may be a small ingredient, but it plays a crucial role in powering electric cars. It’s the equivalent of the cherry on top of a sundae – without it, the dish just wouldn’t be the same. So next time you plug in your electric car to charge, take a moment to appreciate the little cobalt that’s keeping your green dream on the road.
“
FAQs
What is cobalt used for in electric car batteries?
Cobalt is used as a cathode material in the lithium-ion batteries commonly used in electric cars.
Are there any alternatives to cobalt in electric car batteries?
Yes, some companies are developing batteries that use little or no cobalt, such as those that use nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM) or nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) chemistries.
Why is cobalt considered a problematic material for electric car batteries?
Cobalt mining is associated with human rights abuses, child labor, and environmental destruction in some parts of the world. Additionally, cobalt supply chains can be vulnerable to disruptions, which could impact the availability and affordability of electric car batteries.
What steps are being taken to address the ethical and environmental concerns surrounding cobalt mining?
Companies are increasingly taking steps to improve cobalt sourcing practices, such as conducting due diligence on suppliers, supporting community development programs, and investing in alternative materials research. Some investors and consumers are also pushing for greater transparency and accountability in supply chains.