The Dark Side of Electric Cars: The Truth About Cobalt Mining For Batteries
Electric cars are widely known for their eco-friendliness and as a solution to reduce emissions. However, when it comes to the production of the batteries that power these vehicles, a darker side of the story emerges. The raw materials used in electric car batteries, such as cobalt and lithium, are primarily extracted from mines in developing countries where labor rights and environmental regulations are often ignored.
The dangerous and exploitative conditions of these mines can inflict serious social and environmental damages. Furthermore, the manufacturing process of these batteries is highly energy-intensive, emitting significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the environment. The question arises, are electric cars as eco-friendly as we think, or is there a darker side to their production? Let’s dive deeper into the topic.
The Role of Cobalt in Electric Car Batteries
Electric car batteries require the use of cobalt, a metal that is found in small amounts within the Earth’s crust. Cobalt is essential to the production of modern batteries because it increases the energy density of the cells, allowing the batteries to store more energy for longer periods of time. However, there are concerns about the ethics of cobalt mining due to the use of child labor and poor working conditions in some countries.
As a result, major electric vehicle companies are committed to reducing their reliance on cobalt and finding alternative materials for their batteries. Nevertheless, due to the current limitations of technology, cobalt is still widely used in electric vehicle batteries, and its sourcing remains a contentious issue in the industry.
Cobalt Mining: An Overview
Cobalt mining is a crucial part of manufacturing electric car batteries, as this mineral is a key component in producing long-lasting, efficient power sources. Despite its importance, cobalt mining has a dark side, as many of the world’s largest cobalt mines are located in conflict zones or areas with a high risk of child labor. To combat these issues, many automakers and battery manufacturers are exploring alternative sources of cobalt, such as recycling or switching to cobalt-free batteries.
While these changes may require higher upfront investments, they offer a sustainable solution for the future of electric vehicles. By diversifying cobalt sources and reducing our dependence on conflict minerals, we can create a more ethical and environmentally-conscious electric car industry for years to come.

The Social and Environmental Costs
When we think about the environmental impact of electric cars, we often focus on the benefits like lower emissions and reduced dependency on fossil fuels. However, it’s important to also consider the social and environmental costs associated with the extraction and production of the materials that go into these vehicles. One example is cobalt, which is a key component of electric car batteries.
Cobalt mining is associated with child labor and unsafe working conditions in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, where most of the world’s cobalt is sourced. Additionally, cobalt mining produces significant amounts of toxic waste and is a major contributor to deforestation. As consumers, it’s important to consider the full lifecycle of our products and demand greater accountability from companies for the social and environmental costs of their supply chains.
The Search for Alternatives
The search for alternatives to cobalt mining is heating up as the demand for electric car batteries increases. Cobalt is a critical component in the manufacturing of rechargeable batteries, particularly for electric vehicles, due to its ability to maintain stability and increase energy density. However, the process of extracting cobalt is not environmentally friendly, and the working conditions of many miners are highly criticized.
As a result, companies are exploring alternative materials to reduce the reliance on cobalt. Some possibilities include nickel, manganese, and lithium, which are abundant and more accessible. While these alternatives show promise for a more sustainable future, they are not without their challenges.
Each material has its unique properties, and testing must be conducted to ensure they are suitable for industrial use. As companies continue to search for cobalt-free solutions, it is essential to consider their ecological impact and the lives of those involved in the production process.
Reducing Dependence on Cobalt
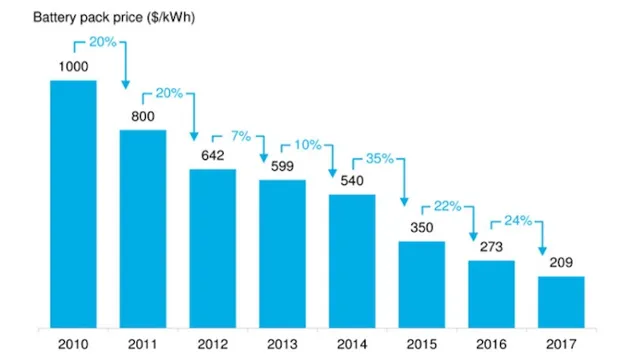
The mining of cobalt has been a major cause of pollution and environmental destruction around the world. Cobalt is an essential component in lithium-ion batteries, which power most of our electronic devices. However, the demand for cobalt has increased dramatically in recent years, leading to skyrocketing prices and unethical sourcing practices.
That’s why researchers and scientists are looking for alternative materials that can replace cobalt. One promising alternative is nickel, which is widely available and much cheaper than cobalt. Other materials being studied include manganese, aluminum, and titanium.
These materials have their own challenges and limitations, but they hold the potential to reduce our dependence on cobalt and create a more sustainable future. It’s a complex process, but the search for alternatives is essential to ensuring that our technology doesn’t come at the cost of our planet.
Exploring New Battery Technologies
As our reliance on technology increases, so does the demand for longer-lasting and more reliable battery technologies. Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most common battery type, but they have limitations such as their potential to overheat and their finite lifespan. This has led to a search for alternative battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries.
Solid-state batteries have a higher energy density, making them a promising alternative, but they are still in the early stages of development. On the other hand, lithium-sulfur batteries have the potential to increase energy capacity significantly, but they currently have a shorter lifespan and are less stable. Other alternatives being explored include flow batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and even microbial batteries.
Each has its unique advantages and challenges, but the race is on to find a battery technology that will meet the growing demands of modern technology.
The Potential of Recycling
Recycling has long been touted as the solution to our waste problem, but the truth is that it only addresses part of the issue. As our society has grown increasingly dependent on plastics and other non-biodegradable materials, the amount of waste we produce has exploded. Recycling is certainly better than simply throwing everything away, but it’s not a perfect solution.
That’s why we need to search for alternatives. The good news is that there are a number of promising technologies under development that could help reduce our reliance on recycling. For example, some companies are experimenting with biodegradable materials that can be easily broken down in the environment.
Others are exploring ways to create new products from waste materials that would otherwise end up in landfills. Still others are developing more efficient ways to produce goods, which would reduce the amount of waste we produce in the first place. One of the most exciting developments in the field of waste reduction is the concept of a circular economy.
Instead of following the traditional model of “take-make-use-dispose,” a circular economy seeks to keep materials in use as long as possible, thereby minimizing waste. This can be achieved through a variety of strategies, including product redesign, the use of renewable energy sources, and the implementation of closed-loop recycling systems. Ultimately, a combination of these approaches will be needed if we truly want to solve our waste problem.
Recycling will continue to play an important role, but it’s not the only answer. By embracing new technologies and concepts, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and the planet.
The Importance of Responsible Sourcing
As electric cars continue to dominate the auto industry, cobalt mining has become a hot topic. Cobalt is a necessary material in the production of electric car batteries, and its demand has led to widespread mining in developing countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo. However, this mining often involves child labor and dangerous working conditions.
It is crucial for companies to practice responsible sourcing and ensure that their cobalt is ethically obtained. Not only is it the right thing to do, but it also helps to mitigate reputational and legal risks. By taking the time to trace the supply chain of their cobalt and guaranteeing that it was sourced ethically, companies can demonstrate their commitment to social and environmental responsibility and help to create a more sustainable future.
The Rise of Ethical Cobalt Mining
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for batteries is also increasing. However, the production of these batteries is not without its ethical concerns, particularly when it comes to cobalt mining. Cobalt is a key component in lithium-ion batteries, making it a valuable resource.
Unfortunately, the mining of cobalt has often been entangled with issues such as child labor, unsafe working conditions, and environmental degradation. However, there is a growing movement towards responsible sourcing and ethical cobalt mining. This involves creating transparency in the supply chain, improving working conditions for miners, and minimizing the environmental impact of mining.
As consumers, we have a responsibility to consider the impact of our purchases and demand responsible sourcing practices from companies. By supporting ethical cobalt mining, we can help ensure that the batteries powering our devices are not tainted by exploitation and environmental harm.
Transparency in Supply Chain Management
The importance of responsible sourcing cannot be overstated when discussing transparency in supply chain management. Companies that prioritize responsible sourcing are able to maintain their social and environmental responsibilities while also ensuring a sustainable supply chain. This means partnering with suppliers who share their values and are committed to ethical and sustainable practices.
In addition to meeting social and environmental standards, responsible sourcing also helps ensure that the products being sourced are of high quality. By working with reputable suppliers who prioritize quality control, companies can provide their customers with consistent products that meet their expectations. Moreover, when companies are transparent about their sourcing practices, they build trust and credibility with their customers.
Consumers today are increasingly interested in knowing where their products come from and how they were made. By providing this information, companies demonstrate their commitment to social responsibility and transparency, which can lead to increased customer loyalty. The bottom line is that responsible sourcing is an essential component of supply chain management.
By prioritizing transparency and working with ethical suppliers, businesses can ensure the sustainability of their supply chains while also meeting customer demand for socially responsible products.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance Between Sustainability and Innovation
In the world of electric cars, cobalt mining is like the sidekick that nobody asked for, but one that we cannot do without. Yes, it may be a troublesome process, but it is an essential ingredient in the batteries that power our clean energy vehicles. As we continue to make strides towards a greener future, let us not forget the importance of responsible and sustainable cobalt mining.
After all, a clean car is only as clean as the resources used to make it.”
FAQs
What is cobalt and why is it used in electric car batteries?
Cobalt is a metallic element that is used in the cathode of lithium-ion batteries found in electric cars. It helps to increase the battery’s energy density and improve its overall performance.
How is cobalt mined for electric car batteries?
Cobalt is primarily mined in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) through both artisanal and industrial mining. However, there have been reports of unethical and inhumane practices in the mining industry, including child labor and poor working conditions.
Are there any alternatives to cobalt for electric car batteries?
Researchers are exploring alternative materials for electric car batteries, such as nickel, manganese, and aluminum. However, these materials have their own drawbacks and may not be as effective as cobalt in improving battery performance.
What actions can car manufacturers take to address the ethical concerns surrounding cobalt mining?
Car manufacturers can work with their suppliers to ensure ethical and sustainable mining practices. This can include using blockchain technology to track the origin of the cobalt and implementing stricter auditing and certification processes. Additionally, investing in research and development of alternative battery materials can help alleviate the demand for cobalt.