Unveiling the Eco-Friendly Marvel: A Close Look at How Electric Car Batteries are Made
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular due to their eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness. However, the heart of every electric car is its battery. Many people wonder how electric car batteries are made, and the answer may surprise you.
These batteries are not like your typical disposable ones; they are complex systems with multiple layers and components. In this blog, we will take a closer look at the process of making electric car batteries and the different materials used. We will also explore the advantages of electric car batteries and their impact on the environment.
So fasten your seatbelts and get ready to explore the fascinating world behind this innovative technology.
What is an electric car battery?
An electric car battery is a rechargeable device that powers electric vehicles. Most batteries in electric vehicles are made up of hundreds or thousands of small cells that store energy. These cells typically use lithium-ion technology, which provides a high energy density compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
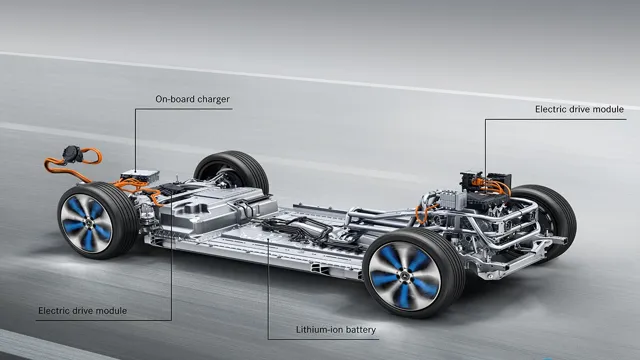
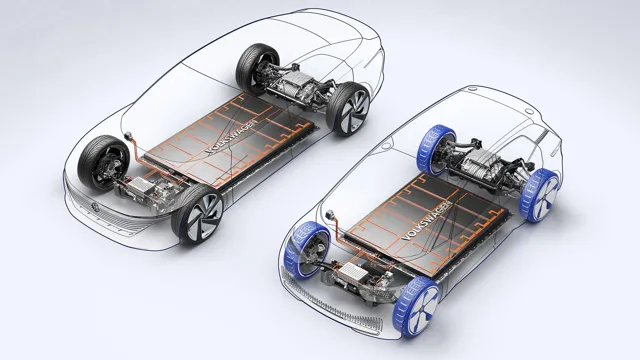
The cells are arranged into modules, which are then assembled into a pack that can be easily installed into an electric vehicle. A battery management system is used to monitor the state of the batteries and ensure that they are charged and discharged efficiently. The production of electric car batteries involves several complex processes, including raw material sourcing, cell manufacturing, and assembly.
With advances in battery technology and increased production, electric vehicles are becoming more mainstream and are seen as a viable alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
Understanding the basics
An electric car battery is the key component that powers an electric vehicle. It stores the energy required to run the electric motor, which propels the car forward. Unlike traditional combustion engines, electric car batteries use stored electricity to power the vehicle’s motor.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used type of electric car battery, as they are efficient, lightweight, and can store a substantial amount of energy. However, there are also other types of batteries, such as lead-acid and nickel-metal hydride, that are used in some electric cars. The battery’s size and capacity can vary depending on the make and model of the car, as well as the range and performance that the manufacturer is trying to achieve.
Overall, the electric car battery is a critical component, and advancements in battery technology are helping to improve the efficiency and range of electric vehicles.

The materials used in making batteries
When it comes to electric car batteries, the materials used are crucial to their success. These batteries contain a combination of metals including lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Lithium-ion batteries have become popular for electric vehicles due to their high energy density and long cycle life.
However, the mining and extraction of these metals can have negative impacts on the environment, such as deforestation and toxic waste. Therefore, battery manufacturers are continually seeking ways to make them more sustainable and environmentally friendly. Additionally, the manufacturing process for electric car batteries requires precision and attention to detail, ensuring that the battery cells are safely and effectively constructed.
Overall, the materials used in making electric car batteries are constantly evolving as technology and sustainability practices progress.
From cobalt to nickel: the metals that matter
Batteries have become an essential part of our daily lives, powering everything from smartphones to electric cars. And while we may take them for granted, the materials used to make these batteries are critical in determining their performance and reliability. Two of the most important metals used in battery manufacturing are cobalt and nickel.
Cobalt has traditionally been the go-to material for making high-performance batteries, but due to concerns about ethical and sustainable sourcing practices, there has been a shift towards using more nickel in recent years. Both metals have their advantages and disadvantages, but ultimately, it is important to choose the right materials based on factors such as cost, performance requirements, and environmental impact. Whether it’s cobalt or nickel, finding the right balance between these factors will be essential in meeting our growing demand for batteries as we move towards a more sustainable future.
The battery production process
Electric car battery how it’s made The battery production process for an electric car involves several stages. First, the manufacturer creates the cells, which are the basic units of the battery. The cells are assembled into modules, which in turn are assembled into packs.
During the assembly process, the cells are coated with a separator material that prevents short circuits. The modules are then connected to a battery management system, which monitors and controls the charging and discharging processes. The final step in the process is to enclose the battery in a protective casing.
The materials used in the production of electric car batteries include lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium, and lead-acid. Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used in electric vehicles due to their high energy density, which allows for a longer driving range. The battery production process requires a high level of precision, as even small variations in the assembly process can have a significant impact on the battery’s performance.
Additionally, manufacturers must ensure that the batteries are safe and reliable, as any defects could lead to serious accidents. This is why quality control is a critical part of the battery production process. Overall, the production of electric car batteries is a complex and intricate process that involves multiple stages of assembly, testing, and quality control.
As demand for electric vehicles continues to grow, manufacturers will need to continue to refine and improve this process to meet the needs of consumers.
Step-by-step guide
Battery production is a complex process involving multiple stages. The first step is to extract the raw materials needed to create batteries, such as lithium, cobalt and nickel. These materials are then transported to a processing facility where they are purified and refined.
Once the materials have been purified, they are combined to create a battery cathode. The cathode is then coated with a protective layer to prevent corrosion. The anode, which is made from graphite, is then manufactured and coated.
The cathode and anode are then placed into a casing along with a separator and electrolyte. The casing is sealed and the battery undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets safety and performance standards. Finally, the batteries are packaged and shipped to manufacturers where they are used to power a wide range of devices, from smartphones to electric cars.
While the battery production process can be complex, it is crucial for powering the technology we rely on every day.
Automation and innovation in battery production
Battery production has undergone much innovation and automation in recent years, thanks to the increased demand for clean energy. Today, the production process involves several stages, including the manufacturing of electrodes and separators, the assembly of cells, and the final assembly of the battery module. Automation is critical in ensuring that these processes occur efficiently and accurately.
For instance, robotic arms are often used to handle the delicate materials used in manufacturing, ensuring that the process is carried out without any contamination. Additionally, automation makes the production process faster, thus reducing the overall cost of production. While human intervention is still required in certain stages of the process, automated battery production has revolutionized the industry.
The result is a more streamlined process that produces batteries of higher quality, with reduced waste and increased throughput.
Challenges in battery production
Electric car batteries, how they’re made, and the challenges in their production are hot topics nowadays. The production process of an electric car battery involves several critical steps, from obtaining raw materials to manufacturing, assembly, testing, and transportation. Some of the most common challenges in battery production include the limited availability and high cost of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
Besides, the manufacturing process for these batteries is quite complex, requiring highly skilled technicians and advanced equipment. Moreover, electric car batteries can be dangerous if not correctly produced, leading to potential safety hazards and recalls. Despite the challenges, the demand for electric vehicles is outstripping what manufacturers can build, driving investment into more effective battery production techniques.
With new innovations in cell design and electric vehicle platforms increasing, it is essential to overcome these production hurdles and invest in sustainable and cleaner energy options, making electric vehicles a reality for everyone.
Social and environmental concerns
As the world moves towards renewable energy, the production of batteries has become essential to store energy efficiently. However, battery production presents some social and environmental concerns. One of the significant challenges in battery production is the mining of lithium to make the lithium-ion batteries.
The increased demand for lithium has raised concerns about the exploitation of regions that produce lithium. The mining of lithium requires a large amount of water, and this could lead to water scarcity and pollution. Additionally, the production process of batteries emits carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change.
The disposal of batteries is also a concern as it can lead to toxic waste and harm the environment. Despite these challenges, efforts are being made to develop sustainable ways of producing batteries, such as recycling used batteries. With proper care, the production of batteries can balance environmental and social considerations.
Costs and efficiency
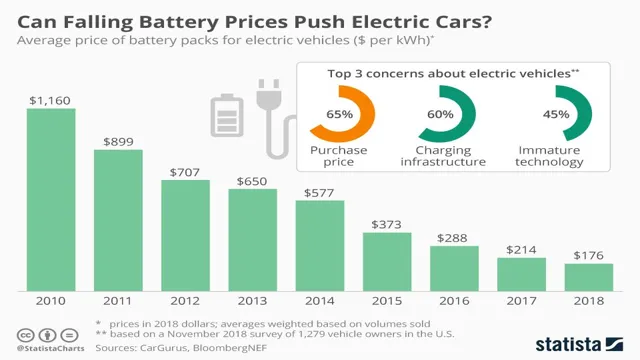
When it comes to battery production, there are several challenges that manufacturers face, particularly related to costs and efficiency. One major hurdle is the high cost of materials used in batteries, such as cobalt, nickel, and lithium. These materials can be difficult to source and process, driving up costs for manufacturers and ultimately consumers.
Additionally, there are concerns around the efficiency of battery production, particularly related to the environmental impact. Producing batteries requires a substantial amount of energy, and many manufacturers still rely on fossil fuels to power their facilities. However, there are steps being taken to address these challenges.
Some manufacturers are exploring alternative materials, such as vanadium and zinc, that could potentially reduce costs and environmental impact. Others are investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to power their facilities. Overall, while there are challenges in battery production, there are also opportunities for innovation and progress towards more sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
The Future of Electric Car Batteries
When it comes to electric car batteries, there are many different types and variations depending on the design and manufacturer. Generally, most electric car batteries are made up of a series of cells that work together to power the vehicle. These cells contain a positively charged cathode and a negatively charged anode, separated by an electrolyte.
The type of electrolyte and materials used for the cathode and anode can vary, but one common type of battery is the lithium-ion battery. Lithium-ion batteries are lightweight, durable, and have a high energy density, making them ideal for powering electric cars. However, there are still some challenges to overcome, such as improving the lifespan and reducing the cost of these batteries.
As technology progresses, we can expect to see new advancements in electric car battery design, such as solid-state batteries, which could offer even greater efficiency and reliability. Overall, the future of electric car batteries looks bright, with continued research and development pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Conclusion
So there you have it, folks – the electrifying journey of how an electric car battery is made! From the mining of materials to the assembly of cells, every step requires specialized skills and technology to ensure the best energy storage and performance. These batteries may not be the easiest things to make, but their eco-friendliness and fuel efficiency make them a vital component in the effort to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. So, the next time you hit the road in your electric vehicle, remember to thank the team of experts that made it all possible!”
FAQs
What materials are used to make an electric car battery?
Electric car batteries are typically made up of materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite.
How is the battery pack assembled?
The battery pack is typically assembled by connecting individual battery cells together. The number of cells varies depending on the car model.
What is the expected lifespan of an electric car battery?
The lifespan of an electric car battery varies depending on factors such as usage and environmental conditions, but it’s typically around 8-10 years.
Can electric car batteries be recycled?
Yes, electric car batteries can be recycled to recover materials such as lithium and cobalt, which can be used to produce new batteries.