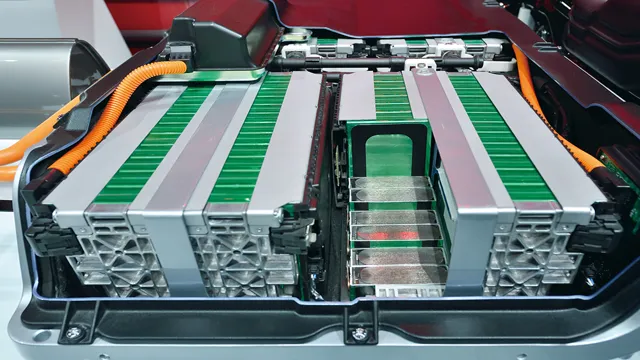
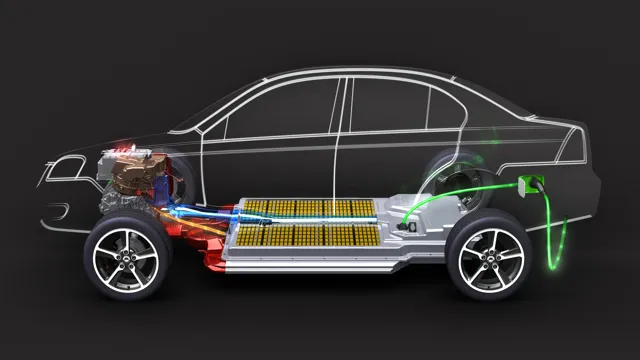
The Future is Bright: A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Car Battery Types
Electric cars are gaining in popularity as people seek more sustainable, environmentally-friendly forms of transportation. However, one aspect that still raises questions for many is electric car batteries. How do they work? How long do they last? And what happens at the end of their lifespan? In this blog post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about electric car batteries.
From the chemistry behind them to the various types available, we’ll delve into the inner workings of these powerhouses and bust some common myths along the way. So let’s plug in and get started!
Battery Types
When it comes to electric car batteries, there are a few different types to choose from. The most common kind is the lithium-ion battery, which is often used due to its high energy density and relatively low weight. Another option is the nickel-metal hydride battery, which can still be found in some older hybrid vehicles.
These batteries are often less expensive than lithium-ion, but they are also less efficient and do not last as long. Some automakers are also experimenting with solid-state batteries, which could potentially offer even higher energy density and longer lifespan than lithium-ion batteries. Ultimately, the choice of electric car battery kind will depend on a number of factors, including cost, efficiency, and availability.
Regardless of which type you choose, however, it is important to consider the environmental impact of your choice and to take steps to ensure that your battery is recycled or disposed of responsibly.
Lithium-Ion vs Nickel-Metal Hydride
When it comes to battery types, there are two main options to choose from: lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride. Both have their pros and cons depending on your needs. Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density and long-life cycle.
They are also lightweight and have a low self-discharge rate. However, they can be expensive and require special care to prevent overheating or damage. On the other hand, nickel-metal hydride batteries are more affordable and environmentally friendly, but they have a lower energy density and shorter lifespan.
They also require frequent use to prevent memory effect. Ultimately, the choice between these two battery types will depend on your specific needs and priorities. Do you value energy density and long-life cycle, or are affordability and eco-friendliness more important to you? Consider these factors when choosing the battery type that is right for you.

Pros and Cons of Each
When it comes to battery types, there are a few options to consider. One option is Alkaline batteries, which are affordable and easy to find in most stores. However, they are not rechargeable and can harm the environment if not disposed of properly.
Another option is Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries, which are rechargeable and more environmentally friendly. However, they can be more expensive upfront and may lose their charge faster than other battery types. Lithium batteries are another option, known for their long life and high performance.
They can also be more expensive, and some types require special handling due to their potential for overheating or explosion. Ultimately, the choice of battery type will depend on individual needs and preferences, as well as the device the battery will be used in. However, it’s important to keep in mind the potential pros and cons of each type to make an informed decision.
Battery Life
One of the most important factors to consider when deciding which electric car to purchase is the kind of battery it uses. There are several different types of electric car batteries available on the market today, each with their own unique advantages and disadvantages. Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most popular option, thanks to their high energy density and long lifespan.
However, they can be more expensive and have a higher risk of overheating compared to other types of batteries. Nickel-metal-hydride batteries are another popular choice, due to their lower cost and better performance in extreme temperatures. Ultimately, the best battery for your electric car will depend on your individual needs and preferences, as well as factors like driving habits and environmental conditions.
By doing your research and comparing the different options available, you can find the battery that best fits your needs and ensures maximum range and longevity for your electric vehicle.
Factors That Affect Battery Life
When it comes to our electronic devices, one of the most important factors to consider is battery life. After all, none of our devices can function without it! But what exactly affects how long our batteries last? One major factor is the type of activity we’re using our device for. Activities that use a lot of power, like gaming or video streaming, will drain the battery much faster than reading an e-book or simply browsing the internet.
Another factor is the age of the device – as batteries get older, they naturally lose their ability to hold a charge, and may need to be replaced. Additionally, temperature can play a role in battery life, as extreme heat or cold can cause the battery to degrade more quickly. By being mindful of these factors, we can maximize our battery life and make sure our devices stay powered up when we need them most.
How to Extend Battery Life
Battery life is essential for all types of devices, from smartphones to laptops. To extend the battery life of your device, there are a few tricks you can try. One of the most effective ways is to reduce the brightness of your screen.
This can often be the biggest drain on your battery, so lowering it to an appropriate level can significantly increase longevity. Another way is to turn off features you’re not using, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS. Background apps can also drain your battery quickly, so it’s definitely worth checking which ones you can close or uninstall.
Finally, investing in an external battery pack can also extend the life of your device. These packs are easy to use and can be a lifesaver when you need that extra bit of juice. By taking a few simple steps, you can extend the battery life of your device and ensure you’re always powered up when you need it most.
Replacing Battery
When it comes to battery life, it’s important to keep an eye on how long your device can go without needing a recharge. Over time, batteries can start to degrade and lose their ability to hold a charge like they used to. This is especially true for older devices or ones that get a lot of use throughout the day.
When you start to notice that your battery is draining faster than usual, it might be time to consider an upgrade. Some devices, like smartphones, may allow you to replace the battery yourself. This can be a cost-effective solution to extending the life of your device, but be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when doing so.
If you’re not comfortable with replacing the battery on your own, consider taking it to a professional. A new battery can give you new life for your device and keep you from having to constantly search for an outlet to charge up. So keep an eye on your battery life, and don’t be afraid to make a change when it’s time.
Charging Options
When it comes to electric car batteries, there are a few different types that are commonly available. The most popular kind of battery is the lithium-ion battery, which is known for its durability and ability to hold a charge for a long time. These batteries are used in most electric cars on the market today.
Another type of battery that is gaining popularity is the solid-state battery, which is more energy-dense than the lithium-ion battery. This means that it can hold more energy in a smaller space, making it attractive for use in electric cars. When it comes to charging options, most electric cars can be charged using a standard 120-volt electrical outlet, but it can take a long time to get a full charge that way.
A faster option is to use a level 2 charging station, which can provide a full charge in just a few hours. Some electric cars also have the option for DC fast charging, which can provide a full charge in as little as 30 minutes. Overall, the type of battery you have in your electric car will determine your charging options, but there are plenty of options available no matter which type you have.
Home Charging vs Public Charging Stations
As electric cars become more popular, people are increasingly considering their charging options. While home charging is convenient and affordable, public charging stations offer a level of flexibility that home charging cannot. With home charging, you have the convenience of charging your car overnight while you sleep, so it’s ready to go in the morning.
Also, you won’t have to worry about waiting in line or dealing with out-of-order charging stations. However, public charging stations offer more significant convenience with the ability to rapidly charge your vehicle while you’re out running errands or on a long trip. Additionally, public charging helps ensure that your car won’t run out of juice halfway through the day, and you won’t be stuck in need of a tow truck.
Ultimately, both options have their advantages and disadvantages, but your choice should depend on your driving habits and lifestyle. If you frequently travel long distances, public charging may be more convenient. However, if you live in a city and don’t drive long distances regularly, home charging may be a better choice.
Fast Charging vs Slow Charging
When it comes to charging your electronic devices, there are usually two options: fast charging or slow charging. The main difference between the two is the speed at which the battery is charged. Fast charging is a quick and convenient option when you need to charge your device quickly.
However, there are some downsides to using this method, such as potential damage to the battery over time. Slow charging is a more traditional and safe option, allowing the battery to charge at a steady and gradual pace. While this may take longer, it is better for the overall health of the battery.
Ultimately, the choice between fast charging and slow charging depends on your individual needs and preferences. If you need a quick boost of battery life, fast charging may be the way to go. But for long-term battery health, slow charging is the safer option.
Conclusion
So there you have it, folks. The electric car battery is not just a mode of power, but a symbol for the future of transportation. It’s clean, efficient, and a step towards a greener world.
Like a superhero’s suit, it gives life to the electric vehicle and powers it through the streets, leaving behind a trail of zero emissions. So let’s charge up and ride out into a brighter, electric future.”
FAQs
What types of batteries are typically used in electric cars?
Lithium-ion, lead-acid, and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries are the most common types of batteries used in electric cars.
Can electric cars use regular car batteries?
No, regular car batteries are not suitable for use in electric cars because they are not designed to handle the high power demands of electric propulsion.
How long do electric car batteries typically last before needing to be replaced?
The lifespan of an electric car battery can vary greatly depending on factors such as usage, temperature, and charging habits. However, most batteries are designed to last anywhere from 8-15 years.
What are some of the benefits of using a lithium-ion battery in an electric car?
Lithium-ion batteries are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can be recharged quickly. They also have a longer lifespan compared to other types of batteries used in electric cars.