A Shocking Evolution: Tracing the Fascinating History of Electric Cars
Electric cars have become a popular topic in recent years, with more and more people taking an interest in this innovative and eco-friendly mode of transportation. But, have you ever wondered about the evolution of electric cars and how they became what they are today? The concept of electric cars dates back to the 1830s, with various prototypes being developed in the years that followed. However, these vehicles had limited range and capabilities, making them less practical for everyday use.
Over time, advancements in technology and improvements in battery storage have enabled electric cars to evolve into the high-performing vehicles we know today. From Tesla’s sleek and stylish models to more affordable options from traditional car manufacturers, electric cars are becoming increasingly accessible and popular. The shift towards electric vehicles represents a significant milestone in the automotive industry, with more and more drivers making the switch for environmental, economic, and practical reasons.
As we continue to see further developments in battery technology and charging infrastructure, it will be interesting to see how the evolution of electric cars continues to unfold.
Early Attempts
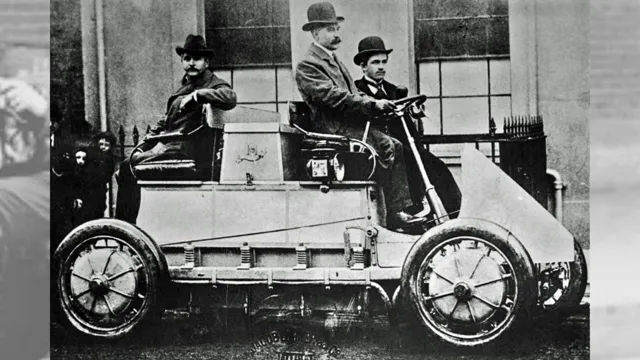
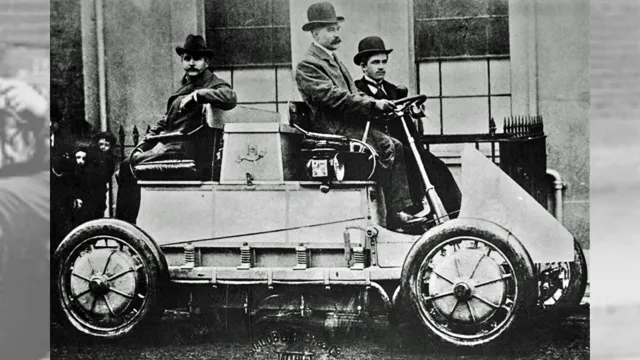
In the early days of electric car history, people had high hopes that electric-powered vehicles would soon replace gasoline-powered cars. However, the early attempts at creating electric cars were not very successful. The first fully electric car was created in 1837 by a Scottish inventor named Robert Anderson.
At the time, the technology was limited and the car could only travel short distances at low speeds, making it impractical for most people. Over the next few decades, various inventors tried to improve upon electric car technology but faced many challenges. One of the biggest obstacles was the lack of a reliable battery.
Batteries were large, heavy, and expensive, and could not store enough energy to power a car for very long. As a result, gasoline engines became the dominant technology for cars, and electric cars were seen as a novelty rather than a serious mode of transportation.
Invention of the First Electric Car
The invention of the first electric car can be traced back to the early 1800s when attempts to create a viable electric vehicle were first made. However, these early attempts were met with limited success due to the lack of infrastructure required to power them. Fast forward to the late 1800s and early 1900s, and major advancements were achieved as the quest for an all-electric automobile continued.
A pivotal breakthrough was made by Thomas Parker, a British inventor, who developed a practical electric car in 188 Although it was not a mass-produced model, Parker’s invention paved the way for the first electric car that was commercially available to the public. The importance of Parker’s invention cannot be understated as it marked the beginning of a new era for electric vehicles, a movement that continues to this day.
Electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular as people become more environmentally conscious. With zero emissions and fuel economy benefits, it is no surprise that more people are turning to electric cars as a viable mode of transportation. Nonetheless, it is worth noting that this trend is not new and is rooted in the early attempts to create the first electric car.
Without the groundbreaking work of inventors such as Thomas Parker, it would not have been possible to develop the all-electric vehicles we have today. As we continue to move forward, it is important to remember the pioneers who paved the way for this exciting and sustainable technology.

Development of Electric Cars in the 19th Century
In the 19th century, some of the earliest attempts at developing an electric car were made. Inventors like Thomas Davenport and Robert Anderson started experimenting with electrical power as a propulsion source for their vehicles. In the 1830s, Davenport built a small electric car that ran on a circular track.
Anderson, on the other hand, developed a crude carriage that was powered by a crude electric motor. Unfortunately, the batteries of the time were not capable of providing a consistent source of power for extended distances. As a result, electric cars remained a novelty and did not gain widespread attention.
Regardless, the early attempts at developing electric cars laid the foundation for the development of modern electric vehicles that are more efficient, affordable and environmentally friendly.
The Rise and Fall of Electric Cars
Electric car history is a fascinating subject that dates back to the early 19th century. The first electric cars were built in the mid-19th century, but it wasn’t until the early 20th century that they became more widespread. However, the rise of oil-powered cars and advancements in internal combustion engines saw the decline of electric cars, and by the 1930s, they were all but obsolete.
It wasn’t until the oil crisis in the 1970s that electric cars once again came into the limelight. However, it wasn’t until the 21st century that electric cars became more popular, with the introduction of the Toyota Prius and Tesla’s Model S. Today, electric cars are becoming more common, and with advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure, they are set to become the future of transportation.
The history of electric cars is a reminder that the rise and fall of technologies is often cyclical, and what was once thought to be obsolete can make a comeback in a big way.
Popularity of Electric Cars in the Early 20th Century
In the early 20th century, electric cars were all the rage. They were quiet, clean, and easy to operate, making them a popular choice for city drivers. But their popularity was short-lived.
As gasoline-powered cars became more affordable and easier to produce, electric cars just couldn’t compete. The invention of the electric starter motor also made gasoline cars more practical for everyday use. By the 1920s, most electric car manufacturers had gone out of business, and gasoline cars became the dominant form of transportation.
It’s a shame, really, because electric cars had the potential to revolutionize the automobile industry. Today, however, we’re seeing a resurgence in electric cars with the development of better battery technology and more charging infrastructure. Who knows? Maybe one day, electric cars will be just as popular as they once were.
Challenges and Decline of Electric Cars
The rise of electric cars was once seen as the future of sustainable transportation. In recent years, however, there have been numerous challenges that have led to a decline in their popularity. One of the main obstacles is the high cost of the technology and materials used in building electric vehicles.
This makes them significantly more expensive than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, which has deterred many consumers from making the switch. Another challenge is the limited range of travel that electric cars offer, with most models only able to travel a few hundred miles on a single charge. Additionally, the lack of charging infrastructure and the time it takes to charge the car has also proven to be a major inconvenience for many drivers.
These combined challenges have led to a decline in the popularity of electric vehicles. However, there is still hope for their resurgence. As technology continues to advance, we may see more affordable, efficient and longer-range models being developed, and as more charging stations are built, the inconvenience of charging may become a thing of the past.
The question remains, can electric cars rise to the challenge and become the future of transportation? Only time will tell.
Revival of Electric Cars in the 21st Century
The revival of electric cars in the 21st century marks a significant shift from the rise and fall of electric cars in the past. Back in the early days of automobiles, electric cars were actually more popular than gasoline-powered cars. However, the invention of the internal combustion engine and the discovery of enormous oil reserves led to a decline in the electric car industry.
Fast forward to the 21st century, and the demand for electric cars has risen again due to concerns about climate change and the desire for more sustainable transportation options. With advances in technology, electric cars have become more efficient and affordable, making them a viable alternative to traditional gas-powered cars. As more and more people become conscious of their carbon footprint, the electric car industry is predicted to continue its upward trend towards mainstream adoption.
Electric Cars Today
Electric cars have been around for over a century, although they have only recently regained popularity with advancements in technology and the need for eco-friendly transportation. The history of electric cars can be traced back to the 1830s, when inventors began experimenting with electric-powered vehicles. One of the earliest examples was the Baker Electric, which was released in 1899 and gained popularity among wealthy consumers due to its smooth and quiet ride.
However, the invention of the internal combustion engine soon led to the decline of electric cars as they were seen as less practical and more expensive. It wasn’t until the 1970s oil crisis that electric cars were once again seen as a viable alternative to gas-powered vehicles. Today, electric cars are becoming more mainstream with the introduction of hybrid and fully electric models from major car manufacturers.
Despite initial concerns over range anxiety and charging infrastructure, the increasing adoption of electric cars highlights a shift towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Electric Cars in the Global Market
Electric Cars Today Electric cars have become increasingly popular in the global market. People are becoming more aware of the environmental impacts of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles and are opting for electric cars instead. Today, there are a variety of electric cars available, from luxurious Tesla models to budget-friendly options like the Nissan Leaf.
These cars are powered by rechargeable batteries and have zero emissions during use. In addition to being better for the environment, electric cars also offer drivers a smooth and quiet ride. Although there are currently some limitations with range and charging infrastructure, the increasing availability and affordability of electric cars is making them a more viable option for many people.
As countries around the world continue to incentivize electric car adoption, we can expect to see even more growth in the marketplace.
Technological Advances and Innovation in Electric Cars
Today, electric cars have revolutionized the automobile industry, thanks to technological advances and innovation. Electric cars have rapidly gained popularity in recent years, and they are becoming increasingly affordable as more brands continue to manufacture them. These cars are powered by rechargeable batteries and emit no harmful pollutants, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuel cars.
With the advancement of electric car technology, the issue of range anxiety has been addressed by the development of batteries with increased capacity and the establishment of a wide charging network. Furthermore, innovations such as regenerative braking, a system that allows the car to generate energy while braking, have extended the driving range of electric cars. Taking into account their eco-friendliness, affordability, and technological advancements, there is no question that electric cars are the future of the automobile industry.
The Future of Electric Cars
The history of electric cars stretches back over a century, with the first electric car being developed in the late 1800s. However, it wasn’t until the mid-2000s that electric cars began to gain mainstream attention. Today, electric cars are more popular than ever, thanks to advancements in technology that have made them more practical, affordable, and accessible.
The future of electric cars is bright, with many car manufacturers and governments around the world investing in the development and promotion of electric cars. As battery technology continues to improve, we can expect electric cars to offer longer ranges and faster charging times. Additionally, as more people switch to electric cars, we can expect to see an increase in the development of charging infrastructure, making it easier for drivers to recharge their vehicles on-the-go.
With all these developments, it’s clear that electric cars will play a significant role in shaping the future of transportation.
Conclusion
Throughout the course of history, there have been many breakthroughs in technology that have revolutionized the way we live our lives. The invention of the electric car is no exception. It represents a turning point in our efforts to reduce our impact on the environment and secure a sustainable future for generations to come.
From the early pioneers of electric vehicles to the modern-day models that are taking over roads worldwide, electric cars represent the ultimate fusion of innovation, technology, and environmental responsibility. In short, the electric car is not only a symbol of progress but also a beacon of hope for a brighter, cleaner, and more sustainable tomorrow.”
FAQs
When was the first electric car invented?
The first electric car was invented in 1837 by Scottish chemist Robert Davidson.
What was the range of early electric cars?
Early electric cars had a range of around 30-40 miles on a single charge.
What caused the decline of electric cars in the early 20th century?
The introduction of the Ford Model T in 1908, which was much more affordable and had greater range than electric cars, caused the decline of electric cars in the early 20th century.
When did interest in electric cars start to re-emerge?
Interest in electric cars started to re-emerge in the 1990s, particularly in response to concerns about pollution and climate change.
What are some notable developments in electric car technology in recent years?
Notable developments in electric car technology in recent years include increased range, faster charging times, and the introduction of self-driving features.