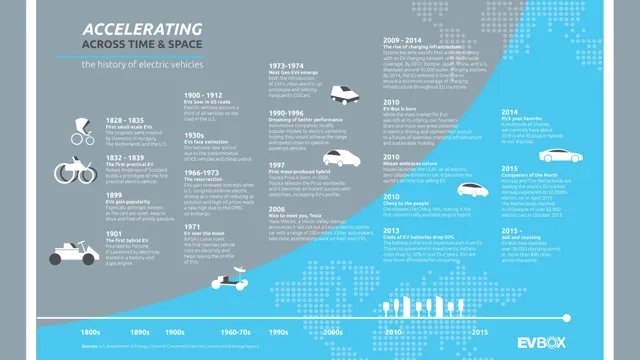
From the First Electric Car to the Road of the Future: A Timeline of Electric Car History
Are you curious about the history of electric cars? Well, you’re in the right place! Over the past few decades, electric vehicles have become increasingly popular due to their environmental benefits and technological advancements. However, electric cars have been around for much longer than you may think, dating back all the way to the early 1800s. In this blog post, we will take a journey through the electric car’s evolution from its humble beginnings to the modern-day models we see on the roads today.
We’ll explore the important milestones and advancements in technology that have led to the electric car’s current state and examine how electric cars continue to revolutionize the automotive industry. What factors influenced the development of electric vehicles, and why did they fall out of favor in the early 20th century? What led to their resurgence in popularity and widespread adoption in the 21st century? With new electric models from major manufacturers such as Tesla, Chevrolet, and Nissan, the current landscape of electric cars is exciting and dynamic. Overall, the history of electric cars is a fascinating tale of innovation, perseverance, and adaptation.
So, buckle up and join us on this journey through the electric car’s timeline!
Early Developments
The history of electric cars dates back to the late 1800s, with early developments made by pioneers such as Thomas Davenport and Robert Anderson. In fact, the first electric car was built in 1837 by a chemist named Robert Davidson. However, it wasn’t until the late 19th century that electric cars gained popularity, with companies such as La Jamais Contente producing electric vehicles that could reach speeds of up to 68 miles per hour.
Electric cars were especially popular in cities, as their clean and quiet operation made them an ideal choice for urban transportation. Despite this early success, electric cars fell out of favor in the early 20th century due to the development of gasoline engines and the discovery of large oil reserves. Nevertheless, the passion for electric cars never completely died out, and it continued to evolve and develop through the exploration of new technologies and advancements in battery power.
Today, electric cars are experiencing a new wave of interest and enthusiasm, with many companies investing in research and development to create more efficient and eco-friendly vehicles.
1832-First electric-powered vehicle
The year was 1832, and the world saw the debut of the first electric-powered vehicle. It was created by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson, who attached an electric motor to a carriage. However, this invention was not practical for everyday use, as the battery required frequent recharging.
Despite its limitations, Anderson’s invention marked the beginning of a new era in transportation. The development of electric cars continued at a slow pace over the next century, with various inventors contributing to the field. By the end of the 19th century, electric cars were competing with gasoline cars in popularity.
It was not until the early 20th century that gasoline-powered cars became the preferred mode of transportation, largely due to the availability of cheap gasoline. Nevertheless, electric cars continued to evolve, and by the 21st century, technological advancements have brought them back into the limelight. Today, electric cars are seen as a cleaner, more efficient, and sustainable alternative to gasoline-powered cars.
The potential for electric-powered transportation in the future is limitless, and we have Robert Anderson to thank for taking the first step towards this revolution.

1881-Electric bicycles
In 1881, the first electric bicycle was developed, and it marked a significant milestone in the history of transportation. This early development sparked an interest in electric bikes, and many inventors started experimenting with various designs. At the time, electric bike batteries were heavy, and the motors were relatively underpowered.
Nevertheless, electric bikes were seen as practical alternatives to traditional bicycles, especially for those who needed to cover long distances. These bikes could be charged overnight and were capable of speeds up to 15 mph. Over the years, the technology behind electric bikes has improved significantly, making them faster, more powerful, and more efficient.
Today, electric bikes are widely used worldwide, and they are considered to be practical and eco-friendly modes of transportation.
First Mass-Produced Electric Vehicles
Electric cars have been around since the 1800s, but they weren’t mass-produced until the late 2000s. The first electric car to be mass-produced was the General Motors EV1 in 199 It was produced for only six years, with the last one being produced in 200
Despite its controversial ending, many people loved the EV1 and were heartbroken when it was discontinued. After the EV1 was discontinued, the Toyota Prius became the most popular hybrid car. The Prius made its debut in Japan in 1997 and became available worldwide in 200
It wasn’t until the Nissan Leaf was introduced in 2010 that the world saw the first mass-produced fully electric car that could be charged at home. The Leaf quickly became popular and has sold over 500,000 units to date. Today, there are many more mass-produced electric cars on the market, making it easier for people to make the switch to electric and help reduce carbon emissions.
1900-1910 Electric cars popular in US & Europe
As the turn of the century approached, electric cars garnered more popularity in both the United States and Europe. This timeframe saw the introduction of the first mass-produced electric vehicles, such as the Columbia Electric Runabout and the Baker Electric. These cars were seen as a luxury item, with many wealthy individuals opting for them for their quiet and smooth ride, as well as their lack of fumes and engine noise.
However, the cost of production and limited battery life proved to be obstacles to mass adoption. Despite this, electric cars were still seen as a promising alternative to gas-powered vehicles, with various electric car companies popping up during this time. While electric cars may have been overshadowed by the rise of the internal combustion engine, the groundwork laid during this period set the foundation for the future of electric vehicle technology.
1912- First car introduced by Cadillac
In 1912, Cadillac introduced its first car, a gasoline-powered luxury vehicle. However, fast forward to present day, and electric vehicles have become a major player in the automotive industry. The first mass-produced electric vehicle was created in 1996 by General Motors; it was called the EV
Unfortunately, the EV1 was discontinued in 2003 due to production costs and lack of consumer interest. But times have changed, and electric vehicles have now become a viable and trendy alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. With advancements in technology, electric vehicles are now capable of driving longer distances, charging more quickly, and offering a multitude of options for consumers.
The keyword here is “electric vehicles,” and they are a force to be reckoned with in the automotive industry. As more and more people become conscious of their carbon footprint, electric vehicles are becoming a popular choice. They offer a cleaner, greener, and quieter way to travel without sacrificing on performance or style.
Decline and Resurgence
The history of electric cars is one of decline and resurgence. The first electric car was invented in the 1830s, but it wasn’t until the late 19th century that they gained popularity. However, with the introduction of the gasoline-powered car in the early 1900s, electric cars began to decline in popularity.
By the 1920s, gasoline-powered cars had all but replaced electric cars on the market. But in recent years, electric cars have made a comeback. With concerns over climate change and the desire for more sustainable transportation, people have turned to electric cars as an alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles.
In addition, advancements in technology have made electric cars more practical and efficient than ever before. Tesla, for example, has led the way in developing high-performance electric cars that can compete with traditional sports cars. Today, electric cars are becoming more and more popular, with major car manufacturers such as BMW, Ford, and Volkswagen all introducing electric models to their lineups.
Governments around the world are also incentivizing the transition to electric cars by providing tax breaks and other benefits. As technology continues to improve and concerns over climate change grow, it’s likely that electric cars will continue to become more prevalent on our roads in the years to come.
1920s- Internal combustion engine dominated market
The 1920s were dominated by the internal combustion engine, which was revolutionizing the transportation industry. Cars and trucks powered by gasoline were becoming more popular, and it seemed like the future would belong to this new technology. However, as time went on, the limitations and drawbacks of these engines began to become clear.
They were inefficient, created too much pollution, and were often too expensive for the average person to afford. As a result, interest in alternative forms of transportation began to grow. In recent years, there has been a resurgence in electric and hybrid vehicles, as well as other forms of alternative transportation like bicycles and scooters.
While the internal combustion engine is still in use, it is clear that the future belongs to these newer, more sustainable technologies. With the right investments and incentives, we can create a transportation system that is more efficient, less polluting, and more affordable for everyone.
1990s- EVs make a comeback with California mandate
In the late 1990s, electric vehicles made their comeback with the California mandate. This landmark legislation required automakers to produce cleaner cars, including electric vehicles, in order to meet California’s strict air pollution standards. The mandate was seen as a major turning point for electric vehicles, as it sparked renewed interest in EV technology and spurred automakers to invest in research and development.
Though early electric vehicles faced some challenges, such as limited range and high costs, the resurgence of EVs in the 1990s set the stage for their eventual mass adoption in the 21st century. Today, electric vehicles are seen as a key part of the transition to a more sustainable transportation system, and they continue to gain popularity among consumers and policymakers alike.
Modern Era of Electric Cars
The modern era of electric cars has come a long way since the early prototypes in the 19th century. The first successful production electric car was created by Thomas Davenport in 183 However, the widespread use of gasoline-powered cars and the discovery of large oil reserves in the early 20th century halted the development of electric cars.
It wasn’t until the 1990s that the rebirth of electric cars began. General Motors produced the EV1, while Toyota developed the Prius and Honda developed the Insight. Fast forward to today, there is a plethora of electric cars available on the market, from Tesla Model 3 to Nissan Leaf, and advancements in technology continue to improve the driving range and charging times.
The future is looking bright for electric cars, and it’s exciting to see how they will continue to evolve and revolutionize the automotive industry.
2008- Tesla Roadster debuts
The year 2008 marked the beginning of a new era for electric cars when Tesla unveiled their Roadster model. This car made a real statement in the market, as it was not only beautiful but also incredibly efficient and fast. The Roadster had a range of over 200 miles per charge and could reach a top speed of 125 mph.
It was a game-changer that made people rethink what electric cars were capable of. With the Roadster’s success, Tesla became a leader in the electric vehicle industry and paved the way for other manufacturers to follow suit. The Roadster’s debut also marked the end of the electric car’s early days, where they were seen as slow, unappealing, and impractical.
The Roadster’s arrival ushered in a new era of electric cars that was stylish, efficient, and thrilling to drive. Thanks to Tesla’s innovation, people were introduced to the modern era of electric cars and haven’t looked back since.
2010s- Major automakers bring EVs to market
The modern era of electric cars began in the 2010s, when major automakers such as Nissan, Tesla, and Chevrolet brought EVs to market. These cars, powered solely by electricity, promised an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. While some consumers were hesitant to switch due to concerns about battery range and charging infrastructure, others embraced the technology and the potential for savings on fuel costs.
As the decade progressed, more automakers joined the EV market and continued to improve on battery technology, driving ranges, and charging capabilities. Today, electric cars continue to gain popularity and are seen as a viable solution for reducing emissions and combating climate change. Despite some challenges, the modern era of electric cars has undoubtedly brought the industry forward in terms of sustainability and innovation.
Conclusion
Through the ups and downs, twists and turns of electric car technology, one thing is clear: the electric car is here to stay. From the early days of short-range vehicles to today’s sleek, high-performance models, the electric car has proven its viability and potential to revolutionize the way we travel. As we continue to push the boundaries of technology, the electric car will undoubtedly evolve and improve, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future.
So buckle up, charge your batteries, and get ready for the ride of your life – the electric car revolution is underway!”
FAQs
What is the timeline of electric cars’ history?
Electric cars were invented in the 1830s, with the first practical electric car built in 1884. However, they only became commercially available in the 2000s, with the release of the Toyota Prius and Tesla Roadster.
Who invented the first electric car?
Scottish inventor Robert Anderson is credited with creating the first crude electric carriage in 1832, while Thomas Davenport invented the first American electric car in 1835.
When did electric cars gain popularity?
Electric cars were popular in the early 20th century, when they made up a third of all cars on the road in the United States. However, the invention of the internal combustion engine made gas-powered cars cheaper and more convenient, leading to a decline in electric car popularity until recent years.
How have government regulations impacted the growth of electric cars?
In recent years, government regulations and incentives have been put in place to encourage the growth of electric cars, such as tax credits for electric car owners and mandates for car companies to produce a certain number of electric cars. This has led to increased production and popularity of electric cars.