Revolutionizing Transportation: A Historic Journey through the Evolution of Electric Cars
Electric cars have been around for longer than most people realize. While they have become increasingly popular in recent years, the history of electric cars dates back to the early 19th century. In the early days of the automobile, electric vehicles were actually more popular than their petrol-powered counterparts.
But as gasoline became cheaper and easier to obtain, electric cars fell out of favor. It wasn’t until the late 20th century that electric cars began to make a comeback as people became more concerned about the environment and the impact of gasoline-powered cars on the planet. Join us as we take a look back at the history of electric cars, from their early beginnings to the modern electric cars of today.
Early Beginnings
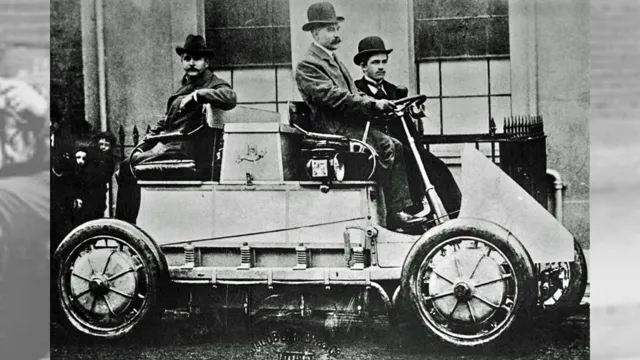
Electric cars have been around since the late 1800s, with the first known electric car built in the 1830s by a Scottish inventor. However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that electric cars gained popularity. In fact, at the turn of the century, electric cars made up around one-third of all cars on the road in the United States.
Back then, electric cars were known for their reliability, ease of use, and lack of noise and pollution. They were especially popular among women, who found them easier to operate than gas-powered cars. However, their popularity declined with the introduction of the Ford Model T in 1908, which was affordable and had a longer range than most electric cars of the time.
Despite the decline in popularity, electric cars have been sold throughout history, and their evolution continues today.
Late 19th Century Inventions
The late 19th century was a period marked by a plethora of inventions which altered the course of human history in a significant way. These inventions changed the way we communicate, travel, and live our daily lives, leading to the development of modern civilization. The early beginnings of this period were characterized by a sense of innovation and a fascination with experimenting with new technologies.
Some of the most significant inventions of this era include the electric light bulb, the telephone, and the phonograph. The electric light bulb, invented by Thomas Edison in 1879, transformed the way we think about indoor lighting and provided a cost-effective alternative to gas lamps. Similarly, the telephone, invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876, revolutionized the way we communicate and paved the way for the development of modern telecommunication systems.
Lastly, the phonograph, invented by Thomas Edison in 1877, allowed people to listen to recorded sound for the first time and changed the way we consume music and other forms of audio entertainment. These early inventions were just the beginning of a period of unprecedented innovation and technological advancement that would transform human society in countless ways.

First Commercially Available Electric Car
The early beginnings of electric cars date back to the mid-1800s when inventors began experimenting with battery-powered vehicles. Many of these early models were impractical and expensive, but they paved the way for the first commercially available electric car. In 1897, the Electric Vehicle Company in Hartford, Connecticut, developed the Columbia Electric Car, which was the first electric vehicle to be mass-produced and sold to the public.
The Columbia Electric was a simple, sturdy car with a range of about 40 miles, making it perfect for local travel. It was primarily used by doctors, businessmen, and women, who appreciated its quiet operation and easy maneuverability. While the Columbia Electric was not a commercial success due to its high price, it set the stage for future innovations and sparked interest in electric cars among the public.
Today, over a century later, electric cars have come a long way, and major automakers offer a variety of electric vehicles that are both cost-effective and practical for everyday use.
Mid-20th Century
Electric cars have been around for a lot longer than many people realize, with a significant number sold during the mid-20th century. In fact, electric vehicles were quite popular in the 1950s and 60s, particularly in Europe and the United States. Automakers like Renault, Citroën, and Messerschmitt produced a range of electric vehicles during this period, including small city cars, utility vehicles, and even some sporty models.
However, the market for electric vehicles started to decline in the 1970s due to factors such as low gas prices and the rise of more advanced gasoline-powered vehicles. Despite this downturn, some automakers continued to produce short-range electric cars throughout the 1980s and 90s, with models such as the Volkswagen Golf Citystromer and the GM EV1 gaining a small following.
Post-WWII Decline in Electric Cars
After the end of World War II, there was a significant decline in the popularity of electric cars. One of the reasons was the abundance of cheap gasoline, which made internal combustion engine vehicles much cheaper to operate. Additionally, new highways were being built, which allowed for faster and more efficient travel, making electric cars appear sluggish in comparison.
As a result, major car manufacturers shifted their focus to gasoline-powered vehicles, ultimately leading to the near extinction of electric cars. However, with recent advances in battery technology and growing concerns about the environmental impact of gasoline-powered vehicles, electric cars are now back on the rise, prompting car manufacturers to adapt to the changing market and invest in electric vehicle production. It’s incredible to think about how far we’ve come in our understanding of energy and the environment since the mid-20th century.
1970s Electric Car Revival
In the mid-20th century, electric cars were experiencing a revival in popularity, particularly in the 1970s. With growing concerns over air pollution and the volatility of oil prices, many people saw electric cars as a viable solution. In fact, major automakers like GM and Ford began developing electric car prototypes during this time.
However, the electric car craze was short-lived as oil prices stabilized and environmental concerns took a backseat to other issues. It wasn’t until the early 2000s, with the introduction of the Toyota Prius and the Tesla Roadster, that electric cars really began to gain mainstream acceptance once again. Nevertheless, the 1970s were an important turning point in the history of the electric car, laying the groundwork for the electric vehicle revolution that we’re experiencing today.
GM’s EV1 and California’s Zero Emissions Mandate
In the mid-20th century, the state of California passed a revolutionary mandate requiring car manufacturers to produce a certain percentage of zero-emissions vehicles. This created a flurry of excitement as automakers scrambled to come up with innovative solutions to meet the mandate. General Motors was one such company, and in response to the mandate, they introduced the EV1 – an all-electric vehicle.
At the time, the EV1 was groundbreaking technology and was seen as the future of the car industry. The car was sleek, stylish, and remarkably efficient, and early adopters flocked to it. However, despite its popularity, the EV1’s lifespan was short-lived.
In the early 2000s, General Motors discontinued the production of the EV1, much to the dismay of its fans. Despite the success of the EV1, the state of California eventually relaxed its zero-emissions mandate, thereby eliminating the need for car manufacturers to produce electric vehicles. The demise of the EV1 was a significant blow to the electric car movement, but it did lay the foundation for the technologies that would eventually lead to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Recent Years
Electric cars have been around since the late 1800s, but it wasn’t until recent years that they gained popularity among consumers. The first surge in electric car sales occurred in the early 2010s, with the introduction of the Nissan Leaf and the Tesla Roadster. However, it wasn’t until Tesla released the Model S in 2012 that electric cars truly began to take off.
In the years that followed, other automakers began to release their own electric vehicles, such as the Chevrolet Volt and the BMW i While the number of electric cars sold each year is still a small fraction of total car sales, the trend towards electric vehicles is expected to continue as technology improves and charging infrastructure becomes more widespread. As of 2021, electric cars make up just over 2% of the total cars sold worldwide, but this number is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years.
Tesla’s Impact on the Electric Car Market
In recent years, Tesla has been a driving force in the electric car market. Their innovative technology and sleek designs have helped to change the perception of electric vehicles from being practical but boring to high-performance and desirable. With their Model S, Model X, and Model 3, Tesla has been able to bring electric cars to the mainstream market, making them a viable option for everyday drivers.
In addition to their impressive range and acceleration, Tesla’s cars are also equipped with advanced safety features and autonomous capabilities, making them some of the safest vehicles on the road. As a result, Tesla has quickly become one of the most prominent players in the electric car market, with other manufacturers racing to catch up with their technology and design.
Government Incentives and Renewed Interest in Electric Cars
In recent years, there has been renewed interest in electric cars, thanks in part to government incentives. Governments around the world have been offering a wide range of incentives to encourage consumers to buy and use electric cars. These incentives include tax credits, subsidies, and rebates, as well as access to carpool lanes and free parking.
As a result of these incentives, more and more people are considering switching to electric cars. This is good news not just for the environment but for the economy as well. Electric cars are more energy-efficient and cost-effective than gasoline-powered cars, which means they can help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and save us money in the long run.
It’s no wonder then that more and more people are taking advantage of these incentives and making the switch to electric cars.
The Future of Electric Cars
Electric cars have come a long way since the first one was sold in the late 1800s. In fact, electric cars were quite popular in the early 20th century, with over 30,000 sold in the United States alone in 191 However, due to the popularity of gasoline-powered vehicles and the lack of technology to support electric cars, their popularity dwindled until the 1990s.
Today, electric cars are making a comeback, with sales reaching over 2 million worldwide in 201 As technology continues to develop, electric cars are becoming more practical and affordable for consumers, with longer battery ranges and faster charging times. The future of electric cars looks promising, with the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
With many countries implementing regulations for fuel efficiency and emissions, electric cars are likely to play a major role in the future of transportation.
Conclusion
As we look back on the history of electric cars, we can see that they have gone from being novelty items to becoming a serious contender in the world of transportation. While there have been highs and lows and plenty of ups and downs, it’s clear that electric cars are here to stay. They may not be able to compete with gasoline-powered vehicles in every area just yet, but with continued innovation and growing environmental concerns, it’s likely that we will see more and more electric cars on the roads in the years to come.
So whether you’re a die-hard electric car fan or simply interested in the future of transportation, one thing is for sure: the electric car revolution is just getting started.”
FAQs
How many electric cars have been sold since they were first introduced in the market?
According to the International Energy Agency, more than 3 million electric cars were sold globally in 2020, and over 10 million electric cars have been sold since they were introduced in the market.
Which country has the highest number of electric cars sold?
As of 2020, China has the highest number of electric cars sold, with over 4.5 million units sold, followed by Europe with over 1.4 million units sold.
How has the sales of electric cars evolved over the years?
Electric cars have seen a gradual increase in sales since they were first introduced in the market, with a notable surge in sales in the past decade due to increased awareness and government incentives for clean energy. In 2010, only about 17,000 electric cars were sold globally, while more than 3 million electric cars were sold globally in 2020.
What is the future outlook for electric car sales?
The future outlook for electric car sales is optimistic, with many countries pledging to transition to clean energy and reduce their carbon emissions. The International Energy Agency predicts that by 2030, there will be over 145 million electric cars on the road globally.