Revolutionizing the Roads: Tracing the History of Electric Cars
Electric cars have become increasingly popular in recent years, with more and more drivers embracing the benefits of eco-friendly vehicles. But did you know that electric cars have been around for over a century? In fact, the very first electric car was built in the late 1880s, predating the gasoline-powered automobile. Since then, electric cars have gone through periods of both popularity and obscurity.
Today, as concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability grow, electric cars are once again at the forefront of the automotive industry. In this blog post, we’ll take a brief look at the history of electric cars, tracing their development from their earliest days to the present day, and exploring the technological advances that have made these vehicles more efficient, affordable, and practical than ever before.
Early Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular in the modern day, but did you know that they actually have a history that dates back over 100 years? Early electric cars were first introduced in the 1830s, but it wasn’t until the late 1800s and early 1900s that they really made a splash. At the time, there were actually more electric cars on the road than gasoline-powered ones. This was due in part to the fact that they were considered cleaner and quieter, and they didn’t require the same amount of maintenance as their gas counterparts.
However, as road infrastructure improved and gas prices became more affordable, electric cars fell out of favor. It wasn’t until recent years that they came back into fashion, largely because of advancements in battery technology. Today, electricity cars are being hailed as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gas-guzzlers, and it’s exciting to see how the technology continues to evolve.
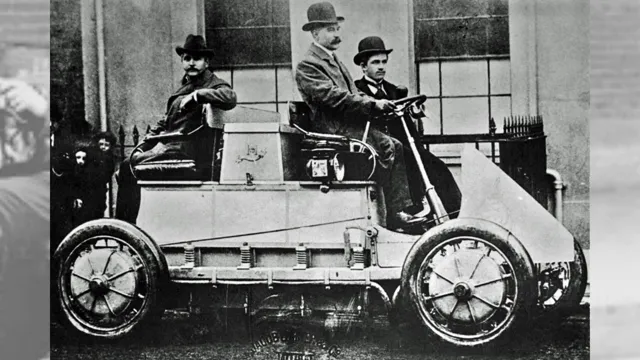
The Birth of the Electric Vehicle
Electric vehicles or EVs have been around for over a century, but many people are unaware of their early history. At the dawn of the 20th century, electric cars were more popular than gasoline-powered cars, as they were more reliable and easier to operate. In fact, the first recorded production electric vehicle was built by Thomas Davenport in 183
However, it wasn’t until the 1890s that electric cars began to compete with gasoline cars commercially. Several factors contributed to the rise of electric cars, including the development of rechargeable batteries and the growing concern over pollution caused by gasoline cars. One of the most popular electric vehicles of the time was the Detroit Electric, which was produced from 1907 to 193
It was an electric car designed for women that could travel up to 100 miles on a single charge. However, with the introduction of the Ford Model T in 1908, gasoline-powered cars became more affordable and accessible, which ultimately led to the decline of electric cars. Nevertheless, the early history of electric vehicles laid the foundation for the modern EVs, which are gaining popularity worldwide due to their efficiency and eco-friendliness.

Electric Cars in the Early 1900s
Electric cars have been around since the early 1900s, during a time when gasoline-powered vehicles were gaining popularity. However, electric cars had some advantages back then that are still relevant today. They were quiet and less polluting than gas-powered cars, which made them a popular choice for urban areas.
But their limited range and slow speed were major drawbacks. Despite these shortcomings, electric cars continued to be developed, with some models reaching top speeds of 40 miles per hour. Unfortunately, the high cost of batteries and the discovery of large reserves of oil made gas-powered cars more affordable and practical, leading to the eventual decline of electric cars.
However, with the growing concern for the environment and the advancements in battery technology, electric cars are now making a comeback and are becoming more mainstream than ever before.
Decline of Electric Cars
Electric cars may seem like the wave of the future, but they actually have a long and tumultuous history. The first electric cars were introduced in the early 1900s and were quite popular, especially in cities where gasoline engines were seen as too noisy and polluting. However, as the price of gasoline dropped and the ease of supplying it increased, electric cars fell out of favor.
It wasn’t until the 1970s, during the oil crisis, that electric cars saw a resurgence in popularity. Unfortunately, this too was short-lived as advances in combustion engine technology once again made gasoline cars the preferred choice. It wasn’t until the turn of the 21st century, with the advent of lithium-ion batteries and increased public awareness of environmental issues, that electric cars began to make a comeback.
While they still make up a small fraction of cars on the road today, electric cars are growing in popularity and may soon become the norm rather than the exception. Despite the long journey of electric cars, strides are continuously made to refine their capabilities and ensure they are a viable option for the future.
Emergence of Gasoline Cars
Gasoline cars have been dominating the automobile industry since they first emerged, but it wasn’t always like that. Back in the early 1900s, electric cars were becoming increasingly popular due to their quiet operation and lack of emissions. However, the decline of electric cars can be traced back to several factors.
One such factor was the discovery of large oil reserves in Texas and the decrease in gas prices that followed, making gasoline more affordable for the average consumer. Additionally, the limited battery capacity of electric cars made them impractical for long-distance travel, while gasoline cars offered greater range and convenience. Finally, the introduction of the electric starter in gasoline cars eliminated the need for hand cranking, a dangerous and unpleasant task that had previously been associated with driving.
As a result, gasoline cars became the norm, and electric cars were relegated to niche markets for decades to come. Nonetheless, with the increasing concerns over climate change and the development of new technologies, electric cars are now making a comeback as a viable alternative to gasoline cars.
Obstacles Faced by Electric Cars
Electric cars have faced several obstacles over the years, causing a decline in their popularity. One significant issue is that the charging infrastructure is not yet fully developed. While more charging stations are popping up around the country, they’re still not as abundant as gas stations.
This can cause anxiety in drivers who worry about running out of charge and being stuck on the side of the road. Along with that, the prices of electric cars are still high, despite incentives offered by some states. This can be a deterrent to those who are looking for a more affordable alternative to gas-powered vehicles.
Additionally, the range of electric cars has been limited, meaning drivers may need to plan their trips more carefully and stop for charging breaks more often. Overall, while electric cars have many benefits, there are still several obstacles to overcome before they become widespread on our roads.
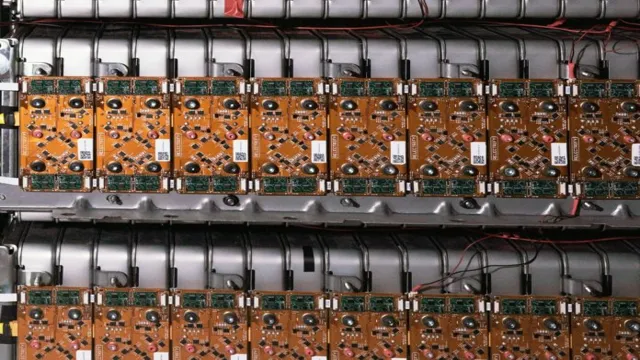
Development of Better Batteries and EV Innovations
The development of better batteries and EV innovations has been a hot topic in recent years as experts try to find solutions to the battery drain problem facing electric cars. Unfortunately, the decline of electric cars has been seen in the market due to several factors including slow charging times, range anxiety, high prices, and lack of proper infrastructure. This has made it a challenge for automakers and EV enthusiasts alike to promote the technology and increase adoption rates in the market.
However, there is still hope and optimism in the industry as the development of new batteries with more energy density and faster charging abilities offers a glimpse of what’s possible in the future of electric cars. Additionally, continued EV innovations such as the concept of wireless charging, autonomous driving, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology are also promising and could lead to a transformation in the way we use and interact with our cars. With all these advancements, the electric car market is sure to rise, and we can expect to see more electric cars on our roads in the years to come.
Revival of Electric Cars
Electricity cars history is a fascinating topic to explore. Did you know that the first electric car was built in 1832, long before the gasoline-powered car? However, it wasn’t until the 1990s that electric cars started to gain popularity, with General Motors releasing the EV1 in 199 Unfortunately, due to a variety of reasons, including lack of infrastructure, expensive battery technology, and minimal government support, the electric car market struggled for many years.
However, in recent years, we have seen a revival of electric cars, with Tesla leading the charge with their sleek and innovative designs. With the rise of environmental awareness, more and more people are turning to electric cars as a way to reduce their carbon footprint. There are more options than ever before, from traditional automakers like Ford and GM to newer companies like Rivian and Lucid.
It’s an exciting time in the electricity cars history, and it will be interesting to see how the market continues to develop in the coming years.
Modern Electric Cars
Electric cars have undergone a remarkable transformation in recent years, becoming a popular and practical choice for drivers worldwide. The revival of electric cars has seen a move away from the stereotype of the early models, which were often seen as impractical and unreliable. Today’s electric cars offer a range of benefits, including lower fuel costs, reduced environmental impact, and cutting-edge technology.
These cars are becoming increasingly accessible, with a growing number of models on the market, and major advances in battery technology driving further improvements in performance and driving range. With a renewed focus on sustainability, concerns over climate change, and increasing investment in the development of electric cars, it seems clear that this trend is only set to continue. As we look to the future, it’s exciting to imagine what the next generation of electric cars will look and feel like.
Impact of Electric Cars on the Environment and the Economy
Electric cars have been making waves in the automobile industry, promising a cleaner and more sustainable future. With the rise of electric cars, there has been a revival of the automotive industry, especially in the production of battery-powered vehicles. This shift to electric cars has a significant impact on both the environment and economy.
Environmentally, electric cars produce far fewer emissions than gasoline-fueled cars, leading to lower air pollution and a reduction in greenhouse gases. This is a significant step in the fight against climate change. Economically, the electric car market has created new job opportunities, particularly in the manufacturing of batteries and other electric components.
It also reduces a country’s dependence on foreign oil imports, leading to a more stable and secure economy in the long run. The revival of electric cars is not just a trend; it is a necessary step towards a more sustainable and prosperous future.
Future of Electric Cars
Electric cars have been around since the 1800s, but it wasn’t until the past decade that their popularity skyrocketed. With concerns about air pollution and climate change, more and more people are turning to electricity cars, which emit fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants than traditional gas vehicles. The history of electricity cars has been marked by breakthroughs and setbacks, but advancements in technology and infrastructure have made them a more viable option for daily use.
As we look to the future of electric cars, we can expect to see continued innovation and improvements in battery capacity, charging speed, and range. Additionally, increased government incentives and support for electric vehicles will likely result in more widespread adoption. It’s an exciting time for the electric car industry, and we can’t wait to see what the future holds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of electric cars has been a rollercoaster ride of ups and downs. From their humble beginnings over a century ago to their current status as a viable alternative to traditional gas-guzzlers, electric cars have come a long way. While they were once viewed as the outcast of the automotive industry, they have now become the rockstars.
The transition hasn’t been easy, but with the advancements in technology and the shift towards renewable energy sources, the electric car is here to stay. So say goodbye to the gas pump and hello to the future of transportation – it’s electric!”
FAQs
What is the history of electric cars?
Electric cars have been around since the mid-19th century, with the first electric vehicle built in 1837. However, they were largely overtaken by gasoline-powered cars in the early 20th century until the 21st century, when there was renewed interest in electric cars due to concerns about climate change and air pollution.
What is an electric car?
An electric car is a vehicle that is powered by an electric motor, rather than a traditional gasoline engine. The power is supplied by a rechargeable battery, which can be charged by plugging the car into an electrical outlet or charging station.
What are the benefits of electric cars?
There are many benefits to electric cars, including that they produce zero emissions, are more energy-efficient than traditional gasoline cars, have lower operating costs, and can potentially reduce our dependence on foreign oil.
How long do electric car batteries last?
The lifespan of an electric car battery can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of the car, the type of battery used, and how often the car is driven and charged. Generally, most electric car batteries are expected to last between 8-10 years or around 100,000 miles.