The Untold Story of the First Electric Car in History: A Revolutionary Step Towards Sustainable Transportation
When we think of electric cars, we often think of new, modern vehicles that rely on the latest technology. However, the first electric car was actually invented in the late 1800s. That’s right, over 100 years ago, electric cars were already being developed and tested.
This may come as a surprise to some, but it’s a fascinating piece of automotive history that shouldn’t be overlooked. In this blog post, we’re going to delve into the topic of the first electric car and explore what it means for the future of transportation. So, buckle up and let’s take a trip down memory lane to learn about the origins of electric cars.
The Birth of the Electric Car
The first electric car in history was created in 1837 by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson. The vehicle was nicknamed the “electric carriage” and consisted of a crude battery-powered motor that powered the carriage forward. Although the vehicle had limited speed and distance capabilities, it marked a significant milestone in automotive history as the first documented instance of an electric-powered vehicle.
It would take a few more decades before the technology had advanced enough to mass-produce electric cars for the general public, but Anderson’s invention paved the way for future advancements in the field. Today, electric cars have become a popular and viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars, with major brands like Tesla and Nissan leading the charge in electric car production. As society continues to shift towards sustainable energy, it is clear that the birth of the electric car was just the beginning of a major technological revolution in transportation.
Early Developments and Inventions
The electric car was first developed in the early 19th century, and the first recorded invention of an electric vehicle is attributed to Scottish inventor Robert Anderson in the year 183 Anderson’s prototype comprised non-rechargeable cells that powered a simple electric motor. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric vehicles were introduced to the market for commercial use.
During that time, electric cars were the preferred choice among many wealthy individuals due to their clean and quiet operation. It wasn’t until the invention of the internal combustion engine that electric cars fell out of fashion, as gasoline-powered cars became easier and less expensive to produce. However, with the development of advanced battery technology, electric cars have made a strong comeback in recent years, with many predicting that they will soon become the dominant mode of transportation.
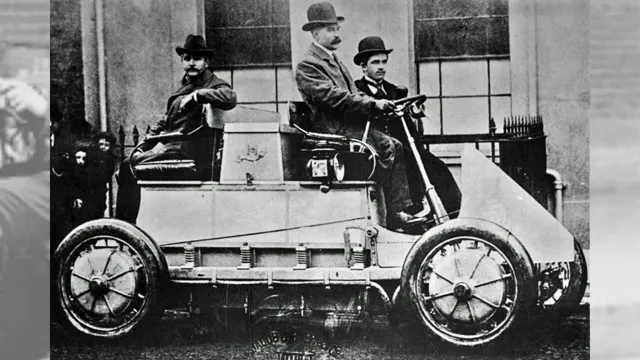
The First Practical Electric Car Invented
The birth of the electric car marked a significant milestone in the history of transportation. The first practical electric car was invented in 1884 by English inventor, Thomas Parker. The battery-powered vehicle was a tram, which could carry up to 62 passengers.
This revolutionary invention paved the way for the development of electric cars and automobiles. However, the electric car struggled to gain widespread acceptance due to the high cost of the batteries and the limited range of the vehicles. It was not until the 20th century that electric cars became more popular, especially with the rise of environmentalism and concerns about the negative impact of gasoline-powered vehicles on the environment.
Today, electric cars are becoming more accessible and affordable, and many people are turning to them as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional cars. The invention of the first practical electric car was the beginning of a journey towards a greener and more sustainable future.
Features of the First Electric Car
The first electric car in history was a remarkable feat of engineering. Invented by Thomas Davenport in 1835, it had a top speed of 4 miles per hour and could travel up to 25 miles on a single charge. The car was powered by a battery and had a simple design with four wheels and a wooden frame.
One of the key features of the first electric car was its silent operation, which was a stark contrast to the noisy steam-powered vehicles of the time. Although it was not a commercial success, the first electric car paved the way for future innovations in electric vehicles. Today’s electric cars have come a long way in terms of design, performance, and sustainability, but we owe it all to the groundbreaking work of Davenport and other pioneers in the field.
Battery Technology and Power Output
Battery technology has been evolving over the years, and with the advent of electric cars, it has had a significant impact on the industry. The first electric car, built in the late 19th century, was powered by a lead-acid battery, which proved to be cumbersome and inefficient. However, it laid the groundwork for future improvements, which led to the development of more advanced battery technologies.
Today, most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, which offer a higher power output and better energy density than lead-acid batteries. This means that modern electric vehicles have longer ranges and can travel at higher speeds than their predecessors. Moreover, lithium-ion batteries are lighter and smaller than lead-acid batteries, making them more suitable for use in cars.
Furthermore, advancements in battery technology have led to the creation of fast-charging stations, which can charge an electric car’s battery up to 80% in just 30 minutes. The first electric car was the pioneer in this field and paved the way for newer, better, and more efficient battery technologies that are being used today.
Range and Speed Limitations
When the first electric car was introduced, it boasted some impressive features such as being emission-free and employing regenerative braking technology. However, there were also some limitations that had to be addressed. One of the main concerns was the range of the vehicle.
The first electric cars were limited in the distance they could travel on a single charge, usually around 40-50 miles. This was a major obstacle, as people were used to the freedom and flexibility of gas-powered cars that could travel much farther before needing a refill. Another limitation was the speed.
The first electric cars were not capable of reaching high speeds, making them less appealing to consumers who enjoyed the thrill of driving a fast car. Despite these limitations, the first electric car was a major step forward in the development of electric vehicles, and paved the way for more efficient and powerful vehicles in the future.
Design and Styling
One of the key features of the first electric car is its design and styling. Unlike traditional cars, which relied heavily on combustion engines and bulky mechanics, electric cars offer a sleek and streamlined appearance. This is due in large part to the fact that electric cars require fewer components under the hood, which allows for more creative freedom when it comes to exterior design.
Many electric car manufacturers take advantage of this flexibility by incorporating elements like aerodynamic curves, futuristic headlights, and eco-friendly materials into their designs. This not only makes electric cars more visually appealing but also helps to increase their efficiency and reduce their environmental impact. So, whether you’re looking for a high-performance sports car or a more practical family vehicle, there’s an electric car out there that can meet your needs and match your personal style.
Impact on Society and the Auto Industry
The first electric car in history, invented in the late 19th century, had a significant impact on both society and the auto industry. At the time, electricity was a novelty, and the prospect of using it to power a vehicle was groundbreaking. The introduction of electric cars challenged the dominance of gasoline-powered vehicles and paved the way for cleaner transportation.
However, due to the high cost of batteries and limited driving range, electric cars quickly fell out of favor. Fast forward to today, and the electric car market is experiencing a resurgence, with efforts towards sustainability and reducing carbon emissions driving demand. This renewed interest has led to more affordable, technologically advanced electric vehicles with significantly improved range.
The success of electric cars has also driven innovation in the auto industry, with companies like Tesla pushing for fully electric, self-driving cars. The first electric car may have been a curiosity, but today it is a symbol of the evolution of transportation and our ongoing efforts to shift to a more sustainable future.
Early Adoption and Popularity
The early adoption and popularity of electric cars have had a significant impact on society and the auto industry. As more people become aware of the benefits of switching to electric vehicles, we can see the gradual shift towards more sustainable transportation. Electric cars have become increasingly popular due to their lower emissions, lower costs in the long run, and the fact they require less maintenance than traditional gas-powered cars.
As a result, several countries and cities have developed policies and regulations to encourage their use and reduce emissions. The rise in the popularity of electric cars has also led to advancements in battery technology, which has improved the performance and range of electric vehicles. The auto industry has responded to this trend by investing heavily in electric car development and manufacturing to cater to a growing market.
As electric cars become more mainstream, it’s only a matter of time before we’ll see fewer gas-powered cars on the road and a cleaner, healthier planet consumed by cleaner energy solutions.
Challenges and Setbacks
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on society and the auto industry alike, presenting numerous challenges and setbacks. With social distancing and remote work becoming the new norm, fewer people were commuting to work or traveling, leading to a significant decline in demand for vehicles. Additionally, many global supply chains were disrupted, resulting in shortages of critical components and materials needed for vehicle production.
As a result, production lines were either idle or working at reduced capacity. However, the pandemic also created new opportunities for automakers, forcing them to shift their focus towards technological advancements and sustainable solutions. For instance, some car manufacturers started producing medical equipment or ventilators, while others invested heavily in electric and autonomous vehicles.
In the end, the industry must adapt to the new normal, embrace change, and turn the challenges into opportunities.
Modern-Day Electric Cars and Innovations
The first electric car in history was invented way back in the late 19th century. Today, electric cars are becoming increasingly popular due to their environmental friendliness and fuel efficiency. Modern-day electric cars come fully equipped with several innovative features such as regenerative braking, which captures the energy lost during braking and feeds it back to the battery, improving the car’s overall efficiency.
Many electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, which are lighter and more efficient than traditional lead-acid batteries. Additionally, advanced charging and battery management systems are emerging, making it easier and quicker to charge electric cars than ever before. The rise of electric cars is not only a boon for the environment but also for those who enjoy the latest technological innovations in the automotive industry.
With more electric cars hitting the roads each year, it’s exciting to see the pace of innovation in this space.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the first electric car in history was a revolutionary invention that represented a major shift towards sustainable transportation. It paved the way for the development of modern electric cars and challenged the traditional dominance of gas-powered vehicles. While it may not have been the most practical or efficient car of its time, it certainly laid the foundation for a greener future.
And let’s face it, without that first electric car, we may still be stuck in traffic, burning fossil fuels, and wondering why our cars smell like gasoline. So cheers to the little EV that could – the first electric car in history – for sparking an electric revolution that has been charged up and ready to go ever since.”
FAQs
What was the first electric car ever produced?
The first electric car was built in 1837 by a chemist named Robert Davidson.
Which company came out with the first mass-produced electric car?
The first mass-produced electric car was made by the company Baker Electric in 1899.
What was the range of the first electric car?
The first electric car had a range of about 50-60 miles on a single charge.
When did gasoline-powered cars start becoming more popular than electric cars?
Gasoline-powered cars started becoming more popular in the early 1900s, due to the lower cost of gasoline and the ability to travel longer distances with a full tank.
Are there still electric cars being produced today?
Yes, there are many companies that produce electric cars today, including Tesla, Nissan, and Chevrolet.






