Ford Electric Car Batteries Powering the Future of Driving
Featured image for ford electric car batteries
Image source: cdn.vox-cdn.com
Ford electric car batteries are revolutionizing sustainable driving with cutting-edge lithium-ion and next-gen solid-state technology, delivering longer range, faster charging, and enhanced durability. Engineered for performance and eco-efficiency, these batteries power Ford’s expanding EV lineup, setting a new benchmark for reliability and innovation in the electric vehicle market. From the F-150 Lightning to the Mustang Mach-E, Ford is driving the future—one charged mile at a time.
Key Takeaways
- Ford’s batteries offer longer range and faster charging times.
- Recyclable materials reduce environmental impact and support sustainability.
- Advanced thermal management ensures optimal performance in all climates.
- Modular designs simplify repairs and lower long-term ownership costs.
- Vehicle-to-grid tech lets cars power homes during outages.
- Over-the-air updates improve battery efficiency and features over time.
📑 Table of Contents
- Ford Electric Car Batteries Powering the Future of Driving
- 1. The Core Technology Behind Ford Electric Car Batteries
- 2. Battery Capacity, Range, and Real-World Performance
- 3. Battery Longevity, Warranty, and Maintenance
- 4. Sustainability and Recycling: Ford’s Commitment to the Environment
- 5. Cost, Incentives, and Total Ownership Value
- 6. The Road Ahead: Ford’s Battery Vision
Ford Electric Car Batteries Powering the Future of Driving
The automotive world is undergoing a seismic shift, and at the heart of this transformation lies the electric vehicle (EV) revolution. Among the pioneers driving this change is Ford Motor Company, an American icon that has seamlessly transitioned from gasoline engines to cutting-edge electric powertrains. Central to this evolution are Ford’s electric car batteries—the beating heart of vehicles like the Mustang Mach-E, F-150 Lightning, and E-Transit. These aren’t just any batteries; they’re the result of years of research, innovation, and strategic partnerships, designed to deliver performance, longevity, and sustainability. As the demand for zero-emission transportation surges, Ford is positioning itself as a leader in the EV space, and its battery technology is the cornerstone of its success.
But what makes Ford’s electric car batteries stand out in a crowded and competitive market? From advanced lithium-ion chemistries to groundbreaking recycling initiatives, Ford is redefining what it means to power an electric vehicle. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an eco-conscious driver, or simply curious about the future of mobility, understanding Ford’s battery strategy is key to appreciating the full scope of its electric ambitions. This blog post dives deep into the science, engineering, and real-world performance of Ford electric car batteries, offering insights into how they’re shaping the future of driving—one charge at a time.
1. The Core Technology Behind Ford Electric Car Batteries
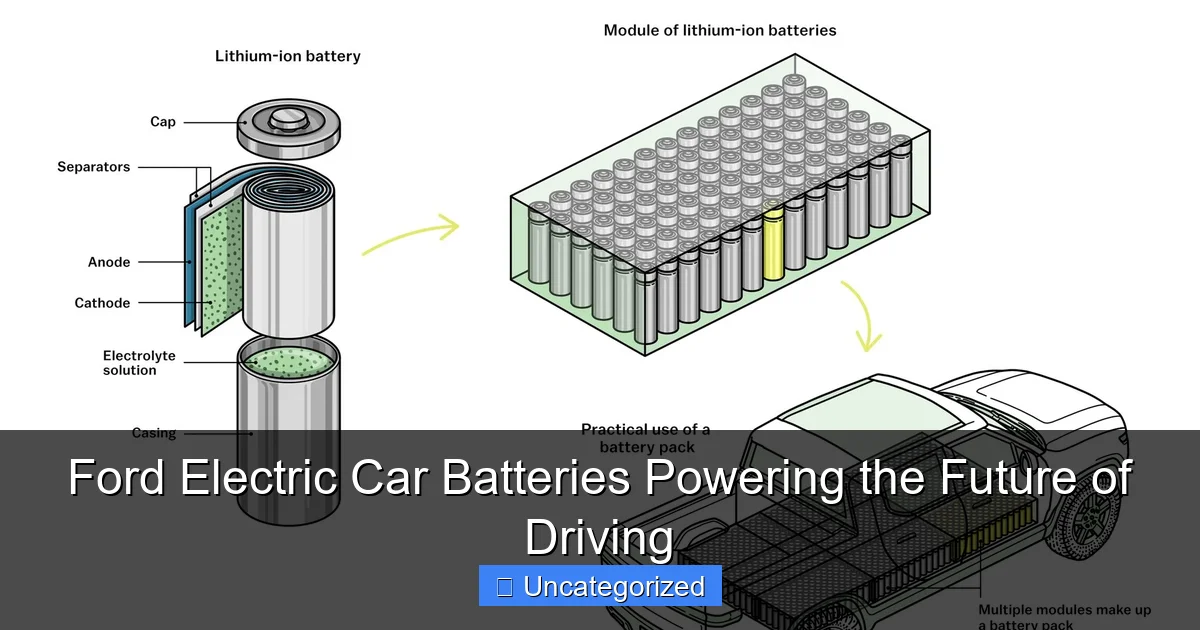
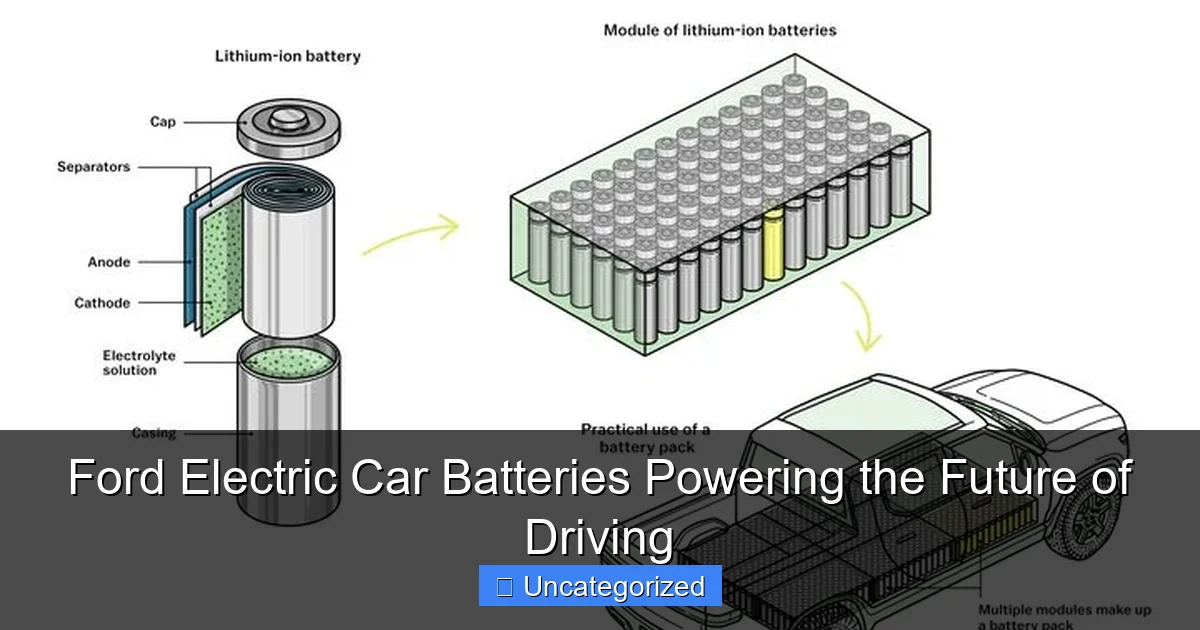
Lithium-Ion: The Foundation of Modern EV Batteries
At the core of every Ford electric vehicle is a lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery pack, the industry standard for energy density, efficiency, and reliability. Unlike older battery types such as lead-acid or nickel-metal hydride, Li-ion batteries offer a higher energy-to-weight ratio, longer cycle life, and faster charging capabilities. Ford uses pouch and prismatic cell formats, which allow for more compact and modular battery designs—ideal for fitting into diverse vehicle platforms, from compact SUVs to full-size trucks.
Visual guide about ford electric car batteries
Image source: cdn.vox-cdn.com
Ford’s Li-ion cells are typically composed of a nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) cathode and a graphite anode, balancing energy capacity with thermal stability. The NMC chemistry provides high energy density (up to 250 Wh/kg in newer models), enabling longer driving ranges without significantly increasing battery weight. For example, the Mustang Mach-E GT Performance Edition achieves a range of over 270 miles on a single charge, thanks to its advanced 88 kWh battery pack.
Proprietary Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Ford’s battery performance isn’t just about chemistry—it’s also about intelligence. Each battery pack is equipped with a proprietary Battery Management System (BMS) that continuously monitors cell voltage, temperature, and state of charge (SoC). The BMS ensures optimal performance by:
- Balancing charge across all cells to prevent overcharging or deep discharging
- Regulating thermal conditions to extend battery lifespan
- Providing real-time diagnostics to the driver and service technicians
- Enabling over-the-air (OTA) updates for improved efficiency and safety
This intelligent system is especially crucial during fast charging, where heat generation can degrade battery health if not properly managed.
Thermal Management: Keeping Batteries Cool and Efficient
One of the biggest challenges in EV battery design is thermal regulation. Ford addresses this with a liquid cooling and heating system integrated into the battery pack. This dual-function system:
- Cools the battery during high-load operations (e.g., fast acceleration or DC fast charging)
- Heats the battery in cold climates to maintain charging speed and efficiency
For instance, the F-150 Lightning can precondition its battery before arriving at a charging station, ensuring it reaches the ideal temperature for maximum charge rate. This feature alone can reduce charging time by up to 25% in sub-zero temperatures.
2. Battery Capacity, Range, and Real-World Performance
Understanding kWh: What Battery Size Means for Drivers
Ford offers a range of battery capacities across its EV lineup, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The larger the kWh, the more energy the battery can store—and the longer the driving range. Here’s a breakdown of current Ford EV battery options:
| Vehicle Model | Battery Size (kWh) | EPA-Estimated Range (miles) | Charge Time (DC Fast Charger, 10-80%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mustang Mach-E RWD | 70 (Standard Range) | 247 | 38 minutes |
| Mustang Mach-E AWD | 88 (Extended Range) | 314 | 38 minutes |
| F-150 Lightning (Standard) | 98 | 240 | 41 minutes |
| F-150 Lightning (Extended) | 131 | 320 | 41 minutes |
| E-Transit Cargo Van | 68 | 126 | 30 minutes |
Note: Range and charge times may vary based on driving conditions, climate, and vehicle configuration.
Real-World Range: What to Expect in Daily Driving
While EPA ratings are useful benchmarks, real-world range depends on several factors. Ford electric car batteries perform best under moderate conditions, but here’s what drivers can expect in various scenarios:
- City driving: Often exceeds EPA estimates due to regenerative braking capturing energy during frequent stops.
- Highway driving: Typically 10–15% below EPA range due to aerodynamic drag at high speeds.
- Cold weather: Battery efficiency drops by 20–30% in sub-freezing temperatures. Preconditioning helps mitigate this.
- Towing (F-150 Lightning): Reduces range by up to 50% when hauling heavy loads. Ford recommends using the extended-range battery for regular towing.
Tip: Use Ford’s Intelligent Range feature, which analyzes weather, traffic, and elevation to provide a more accurate range prediction.
Charging Speeds and Compatibility
Ford electric car batteries support both Level 2 (AC) and DC fast charging. With a DC fast charger (150–350 kW), most Ford EVs can go from 10% to 80% in under 45 minutes. At home, a Level 2 charger (7.2–11.5 kW) fully charges the battery in 8–12 hours—ideal for overnight charging.
All Ford EVs use the Combined Charging System (CCS) connector, compatible with most public charging networks (Electrify America, ChargePoint, etc.). Ford also offers the FordPass Charging Network, giving drivers access to over 19,500 fast chargers across North America.
3. Battery Longevity, Warranty, and Maintenance
How Long Do Ford EV Batteries Last?
Ford electric car batteries are engineered for longevity. Under normal driving conditions, most battery packs are expected to last 10–15 years or 100,000–150,000 miles before capacity drops below 70–80% of original levels. This degradation is normal and gradual, not sudden failure.
Factors influencing battery lifespan include:
- Charging habits: Frequent DC fast charging can accelerate wear. Ford recommends using Level 2 charging for daily use.
- Temperature exposure: Prolonged exposure to extreme heat or cold reduces battery health.
- State of charge: Keeping the battery at 100% or 0% for extended periods stresses the cells. Aim for 20–80% for optimal longevity.
Ford’s Battery Warranty: Peace of Mind for Owners
Ford offers one of the most comprehensive battery warranties in the industry:
- 8 years or 100,000 miles (whichever comes first) for all EV models
- Covers battery defects and capacity loss below 70%
- Transferable to subsequent owners
This warranty exceeds the federal requirement (8 years/100,000 miles) and reflects Ford’s confidence in its battery durability. For example, early Mustang Mach-E owners have reported only 5–8% capacity loss after 50,000 miles—well within expected parameters.
Maintenance Tips to Maximize Battery Health
Unlike internal combustion engines, EV batteries require minimal maintenance, but smart habits can extend their life:
- Avoid deep discharges: Recharge before the battery drops below 10%.
- Use scheduled charging: Set charging to complete just before departure to reduce time spent at 100%.
- Store properly: If leaving the vehicle unused for weeks, keep the battery at 50% charge.
- Precondition in cold weather: Use the FordPass app to warm the battery before driving.
Pro Tip: Monitor battery health through the vehicle’s infotainment system. Ford provides a Battery Health report showing capacity trends over time.
4. Sustainability and Recycling: Ford’s Commitment to the Environment
Reducing the Carbon Footprint of Battery Production
Ford recognizes that EV batteries must be sustainable from cradle to grave. The company has invested heavily in green manufacturing at its battery plants, including:
- Using renewable energy (solar, wind) at facilities like the BlueOval SK plant in Kentucky
- Partnering with suppliers to reduce mining impacts (e.g., responsibly sourced cobalt and lithium)
- Implementing closed-loop water systems to minimize resource use
For example, Ford’s collaboration with SK Innovation has resulted in battery production with a 30% lower carbon footprint compared to industry averages.
End-of-Life Recycling and Second-Life Applications
When Ford electric car batteries reach end-of-life, they’re not destined for landfills. Instead, Ford has established a battery recycling program through its partnership with Redwood Materials. This program:
- Recovers up to 95% of critical metals (lithium, cobalt, nickel)
- Reuses materials in new battery production
- Reduces the need for new mining by 50% over the next decade
Additionally, Ford is exploring second-life battery applications, such as:
- Grid storage for renewable energy (e.g., solar farms)
- Backup power for commercial buildings
- Mobile charging stations for rural areas
The F-150 Lightning, for instance, can power a home for up to 3 days during outages—showcasing the versatility of EV batteries beyond driving.
Future Innovations: Solid-State and Beyond
Ford is investing in next-gen battery tech, including solid-state batteries through its joint venture with SK On. Solid-state batteries promise:
- Higher energy density (500+ Wh/kg)
- Faster charging (under 15 minutes for 80%)
- Improved safety (no flammable liquid electrolytes)
Ford aims to introduce solid-state battery-powered vehicles by 2030, potentially doubling EV range and slashing charging times.
5. Cost, Incentives, and Total Ownership Value
Upfront Costs vs. Long-Term Savings
While Ford electric car batteries contribute to higher upfront vehicle costs, the total cost of ownership (TCO) is often lower than gasoline vehicles. Consider:
- Lower fuel costs: Electricity is cheaper than gasoline (average $0.15/kWh vs. $3.50/gallon).
- Reduced maintenance: No oil changes, spark plugs, or transmission fluid.
- Longer lifespan: EV batteries last longer than ICE engines.
For example, the F-150 Lightning saves owners an estimated $1,500/year in fuel and maintenance compared to a gas-powered F-150.
Federal and State Incentives
Buyers of new Ford EVs may qualify for incentives, including:
- Federal tax credit: Up to $7,500 (subject to battery sourcing requirements)
- State rebates: Varies by location (e.g., $2,000 in California, $5,000 in Colorado)
- Utility discounts: Many providers offer reduced rates for EV charging
Tip: Use the U.S. Department of Energy’s Alternative Fuels Data Center tool to find local incentives.
Resale Value and Depreciation
Historically, EVs depreciated faster than gas vehicles, but Ford’s strong brand and battery warranty are changing that. The Mustang Mach-E now retains ~55% of its value after 3 years, comparable to top-performing SUVs. The F-150 Lightning, with its unique capabilities, often holds value even better.
6. The Road Ahead: Ford’s Battery Vision
Scaling Production for Mass Adoption
Ford plans to produce 2 million EVs annually by 2026, requiring massive battery capacity. To meet this goal, the company is:
- Building four new battery plants in the U.S. (BlueOval City, Tennessee; BlueOval SK, Kentucky)
- Partnering with CATL for LFP (lithium iron phosphate) batteries, which are cheaper and longer-lasting
- Investing $50 billion in electrification through 2026
Expanding the EV Lineup
Ford’s battery strategy supports a growing portfolio, including:
- Explorer EV (2025): A three-row SUV with 300+ mile range
- All-electric Ranger (2024): A midsize pickup with off-road capabilities
- Next-gen E-Transit: With improved range and payload capacity
Empowering Drivers and Communities
Beyond vehicles, Ford is using its battery expertise to:
- Launch Ford Pro charging solutions for fleets and businesses
- Develop vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology to stabilize power grids
- Educate consumers on EV ownership through the FordPass app
Ford electric car batteries are more than just power sources—they’re catalysts for a cleaner, smarter, and more connected future. From cutting-edge chemistry to circular economy practices, Ford is proving that sustainability and performance can go hand in hand. As battery technology evolves and charging infrastructure expands, the dream of accessible, zero-emission driving is becoming a reality. Whether you’re charging at home, powering your house during a blackout, or recycling your old battery for a second life, Ford’s vision extends far beyond the road. The future of driving isn’t just electric—it’s powered by innovation, responsibility, and the relentless pursuit of progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do Ford electric car batteries last?
Ford electric car batteries are designed to last 8–10 years or 100,000–150,000 miles, depending on usage and charging habits. Ford also offers an 8-year/100,000-mile warranty for added peace of mind.
Can I replace or upgrade my Ford electric car battery?
Yes, Ford provides battery replacement services at authorized service centers, often with upgraded capacity options. While DIY upgrades aren’t recommended, Ford’s network ensures safe, certified installations.
What type of battery does Ford use in its electric cars?
Ford electric car batteries use advanced lithium-ion chemistry, with newer models featuring nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) variants for improved range and longevity.
How fast can Ford electric car batteries be charged?
With DC fast charging, Ford electric car batteries can charge from 10% to 80% in as little as 30–40 minutes. Home charging (Level 2) typically takes 8–10 hours for a full charge.
Are Ford electric car batteries recyclable?
Yes, Ford partners with recycling firms to recover up to 95% of battery materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The company also repurposes used batteries for energy storage systems.
What affects the lifespan of Ford electric car batteries?
Frequent fast charging, extreme temperatures, and deep discharges can shorten battery life. Ford mitigates this with thermal management systems and battery health monitoring tools in all models.





