The Evolution of Electric Car Batteries: A Journey Through History
If you’ve been following the development of electric cars, you may be curious about the history of the batteries that power them. Electric car batteries have come a long way since the first crude models were invented in the early 19th century. Back then, electric vehicles were a novelty, and the batteries that powered them were bulky, expensive, and had limited range.
But as technology advanced, so did electric car batteries. Today’s electric car batteries are more efficient, have longer ranges, and are significantly cheaper than their predecessors. They’re also much lighter and more compact, making them ideal for use in everything from small city cars to heavy-duty trucks and buses.
But how did we get here? What were the milestones in the development of electric car batteries? And what challenges did engineers face along the way? In this brief history, we’ll take a look at the evolution of electric car batteries and how they’ve contributed to the rise of electric vehicles. So buckle up and join us as we explore the fascinating world of electric car batteries!
Early Development
In the early development of electric cars, one of the biggest challenges was finding an efficient and reliable battery. The history of electric car batteries dates back to the mid-1800s when rechargeable lead-acid batteries were first invented. These batteries were heavy and inefficient, making them impractical for use in vehicles.
In the early 1900s, nickel-iron batteries were developed, which were more durable and weather-resistant than lead-acid batteries, but still had limited capacity and were expensive to produce. It wasn’t until the 1970s that advancements were made in the development of lithium-ion batteries, which are still used in modern electric cars today. These batteries are much lighter, have higher energy density, and are more environmentally friendly than their predecessors.
As technology continues to advance, the future of electric car batteries looks bright and promising, with the potential for even more efficient and sustainable battery options in the years to come.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have a long history of development since their invention in the mid-19th century. The early prototypes were bulky and had a low energy density, but over the years, significant improvements were made. One of the early developers was the French physicist Gaston Planté, who invented the first lead-acid battery in 185
He used two sheets of lead and immersed them in a solution of sulfuric acid to create an electrical charge. The battery was rechargeable and became popular in various industries, including transportation, telecommunications, and aviation. Lead-acid batteries are still used today, but their design and performance have undergone extensive modifications to keep up with the demands of modern technologies.
For example, the development of sealed lead-acid batteries (SLA) solved the issues of electrolyte leakage and maintenance that were associated with the original design. SLA batteries are commonly used in backup power systems and emergency lighting systems. Overall, the early development of lead-acid batteries paved the way for many other battery technologies that we use today.
While new battery technologies are emerging, lead-acid batteries remain an essential part of many industries, and their relevance will continue well into the future.

Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
Nickel-cadmium batteries, also known as NiCad batteries, were developed in the early 1900s. These were the first rechargeable batteries to be commercially available and were initially used in portable radios, flashlights, and early computers. NiCad batteries were popular due to their high energy density and long life cycle.
However, they had a few drawbacks, such as the “memory effect” (where the battery would lose its maximum capacity if it wasn’t discharged fully before recharging) and the use of toxic heavy metals like cadmium. Despite these limitations, NiCad batteries remained popular until the 1990s when more environmentally friendly options like Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) and Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) batteries were introduced. Today, NiCad batteries are still used in some applications, such as emergency backup systems and certain power tools.
Advancements in Battery Technology
The history of electric car batteries is long and complex, with advancements in technology constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Early batteries were bulky and inefficient, using lead-acid technology that required constant maintenance. However, over time, these batteries improved in both capacity and lifespan, allowing electric cars to travel longer distances without needing a recharge.
The introduction of lithium-ion batteries in the 1990s was a game-changer, offering a significantly higher energy density and longer lifespan than previous battery types. Today, researchers are exploring new technologies such as solid-state batteries, which could offer even greater energy densities and faster charging times. With each new advancement, electric cars become more practical and efficient, someday becoming the norm on our roads and highways.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized the way we power our daily lives, and advancements in battery technology have made them even more efficient and reliable. These batteries are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and industrial applications due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rate. The latest developments in lithium-ion battery technology have focused on increasing their energy density and output power while reducing their size and weight.
For instance, some manufacturers have developed new materials and architectures, such as silicon anodes and solid-state electrolytes, that could significantly improve battery performance. Additionally, researchers are exploring new charging algorithms and intelligent battery management systems that can optimize battery usage and prolong their lifespan. With these advancements, we can expect lithium-ion batteries to continue playing a vital role in powering our modern world.
Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are the newest advancements in battery technology, promising to significantly improve battery performance. These batteries use solid electrode materials, unlike traditional batteries that use liquid or gel electrolytes. Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density, longer battery life, and faster charging times.
They are also safer as there is no risk of leakage or explosion, making them ideal for use in electric vehicles and mobile devices. However, solid-state batteries are still in the research and development phases, and it may take several years before they become widely available. Researchers are currently working on improving the durability and reliability of solid-state batteries while also reducing their cost of production.
Overall, solid-state batteries offer a promising future for battery technology and show immense potential to revolutionize various industries.
Graphene Batteries
Advancements in Battery Technology have led to the creation of Graphene Batteries, a new generation of batteries with incredible potential. These batteries use Graphene, a material known for its incredible strength, conductivity, and flexibility, to store and deliver energy more efficiently than ever before. Unlike traditional Lithium-ion batteries that rely on heavy metals, Graphene Batteries are lightweight, non-toxic, and have a longer lifespan.
They can charge faster, hold more energy, and last longer than other batteries, making them an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, from electric vehicles to smartphones. With the ever-increasing demand for energy storage solutions, Graphene Batteries are set to revolutionize the battery industry.
Current State of Electric Car Batteries
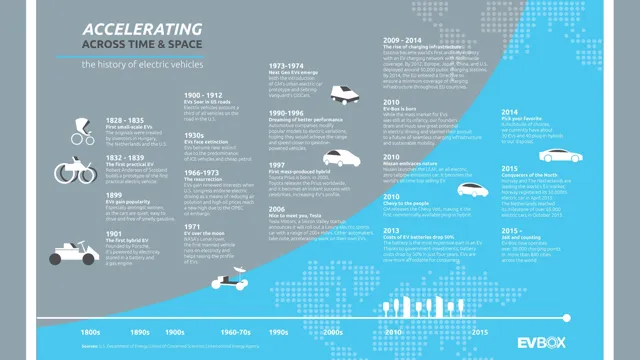
The history of electric car batteries dates back to the 1800s, where various attempts were made to manufacture an electric car that was practical, reliable and cost-efficient. It wasn’t until the early 1990s when the first commercially available electric cars were introduced, though most of these were either niche models or prototypes. Early battery-powered electric vehicles had a range of just around 50-100 miles per charge, making them impractical for long commutes or road trips.
However, advancements in technology have steadily improved electric car batteries’ efficiency and lifespan. Today’s electric cars boast an average range of 250-350 miles per charge, while also offering faster charging times, reduced costs, and increased power. With more manufacturers joining the market and investing in developing advanced battery technologies, it’s becoming more apparent that the future of transportation is indeed electric.
Battery Sizes and Ranges
As electric cars become more popular, there’s been a lot of buzz about battery sizes and ranges. The current state of electric car batteries is quite impressive, with sizes ranging from 40 kWh to over 100 kWh. This means that electric cars can have ranges anywhere from 100 miles to over 300 miles on a single charge.
As battery technology continues to improve, we can expect even longer ranges in the future. Additionally, the cost of electric car batteries has been steadily decreasing, making them more affordable for consumers. So not only do electric cars have impressive ranges, but they’re also becoming more accessible to the average person.
It’s an exciting time for electric car technology, and we can’t wait to see what the future holds.
Charging Infrastructure
When it comes to electric vehicles, the battery is one of the most important components. These batteries are responsible for providing power to the vehicle’s electric motor, and they determine how far the vehicle can travel on a single charge. Currently, electric car batteries have come a long way, and they are much more efficient than they were just a few years ago.
Today’s electric vehicles can travel anywhere from 100 to 400 miles on a single charge, depending on the make and model. However, there is still room for improvement. Car manufacturers are constantly looking for ways to improve battery technology, with the goal of making electric vehicles more practical and affordable for the masses.
Advances in battery chemistry, charging infrastructure, and energy density are just a few of the areas where progress is being made. Despite the current limitations, the future of electric vehicles looks promising, and we can expect to see significant improvements in the coming years.
The Future of Electric Car Batteries
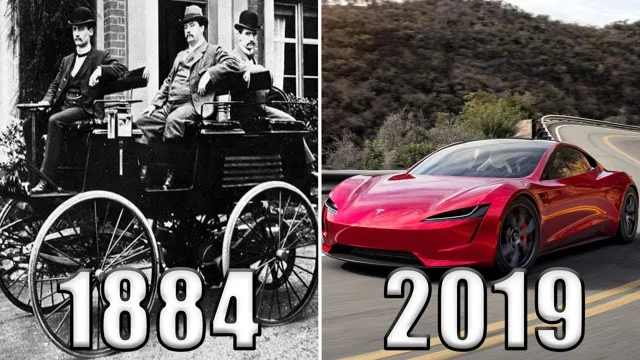
The history of electric car batteries has been a long one, filled with numerous advancements and setbacks. The first electric car battery was invented in the late 1850s by French scientist Gaston Planté, and since then, there have been countless innovations aimed at improving their efficiency and range. One major breakthrough came in the early 1990s with the development of the lithium-ion battery, which is still widely used in electric vehicles today.
However, as demand for EVs continues to rise, researchers are exploring new battery technologies that can provide even greater energy density and faster charging times. One promising development is the solid-state battery, which uses a solid electrolyte instead of the traditional liquid electrolyte. The industry is also looking into alternative materials, such as sodium-ion and zinc-air batteries, that could offer similar benefits to lithium-ion at a lower cost.
As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, the future of electric car batteries looks brighter than ever before.
Conclusion
After centuries of experimentation and innovation, the history of electric car batteries has shown that the quest for a clean and efficient mode of transportation is an ongoing process. From lead-acid to lithium-ion, the technology has come a long way, but it’s clear that there’s still more to be discovered and improved. Perhaps in the near future, we’ll see new game-changing battery technologies, leading to more eco-friendly electric cars on our roads, leaving behind the smoke and noise of gasoline vehicles.
Remember, the future is electric, the future is sustainable, and who knows, maybe even the future seems bright for the “fully charged”!
FAQs
What is the history of electric car batteries?
The history of electric car batteries can be traced back to the 1800s when the first electric vehicles were invented. However, it was not until the late 1990s that modern electric car batteries were developed, which enabled them to become a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
How do electric car batteries work?
Electric car batteries work by converting chemical energy stored in the battery into electrical energy, which powers an electric motor to drive the wheels of the vehicle. The energy can be replenished by plugging the car into an electric outlet or a charging station.
Are there different types of electric car batteries available?
Yes, there are different types of electric car batteries available, including lithium-ion batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, and lead-acid batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used type of electric car batteries due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
What are the advantages of using electric car batteries?
There are several advantages of using electric car batteries, including lower emissions, reduced operating costs, and improved performance. Electric cars are also quieter than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, making for a more comfortable driving experience. Additionally, since electric cars do not require gasoline, there is less dependence on fossil fuels and a reduced risk of price fluctuations.