From Ancient Innovations to Modern Marvels: Tracing the Fascinating History of Electric Cars
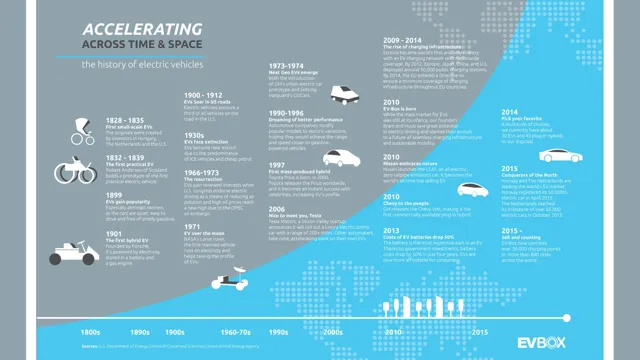
Electric cars are not a new phenomenon. In fact, they have been around since the 19th century! However, it wasn’t until recently that electric cars have begun to gain popularity as a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Many people are curious about the history of electric cars, and how they have evolved over time.
This blog will take you through a brief history of electric cars, from their early beginnings to the present day. From the first electric vehicles in the 1820s to the sleek Teslas of today, the history of electric cars is both fascinating and enlightening. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating history of electric cars!
Early Years
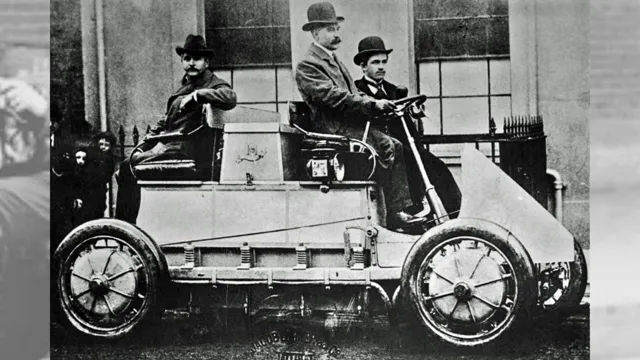
When it comes to the early years of electric cars, it’s fascinating to see how they actually predate gasoline-powered cars. In fact, the first electric car was built in the 1830s by a Scottish inventor named Robert Anderson. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric cars became more practical and commercially available.
During this time, companies such as Baker, Columbia, and Detroit Electric were established and produced electric cars that were popular among the elite. Electric cars met their peak popularity in 1912, accounting for nearly 40% of all American cars on the road. But the invention of the electric starter motor for gasoline-powered cars, along with the discovery of abundant oil reserves, ultimately led to a decline in electric car production.
Nevertheless, the early years of electric cars set the foundation for the technologies we see today and paved the way for a brighter future in sustainable transportation.
Invention of the Electric Carriage
The electric carriage is known as the predecessor of our present-day electric cars, and its early years date back to the mid-19th century. The first electrical vehicle was invented by Robert Anderson, a Scottish inventor, in 1832, but it was inefficient and slow. Then, in the 1850s, battery-powered buggies and tricycles became a common sight in European cities.
However, it wasn’t until the 1880s that the first successful electric carriage was introduced to the market. Thomas Parker, a British inventor, designed a high-capacity battery and used it to power an electric carriage. He introduced this innovation to London in 1884 and was very popular despite its high cost, leaving horse-drawn carriages behind.
With this innovation, the world began to see the potential for electric vehicles and the many environmental benefits they could provide. The early years of electric car development show us how far technology has come in a relatively short amount of time.

First Commercial Electric Cars
The early years of commercial electric cars were quite humble, but they set the stage for what was to come. The first electric car was built in the 1830s, but it wasn’t until the late 19th and early 20th century that they started to gain popularity. Electric cars were seen as a cleaner and quieter alternative to gasoline-powered cars.
In fact, electric cars outsold gasoline cars in the US until the 1920s. However, the invention of the electric starter for gasoline cars made them much easier to use, and the discovery of large oil reserves made gasoline much cheaper. As a result, electric cars were relegated to niche markets, such as delivery vehicles and taxis.
Despite this setback, the early years of electric cars paved the way for the development of new technology and the eventual resurgence of electric cars in the 21st century.
Challenges and Advances
The history of electric cars has been a story of challenges and advances. Despite initial attempts to introduce electric vehicles (EVs) in the early 20th century, their adoption was hindered by limited driving range, costly battery production, and concerns about maintaining a charging infrastructure. It was not until the last decade that EVs began to gain traction as technological advancements made them more practical and affordable.
Today, EVs have become a viable alternative for many consumers, with models that offer impressive range, fast charging, and sleek design. Advances in battery technology have also resulted in longer-lasting batteries that are more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. However, challenges still remain, as EVs require significant investment in charging infrastructure and battery recycling.
Nonetheless, with the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality, the future of electric cars looks bright, with continued growth and innovation on the horizon.
Limited Driving Range and Battery Technology
Electric vehicles have been around for quite some time now, but there is still one issue that remains prevalent – limited driving range. This limitation is caused mainly by the current battery technology used in electric vehicles. However, advances in battery technology have been made that will increase the driving range of electric vehicles.
Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in electric vehicles, have experienced significant improvements in energy density and are becoming more affordable to produce. A new type of battery technology called solid-state batteries is also in development. These batteries have the potential to increase driving range substantially and have a higher level of safety.
However, solid-state batteries are not yet commercially available, and there are still challenges that need to be addressed before they can be mass-produced. The advancement in battery technology will enable electric vehicles to become more practical and mainstream. As a result, more people will be encouraged to make the switch to electric vehicles, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and ultimately benefiting the environment.
Development of More Efficient Motors and Batteries
The development of more efficient motors and batteries is vital for advancing the future of electric vehicles. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed to achieve this goal. One of the significant challenges is ensuring that the batteries used in electric cars can provide sufficient power and have a longer lifespan.
Researchers are currently working on developing new types of rechargeable batteries that can store more energy and operate for more extended periods. Another critical challenge is developing more efficient motors that can convert electricity into motion with minimal energy wastage. Advances in motor technology, including the use of lightweight materials and advanced control systems, are currently being explored by experts to increase efficiency and reduce energy loss.
With investments in research and advancements in technology, we can expect to see a significant leap in the efficiency of motors and batteries used in electric cars in the near future.
The Rise of Gasoline-Powered Cars
As gasoline-powered cars rose in popularity, several challenges and advances accompanied their emergence. With more cars on the road, there was an increased need for efficient fuel delivery and distribution systems. This led to the construction of new gas stations and the development of fuel pipelines to transport gasoline across longer distances.
Additionally, advancements in refining technologies improved the quality of gasoline, leading to better fuel efficiency and increased engine performance. However, the widespread use of gasoline-powered cars also brought challenges, including environmental concerns and safety issues. As we continue to depend on these vehicles for transportation, it is crucial to recognize these challenges and work towards sustainable solutions.
While electric cars are a promising alternative, gasoline-powered cars are still prevalent and will likely remain so for the foreseeable future. By implementing modern safety features and continuing to refine gasoline and fuel delivery systems, we can minimize the challenges associated with these vehicles and safely enjoy their benefits.
Modern Era
The modern era of electric cars stems from the 1990s, when advancements in battery technology and an increased focus on the environment prompted car manufacturers to begin producing electric vehicles. While early electric cars had limited ranges and lacked the convenience of gasoline vehicles, technological advancements have made modern electric cars a viable alternative that can compete with traditional vehicles in terms of range, speed, and performance. Today, consumers can choose from a wide range of electric vehicles, from the Tesla Model S to the Chevrolet Bolt, and the shift towards electric cars shows no signs of slowing down.
As more manufacturers produce electric vehicles and governments push to reduce emissions, it is likely that electric cars will become even more widespread in the years to come. The history of electric cars is a fascinating subject that highlights the role of innovation and environmentalism in shaping the future of transportation.
Revival of Interest in Electric Cars
The revival of interest in electric cars during the modern era can be attributed to various factors. One of these is the growing concern about climate change and the need to reduce carbon emissions. Electric vehicles are seen as a solution to this problem as they produce zero emissions.
Additionally, advancements in technology have also made electric cars more practical and appealing to consumers. Battery technology has improved significantly, allowing electric vehicles to have a longer range and shorter charging times. The availability of charging infrastructure is also expanding rapidly, making it easier for people to transition to electric cars.
Furthermore, governments around the world are offering incentives such as tax credits and subsidies to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. This has led to an increase in demand for electric cars, with manufacturers racing to produce models that meet the needs and preferences of consumers. As a result, electric cars are becoming more mainstream, and it looks like this trend will continue into the future.
Government Support and Investment
In the modern era, government support and investment has played a crucial role in shaping economies across the world. From providing funding for research and development to creating infrastructure and opportunities for entrepreneurs, government support has helped spur growth and innovation in many industries. For example, in the United States, government funding has been instrumental in the development of key technologies such as the internet and GPS.
Additionally, programs such as the Small Business Administration have assisted countless entrepreneurs in starting and growing their businesses. While some critics argue that government investment can be wasteful or misused, many experts believe that targeted investment can be a highly effective way to stimulate economic growth and create new opportunities for citizens. Ultimately, the success of government support initiatives depends on a number of factors, including the quality of leadership, the strength of the overall economy, and the ability of entrepreneurs and innovators to take advantage of the opportunities presented to them.
Future of Electric Cars
The history of electric cars is fascinating, dating back to the early 1800s when inventors first began experimenting with electric-powered vehicles. However, it wasn’t until the early 2000s that electric cars began to gain mainstream popularity as concerns about climate change and oil dependency grew. Despite their slow start, electric vehicles have come a long way over the past decade.
Today, they offer a range of benefits, including reduced emissions, lower ownership costs, and a smoother, quieter ride. As technology continues to improve, many experts believe that electric cars will become increasingly popular, eventually overtaking traditional gasoline-powered vehicles and leading the way in sustainable transportation. With advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure, the future of electric cars is bright, and it’s no wonder why more and more people are starting to consider making the switch.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of electric cars is a lesson in perseverance and innovation. From the early electric car prototypes that struggled to make it up hills to the sleek, modern electric vehicles of today, the technology has come a long way. Despite initial setbacks and the dominance of gasoline-powered cars, electric cars have managed to carve out a niche for themselves in the market.
With advancements in technology and increasing concern for the environment, electric cars are poised to become even more popular in the years to come. So the next time you see a sleek electric car gliding silently down the road, take a moment to appreciate the history and ingenuity that made it possible. After all, it takes a lot of power to be this green.
“
FAQs
What is the history of electric cars?
Electric cars have been around since the 19th century, but they didn’t gain popularity until the 21st century due to advancements in battery technology and a growing concern about climate change.
How do electric cars compare to gasoline cars in terms of cost?
Electric cars are generally more expensive to buy than gasoline cars, but their operating costs (i.e., electricity vs. gasoline) are typically much lower, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
Can electric cars be charged at home?
Yes, most electric cars can be charged at home using a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated charging station. However, the time it takes to charge can vary, depending on the car and the charging method.
What is the range of an electric car?
The range of an electric car varies depending on the model and the battery size, but most modern electric cars have a range of at least 100 miles on a single charge. Some electric cars, such as the Tesla Model S, have a range of over 300 miles.