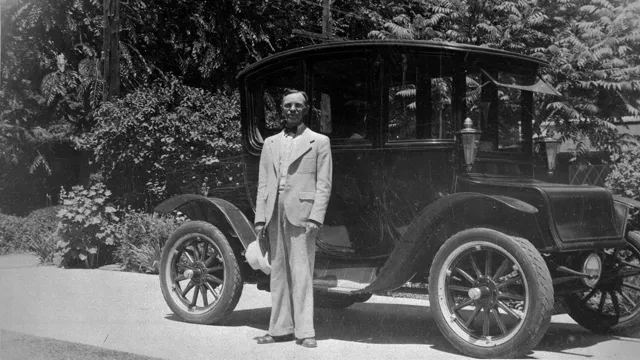Revolutionizing Transportation: A Comprehensive Timeline of the History of Electric Cars
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become ubiquitous in today’s world as people search for environmentally-friendly alternatives to gasoline-powered engines. But did you know that the concept of an electric car dates back to the mid-19th century? With the emergence of new technologies and a desire to reduce emissions, electric cars have seen a resurgence in popularity. In this History of Electric Cars Timeline, we take a look at how this mode of transportation has evolved over the years, from its early beginnings to its current state of innovation.
So, strap in and let’s explore the electrifying journey of the electric car!
Early Development
The history of electric cars timeline dates back to the early 19th century when inventors first began experimenting with electric engines. In 1837, a Scottish chemist named Robert Davidson built the first electric locomotive, which ran on a track on a local road. Later, in the 1850s, French physicist Gaston Plante invented the lead-acid battery, which was the primary power source for electric cars for many years.
The first low-speed electric car, the Riker Electric, was invented in 1896 by Andrew Riker, an American electrical engineer. However, it wasn’t until the turn of the 20th century that electric cars rose in popularity, particularly for urban transportation. By 1900, there were about 2,000 electric cars registered in the United States.
Unfortunately, advancements in gasoline-powered cars and the discovery of oil in the United States led to the decline of electric cars. It wasn’t until the 1960s, during the oil crisis, that electric cars saw another resurgence in popularity.
1832-1839: First electric vehicle built
The early 1830s saw the first steps towards the development of electric vehicles. In 1832, Scottish inventor Robert Anderson built the first electric carriage, which was powered by non-rechargeable cells. That same year, Thomas Davenport, an American inventor, built a small electric car powered by a battery.
In 1835, Professor Sibrandus Stratingh of Groningen, the Netherlands, and his assistant Christopher Becker developed a small electric car that was powered by primary batteries. The vehicle could carry four people and reach a speed of around 15 kilometers per hour. In 1839, Scottish inventor Robert Davidson built an electric carriage that was powered by a galvanic cell.
The vehicle was capable of carrying up to six passengers and was used to transport goods and passengers between Edinburgh and Glasgow. These early electric vehicles were crude in design, but their invention paved the way toward developing more sophisticated and efficient EVs in the future.

1859: Gaston Planté invented rechargeable lead-acid battery
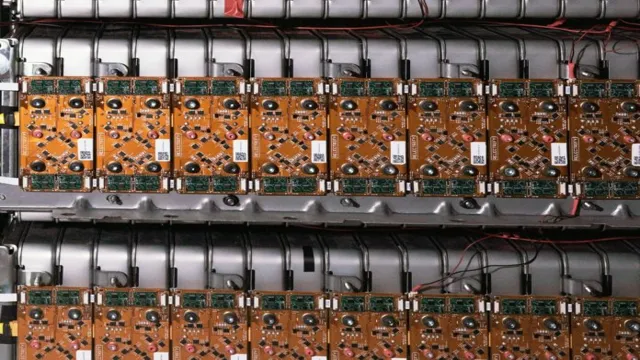
In 1859, Gaston Planté revolutionized energy storage forever by inventing the first rechargeable lead-acid battery. This invention paved the way for modern technology, powering everything from cars to cell phones. While Planté’s battery was not the first storage technology, it was one of the most significant for early energy storage development.
The battery worked by using lead plates submerged in an acid solution, which could be recharged by reversing the electrical current. This allowed for the battery to store electricity and use it again, making it a game-changer in energy storage. Although the early lead-acid batteries were bulky and had low energy density, they marked the beginning of a new era of energy storage technology.
Today, millions of rechargeable lead-acid batteries power a plethora of devices and systems, solidifying their legacy in energy storage technology.
1900s-1990s: Rise and Fall of Electric Cars
The 1900s saw the rise of electric cars as they became more popular due to their quiet operation and easy maintenance. They were the preferred vehicles for short trips and were used by doctors, postal workers, and even milkmen. However, the invention of mass-produced gasoline cars in the early 1900s led to the decline of the electric car industry.
By the mid-1920s, electric vehicles were nearly extinct as gasoline engines gained dominance due to their longer range and ease of refueling. The oil crisis of the 1970s sparked renewed interest in electric cars, and companies like General Motors and Ford started experimenting with prototypes. However, the high production costs and lack of infrastructure for charging stations made them impractical.
It was not until the late 1990s that electric cars started making a comeback, with companies like Toyota and Tesla developing more affordable models and improving battery technology. Today, electric cars are becoming more popular than ever as concerns about climate change and sustainability continue to grow.
1908-1912: Electric cars made up 38% of U.S. cars
In the early 1900s, electric cars were all the rage, making up a whopping 38% of all cars in the United States between 1908-191 People saw the potential in electric cars, with their quiet engines and lack of fumes, as a more environmentally-friendly and convenient mode of transportation compared to their steam and gasoline counterparts. However, as time went on and the demand for longer range and faster speeds grew, electric cars fell out of favor.
The rise of gasoline-powered cars, which had more efficient engines and the ability to refuel on the go, pushed electric cars to the sidelines for decades. Not until recent advances in battery technology and environmental concerns about fossil fuels did electric cars start to make a comeback. Now, electric cars are starting to become a more common sight on the roads, proving that everything old can become new again with the right technology and innovation.
1970s-1990s: Low demand for electric cars due to low gas prices
The 1970s to 1990s saw a dip in demand for electric cars, largely due to low gas prices. This period marked both the rise and fall of electric cars in the automobile industry. In the early 1900s, electric cars were quite popular for their silent operation and lack of fumes.
However, internal combustion engine cars soon took over due to cheaper gas prices and longer driving ranges. It wasn’t until the 1970s, during the oil crisis, that electric cars saw a resurgence in interest. However, once gas prices dropped back down, the demand for electric cars dwindled once again.
Despite advancements in electric car technology, such as longer driving ranges and improved battery life, they were still largely seen as impractical and expensive alternatives to gasoline-powered vehicles. It wasn’t until the 2000s that demand for electric cars once again began to rise, with consumers becoming more conscious of their impact on the environment and oil prices once again fluctuating. Today, electric cars have become more mainstream, with major car manufacturers producing models of their own.
21st Century: Resurgence of Electric Cars
The history of electric cars timeline goes back to the early days of automobiles, when electric vehicles were the norm. However, the rise of gasoline-powered engines led to a decline in electric cars by the 1920s. It wasn’t until the late 20th century that electric cars saw a resurgence.
In the 1990s, advancements in battery technology allowed for the development of more practical electric cars. This led to the first modern electric car, the GM EV1, in 199 However, it was short-lived, and production was halted in 200
It wasn’t until the early 2010s that electric cars once again gained momentum, with the introduction of the Nissan LEAF and Tesla Model S. Today, electric cars are becoming more affordable and practical for everyday use, and with the push for environmentally friendly transportation options, it’s likely that electric cars will continue to grow in popularity.
2008-2012: Electric cars make a comeback with Tesla Roadster
The years 2008 to 2012 saw a resurgence in electric cars, all thanks to the Tesla Roadster. The Roadster was a game-changer as it offered an impressive 245 miles per charge, something unheard of in the EV market. The success of the Roadster paved the way for Tesla’s other models and sparked a wave of interest in electric vehicles.
The market was booming, and other automakers like Nissan, Chevrolet, and BMW soon followed suit with their own electric models. However, it wasn’t just the range that made the Roadster a hit. Its sleek design and outstanding performance also caught people’s attention.
The car was quick, silent, and had no emissions, making it both efficient and environmentally friendly. It was clear that the electric car had come a long way since the days of the GM EV1, and Tesla had made a significant impact on the automotive industry. As we enter the new decade, electric cars seem to be the future of mobility, and it’s exciting to see what innovations will come next.
2010s-present: Increase in popularity of electric cars with more models available
Electric cars have become increasingly popular in the 21st century due to a range of factors, including advancements in technology, growing concern about the environment, and changing consumer preferences. The availability of more electric car models, such as the Tesla Model S and Nissan Leaf, has also played a significant role in driving their resurgence. These cars are powered by batteries that can be recharged through an electric grid, making them a sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Not only are they better for the environment, but they also offer a smoother and quieter driving experience. Additionally, as more charging stations are added to public places and driving range extends, electric car owners can feel more confident about traveling longer distances. With these benefits in mind, it’s no surprise that electric cars are quickly becoming a more practical and attractive option for drivers looking for a more sustainable future.
Future of Electric Cars
Looking back at the history of electric cars timeline, it’s fascinating to see how far we’ve come. The very first electric car was built in the late 1800s, but they didn’t become popular until the late 1900s and early 2000s. This is when car companies like Tesla began producing electric cars that were more affordable, had longer ranges, and were more reliable than previous models.
Today, we’re seeing a shift towards electric cars being the norm, with more and more car companies investing in electric technology. Not only are electric cars better for the environment, but they’re also more cost-effective in the long run. As technology continues to advance and more people make the switch to electric, we can only imagine what the future will hold.
Perhaps we’ll see even longer ranges, faster charging times, and even more affordable prices. One thing’s for sure: the future of electric cars looks bright.
Continued growth with advancements in technology and government incentives
The future of electric cars looks bright with continued advancements in technology and government incentives. As more and more people become environmentally conscious, the demand for electric cars is expected to rise sharply. The production of cars that run on electricity has gone up significantly in recent years, thanks to the rapid progress in battery technology.
In addition to this, governments are offering tax incentives and other benefits to people who choose to purchase electric cars. This has made it easier for many people to switch to electric cars without worrying about the higher initial cost. As a result, electric cars are becoming more mainstream, and we can expect this trend to continue in the coming years.
With the development of better and cheaper batteries and the continuous support of governments, the future of electric cars looks promising. It won’t be long before we have eco-friendly cars on most of our roads, promoting a cleaner and healthier environment for everyone.
Conclusion
Looking back on the history of electric cars, it’s clear that they’ve come a long way. From early experiments in the 1800s to the modern, sleek electric vehicles of today, electric cars have constantly evolved and improved. While some may argue that they’re still not quite as widespread as gas-powered vehicles, it’s hard to deny that they’re getting there.
And as we continue to explore new ways to power our transportation, it’s safe to say that electric cars will play an increasingly important role in our lives. Who knows what the future holds – but one thing’s for sure, electric cars are definitely on the rise.”
FAQs
When was the first electric car invented?
The first electric car was invented in 1828 by Ányos Jedlik, a Hungarian inventor.
When did electric cars become popular?
Electric cars gained popularity in the 2000s, with the launch of hybrid electric vehicles like the Toyota Prius and fully electric vehicles like the Nissan Leaf.
What is the current state of the electric car industry?
The electric car industry is rapidly growing, with major car manufacturers like Tesla and GM investing heavily in electric vehicle production.
What are the benefits of electric cars?
Electric cars have lower emissions, are more efficient, and have lower operating costs compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. They are also more environmentally friendly and reduce our dependence on oil.