The Shocking Journey of the First Electric Car: Exploring Its Revolutionary History
Electric cars are taking the world by storm. With increasing concerns over climate change and a shift towards sustainable living, electric cars have become a popular choice for drivers worldwide. But did you know that the first electric car was invented over 100 years ago? The history of the first electric car is a fascinating journey that dates back to the 1800s.
From the invention of the first electric vehicle to the development of modern-day electric cars, electric vehicles have come a long way. In this blog post, we’ll explore the history of the first electric car and how it paved the way for the electric cars we know and love today. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s dive in!
Invention and Early Development
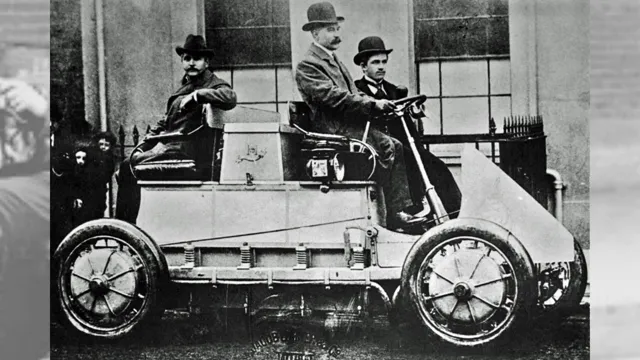
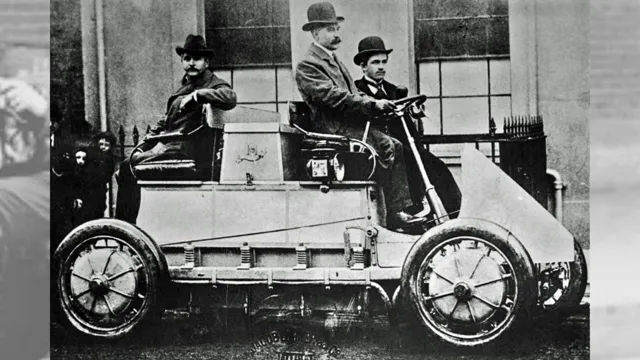
The first electric car was invented in the mid-19th century by Thomas Davenport, a Vermont blacksmith. He created a small-scale electric-powered vehicle that ran on a primitive battery, proving the concept of electric propulsion. However, it wasn’t until the early 20th century that electric cars began to make a significant impact.
In 1897, the Electric Vehicle Company in New York City introduced the first commercially successful electric car. Known as the Columbia Electric, it had a range of 40 miles and a top speed of 15 miles per hour. It was marketed primarily to women due to its ease of use and lack of the noxious fumes that gasoline cars produced at the time.
The electric car’s popularity continued to grow and by the early 1900s, electric cars made up approximately one-third of all cars on the road in the United States. However, the popularity of gasoline-powered cars and the discovery of vast oil fields led to a decline of electric cars in the early 1920s. It wasn’t until the oil crisis of the 1970s that electric cars would begin to re-emerge as a viable alternative to gasoline-powered cars.
Intro to 19th Century Electric Cars
Electric cars have come a long way since their inception in the late 19th century. The first electric vehicles (EVs) were invented in the mid-1800s and were mainly used for short trips in urban areas. Robert Anderson created the first crude electric carriage in Scotland in 1832, and Thomas Davenport invented the first electric car in 183
The main breakthrough in EV development, however, came in 1859 when French physicist Gaston Planté invented the lead-acid battery. This made it feasible to produce a vehicle that would run efficiently and effectively on electric power alone. In the late 1800s, electric cars were marketed primarily to women as they were quiet, easy to operate, and required no strenuous hand-cranking to start.
Despite their initial success, internal combustion engines soon became the dominant technology for cars, and electric cars were all but forgotten for a century. However, the 21st century has seen a resurgence of electric vehicles, as a cleaner and more sustainable transport option.

Creation of the First Electric Car Prototype
The creation of the first electric car prototype was a major breakthrough that revolutionized the automotive industry. The inception of electric cars can be traced back to the early 1800s, but it wasn’t until the late 1800s that a viable electric car prototype was invented. The first electric vehicle was designed and built by Thomas Parker in London in 188
Parker was a British inventor and engineer who had previously worked on tram systems, and he saw the potential of electric vehicles for transportation. His prototype had a top speed of 14 miles per hour and could travel up to 40 miles on a single charge. His innovative design included rechargeable batteries that could be easily swapped out, ensuring that the car was usable for extended periods.
Although initially slow to gain widespread popularity, the creation of the first electric car prototype paved the way for the development of modern electric vehicles and continues to inspire innovation in the industry today.
Inventors and Innovators Involved
The invention and early development of the telephone was a collaborative effort by multiple innovators and inventors. The idea of a device for transmitting sound over long distances dates back to the early 1800s. However, it was Alexander Graham Bell who is credited with inventing the first practical telephone in 187
Bell was assisted by Thomas Watson, his assistant, in building the first prototype of the telephone. The initial model, known as the “liquid transmitter,” used a needle to transmit sound vibrations. This technology was later replaced by the “carbon transmitter,” which was more efficient and effective.
Bell’s invention quickly gained popularity and soon became a global phenomenon, resulting in the establishment of the first telephone exchange in New Haven in 187 Other inventors who made significant contributions to the early development of the telephone included Elisha Gray, Thomas Edison, and Antonio Meucci, among others. Their inventions and innovations helped improve the telephone’s sound quality, reliability, and range.
Overall, the invention and early development of the telephone was a result of the collective effort of various inventors and innovators, each putting their unique skills and knowledge to work.
Commercialization and Modernization
The history of the first electric car dates back to the late 1800s when inventors were experimenting with electricity as a means of powering vehicles. While Thomas Parker, a British inventor, is often credited with creating the first electric car, there were actually several inventors around the world working on similar projects simultaneously. By the early 1900s, electric cars were popular for short distance travel, particularly in cities where their lack of noise and pollution made them more favorable than gasoline-powered cars.
However, as the 20th century progressed, the convenience and availability of gasoline made it the preferred fuel source, and electric cars fell out of favor. Today, we find ourselves in a similar situation, with electric cars slowly gaining popularity again due to concerns over air pollution and climate change. The commercialization and modernization of electric cars offer an exciting opportunity to reduce our carbon footprint and transition to a more sustainable future.
Emergence of Practical Electric Cars
The emergence and commercialization of practical electric cars are one of the most significant technological advancements in recent years. With rising concerns over climate change and the need for more sustainable modes of transportation, electric cars are paving the way for a cleaner future. Modern electric cars offer a range of benefits, including reduced emissions, improved fuel efficiency, and lower maintenance costs.
They are also becoming increasingly affordable and accessible, with several established automakers, such as Tesla, Nissan, and BMW, investing heavily in the development of practical electric cars. The increasing modernization and commercialization of these vehicles are making them a more practical and viable option for everyday consumers. As more people are switching to electric cars, it is becoming clear that they have the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry and significantly impact our environment positively.
Early Electric Car Manufacturers and Models
The early days of commercialized electric cars saw a variety of manufacturers and models emerge onto the scene. These vehicles were often used for local travel, with batteries that needed frequent charging. However, the market for electric cars collapsed in the early 20th century as gasoline-powered vehicles became more popular due to their greater range and power.
In recent times, however, electric cars have been making a comeback in popularity due to concerns about climate change, environmental pollution and sustainability. With modern advancements in battery technology, electric cars are now able to travel further distances and offer more power than ever before. Many major automakers now produce electric car models alongside their traditional gas-powered ones, and the future of the electric car industry looks bright.
Decline and Resurgence of Electric Cars
The decline and subsequent resurgence of electric cars have been nothing short of extraordinary. Many factors have contributed to this phenomenon, including advances in technology and increased environmental awareness. However, it is the commercialization and modernization of electric vehicles that have truly made a difference.
Companies such as Tesla have revolutionized the concept of electric cars, showcasing how they can be a sleek and stylish option for drivers. In addition, the widespread availability of EV charging stations has made electric vehicles a more practical choice. Moreover, governments worldwide are mandating stricter emissions regulations, further incentivizing the shift to electric cars.
It is an exciting time for the automotive industry, and electric cars are at the forefront of this transformation. The question now is not whether electric vehicles will become mainstream, but when.
Impact and Future of Electric Cars
The history of the first electric car dates back to the 1830s, when Robert Anderson of Scotland built the first electric carriage. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s when electric vehicles (EVs) become more common in cities, especially among wealthier individuals. In fact, by the turn of the century, EVs made up around a third of all vehicles on the roads.
However, the Model T Ford’s success and the growth of gasoline-powered cars resulted in the decline of electric vehicles’ popularity. Fast forward to the present day, and electric vehicles are enjoying a resurgence thanks to advancements in technology and concerns over climate change. Major automakers such as Tesla, General Motors, and Ford are investing heavily in EVs as consumers demand more eco-friendly options.
As technology continues to improve, it’s likely that EVs will become even more widespread, with some speculating that they may eventually replace gas-powered cars altogether.
Environmental and Economic Benefits of Electric Cars
Electric Cars Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular due to their environmental and economic benefits. They produce fewer emissions compared to gasoline-powered cars, which helps reduce air pollution and combat climate change. Electric cars also have lower operating costs and require less maintenance than traditional gas vehicles.
Overall, they are cheaper to operate and can save drivers a significant amount of money in the long run. Despite the initial cost of purchasing an electric car being higher than a gas-powered vehicle, government incentives and tax rebates can help offset the expense. Additionally, as more people switch to electric cars, the demand for electric battery technology is increasing.
This means that prices are likely to decrease in the future, making electric cars more accessible to a wider range of consumers. With advancements in technology and more focus on sustainability, the future looks promising for electric cars and their positive impact on the environment and economy.
Advancements and Challenges in Electric Car Technology
Electric cars have come a long way since they were first introduced in the market. With continuous advancements in technology, electric vehicles have become more popular than ever before. One of the biggest benefits of electric cars is their lower carbon footprint, making them an excellent alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles.
Additionally, they are cheaper to run and maintain, providing long-term savings for drivers. However, there are still some challenges faced by electric car technology, such as limited driving range and the lack of charging infrastructure. Despite these obstacles, the future looks bright for electric cars, as more and more companies are investing in their development.
In the coming years, advancements such as fast charging, higher capacities, and longer driving ranges are likely to become commonplace. The impact of electric cars on the environment and our daily lives is significant and will only continue to grow. As more people embrace eco-friendly alternatives, electric cars will play a crucial role in reducing our carbon footprint and building a sustainable future for all.
Conclusion
And with that, we come to the end of our journey through the history of the first electric car. From its humble beginnings as a glimmer of an idea in the minds of inventors like Thomas Davenport and Robert Anderson, to the modern day electric vehicles that silently zoom past us on our daily commutes, the electric car has certainly come a long way. Along the way, it has weathered its fair share of setbacks, controversies, and competing technologies, but through it all, its proponents have continued to push forward, driven by a vision of a cleaner, more sustainable future for us all.
Whether you’re a die-hard fan of the electric car or still firmly rooted in the internal combustion engine camp, there’s no denying that the history of the first electric car is a fascinating tale of human ingenuity and innovation.”
FAQs
What was the first electric car ever invented?
The first electric car was invented in 1837 by a Scottish inventor named Robert Anderson.
When did the first mass-produced electric car become available?
The first mass-produced electric car, the Baker Electric, became available in 1899.
What was the driving range of the first electric cars?
The earliest electric cars had a maximum driving range of between 30 and 50 miles.
When did electric cars first start to gain popularity?
Electric cars were popular in the early 20th century, but by the 1920s they had been largely supplanted by gasoline-powered cars.
What advancements have been made in electric car technology since the early days?
Modern electric cars have much longer driving ranges than their early counterparts, with ranges of over 200 miles becoming increasingly common. Additionally, advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure have made electric cars much more practical for everyday use.