The Shocking History of Battery-Only-Powered Cars: Unveiling the Rise of Electric Automobiles [PDF]
Electric car batteries have been at the forefront of discussions on sustainable energy and transportation in recent years. But did you know that the history of electric car batteries dates back much further? In fact, the concept of storing electrical energy for transportation dates back to the 1850s, when rechargeable lead-acid batteries were first invented. These early batteries were heavy, cumbersome, and had limited range, but they laid the groundwork for the development of modern electric car batteries.
Over the years, electric car batteries have gone through a series of improvements, from nickel-iron batteries in the early 1900s to the more familiar nickel-cadmium and lithium-ion batteries of today. The introduction of lithium-ion batteries in the 1990s was a game-changer, as they offered significantly improved energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging times. The evolution of electric car batteries has enabled the widespread availability and adoption of electric vehicles, which have become increasingly popular due to their lower carbon emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Today, manufacturers are continuing to push the boundaries of battery technology, exploring new materials and designs that promise to make electric cars even more efficient and practical for everyday use. As we look to the future of electric cars and renewable energy, it’s important to remember the rich history of electric car batteries and the constant innovation that has led us to where we are today.
Early Days of Electric Cars
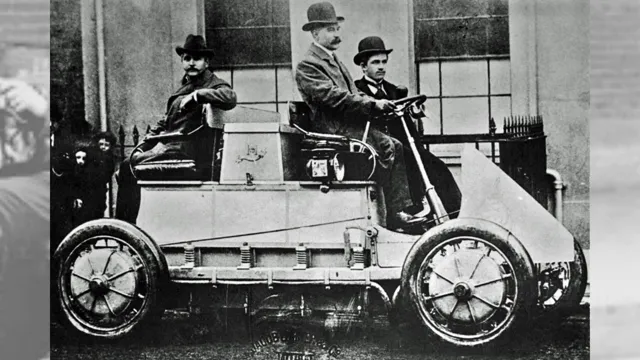
The history of electric cars dates back to the early 19th century when inventors started experimenting with battery-powered vehicles. After several prototypes, Thomas Davenport built the first American electric car in 183 These early electric cars were slow, expensive, and suffered from range anxiety due to battery limitations.
However, in the late 1800s, with the advent of improved battery technology, electric cars gained popularity as a reliable means of transportation, particularly in cities. By 1900, electric vehicles accounted for one-third of all cars on the roads in the US. But with the widespread availability of gasoline and the low cost of petroleum-based products, electric cars gradually lost their appeal.
Nonetheless, the resurgence of electric vehicles in the 21st century reflects the viability and sustainability of battery-only powered cars. The future of electric cars is bright as modern technology continues to improve, and concerns over climate change and environmental protection are driving demand for eco-friendly transportation alternatives.
1. The Birth of the Electric Car
The concept of electric cars is not a new one, with the earliest versions dating back to the 1800s. In fact, the first electric car was built in 1837 by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric cars started to become more common on the roads.
At the time, these vehicles were often used as city taxis because they were quiet, produced no emissions, and were easy to drive. However, the limited battery technology of the time meant that electric cars couldn’t travel very far or at high speeds. Despite this, electric cars continued to gain popularity, with many notable figures, including Thomas Edison and Henry Ford, expressing interest in the technology.
It wasn’t until the 1920s, with the invention of the electric starter, that gasoline-fueled cars began to dominate the market. However, the early days of electric cars laid the foundation for the modern-day electric vehicles that we see today. As companies continue to innovate and improve upon battery technology, we may see a shift back towards more eco-friendly modes of transportation.

2. Davis and Other Electric Cars
In the early days of electric cars, the Davis Electric was one of the most popular models on the market. The company was founded in 1892 by Harvard professor S. S.
Davis, and their vehicles were designed to be perfect for city driving. While the Davis Electric had a top speed of just 20 miles per hour, it had a range of up to 100 miles per charge, making it an ideal choice for urban commuters. But the Davis Electric wasn’t the only electric car on the road in those days.
Baker Electric and Detroit Electric were two other popular brands, with the latter even boasting a famous spokesperson in the form of actress Clara Ford, wife of car manufacturing magnate Henry Ford. Despite their early popularity, however, electric cars struggled to maintain their foothold in the market as gasoline-powered cars became more prevalent. By the early 1920s, almost all electric car manufacturers had gone out of business, leaving gasoline-powered cars as the dominant force in the automotive industry.
It would take more than a century before electric cars were able to make a comeback, thanks in part to advances in technology and growing concerns about climate change.
3. The Impact of the Edison Battery
The early days of electric cars were heavily influenced by the invention of the Edison battery. This innovation allowed for the creation of more practical and efficient electric vehicles that could compete with their gasoline counterparts. The impact of the Edison battery was immense, as it allowed electric cars to have longer ranges and greater speeds, making them a more viable option for everyday use.
In fact, the first electric taxis in New York City were powered by the Edison battery in the early 1900s. With the increased popularity of electric cars, there was a growing demand for more efficient batteries that could provide even longer ranges. This led to the development of new types of batteries, such as the lead-acid battery, which became the standard for electric vehicles for many years.
While the Edison battery may no longer be the dominant technology in the world of electric cars, its impact on the early days of this industry cannot be overstated.
Post-War Period
The post-war period brought a resurgence of interest in electric cars powered solely by batteries. People were looking for more efficient, cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to gasoline-powered vehicles. In the 1960s, electric cars began to be produced on a larger scale by companies like General Motors and Citroen.
However, the batteries used at the time were heavy and expensive, making electric cars less practical and more expensive than their gas-guzzling counterparts. Moreover, the battery technology did not improve much until the late 1990s when research and development of lithium-ion batteries began. Lithium-ion batteries revolutionized the electric car market by offering higher energy density and longer life spans.
They also became more affordable, which encouraged more consumers to purchase battery-powered cars. Nowadays, electric cars have become increasingly popular and accessible, with many major car manufacturers investing in their production and development. The history of the electric automobile battery-only powered cars pdf has been one of innovation, finding ways to make electric cars more efficient and practical for everyday use.
1. The Rise of Oil-Driven Cars
During the post-war period, the world saw a rapid and significant rise in the popularity of oil-driven cars. Cars became more affordable and accessible to the general public, and with the discovery of new oil reserves and the rise of oil companies, fuel became relatively cheap. This led to a surge in car ownership, as people were able to travel more easily and comfortably than ever before.
The iconic American 1950s “gas-guzzler” was born, representing not just a way to get around but also a symbol of success and freedom. However, as we now know, this dependence on oil has led to a host of environmental problems, from air pollution to climate change. We must now work towards finding sustainable alternatives to petrol and diesel-powered vehicles to ensure a more sustainable future for us and our planet.
2. Electric Cars in the UK
In the post-war period, electric cars began to make an appearance on the roads of the UK. A notable example was the G-Wiz, an electric car that was imported from India in 200 Although it received criticism for its lack of safety features, the G-Wiz was embraced by environmentally conscious consumers who were looking for a car that emitted zero emissions while driving.
The post-war period also saw the development of electric cars by major automobile manufacturers, such as the Nissan Leaf and the BMW i These cars offered better safety features and a longer driving range, which made them more practical for everyday use. However, they were still relatively expensive compared to their petrol-powered counterparts, which limited their appeal to a niche market.
Despite this, the popularity of electric cars in the UK continued to grow throughout the 2010s, with more and more people looking for ways to reduce their carbon footprint. Today, electric cars are becoming more commonplace on UK roads, and the government has set a target for all new cars to be zero-emissions by 2030.
Modern Times
The history of the electric automobile battery-only powered cars pdf is fascinating. In the early 1800s, electric cars were invented, with their main source of power being the battery. However, the batteries used were heavy and had limited range, making them less practical for everyday use.
It wasn’t until the late 1800s that improvements in battery technology were made, allowing for longer driving distances. In the early 1900s, electric cars were popular, but with the advent of the gasoline-powered engine, they lost popularity. Fast forward to the modern era, and we are seeing a resurgence of interest in electric cars powered by more efficient, lighter weight batteries.
With the growing concern over climate change, there is a renewed push towards reducing emissions in transportation, and the battery-only electric car is poised to play a significant role in that effort. As battery technology continues to advance, and electric cars become more affordable, it’s expected that we will see a significant increase in the number of people switching to electric cars as their primary mode of transportation.
1. The Emergence of Modern Lithium-ion Batteries
Modern Lithium-ion Batteries The emergence of modern lithium-ion batteries revolutionized the world of technology. These batteries were first manufactured in the early 1990s by Sony Corporation and have since gained immense popularity due to their high energy density and long-term performance. Lithium-ion batteries are now used in a wide range of applications, from portable electronics like smartphones and laptops to electric cars and renewable energy storage systems.
With the growing need for clean energy, lithium-ion batteries have become an essential component in the fight against climate change. These batteries use lithium cobalt oxide, a chemical compound that allows for the storage and release of electrical energy. The development of modern lithium-ion batteries has been a game-changer in the field of technology, allowing for greater convenience, efficiency, and sustainability in our daily lives.
As technology continues to advance, so will the potential uses for these batteries, making them a vital part of our future.
2. The Rise of Tesla and Other Electric Vehicle Companies
Electric vehicles have been gaining momentum in recent times, with Tesla leading the way in the industry. As more people become aware of the impact of carbon emissions on the environment, they are opting for EVs over traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Tesla has been at the forefront of this revolution with their line of sleek and innovative electric vehicles that offer high performance and long range capabilities.
Other companies such as Nissan, BMW, and Chevrolet have also entered the market with their own versions of electric vehicles. The rise of EVs has been driven by advances in technology, government incentives, and a growing awareness of the environmental impact of conventional transportation. With more companies investing in electric vehicles, it is clear that the trend is here to stay.
As our world becomes more dependent on sustainable energy sources, electric vehicles will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of transportation.
The Future of Electric Car Batteries
The history of electric car batteries dates back to the 1800s, with a gradual evolution in technology leading to the batteries we use today. While the early batteries were bulky and inefficient, advancements in chemistry and physics paved the way for modern lithium-ion batteries that power most electric cars on the market. These batteries are highly efficient and have a better power-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for electric cars.
The future of electric car batteries, however, lies in further advancements in technology, with a focus on increasing their energy density and reducing the cost of production. This will not only make electric cars more accessible but also increase their range, making them a more viable option for long-distance travel. As the demand for clean energy alternatives continues to grow, we can expect to see more innovative solutions in the field of electric car batteries, making the shift towards sustainable transportation a reality.
1. Advancements in Battery Technology
The future of electric car batteries is bright with advancements in battery technology. The technology behind these batteries is constantly being improved to enhance their efficiency and increase their capacity. The use of solid-state batteries is one such advancement that promises to revolutionize the electric vehicle industry.
The use of solid-state batteries could eliminate many of the problems associated with traditional Li-ion batteries, such as their tendency to catch fire. Furthermore, solid-state batteries offer higher energy density, resulting in a longer driving range for electric cars. This means that the days of limited driving ranges for electric cars could soon be a thing of the past.
While the technology is still in its early stages, the potential for solid-state batteries is limitless, and the future of electric car batteries is looking brighter than ever.
2. The Role of Electric Cars in Tackling Climate Change
The future of electric car batteries looks very promising. With the push towards renewable energy and sustainability, the development of better and more efficient batteries is a top priority for car manufacturers. While current electric car batteries have come a long way, they still have some limitations such as their range.
However, the technology used in electric car batteries is constantly evolving, and innovations such as solid-state batteries have the potential to make electric cars more practical than ever before. This means that in the not-too-distant future, we may see electric cars with longer ranges and faster charging times. In fact, some experts predict that electric car batteries could eventually become so efficient that they will be able to power other devices in our homes.
Ultimately, the development of better electric car batteries is crucial for reducing carbon emissions and making sustainable transportation more accessible.
3. The Potential of Electric Cars for Lowering Energy Costs
Electric Car Batteries The future of electric car batteries is incredibly promising when it comes to lowering energy costs. Modern electric car batteries have greatly improved and increased in efficiency, boosting the potential of electric vehicles to revolutionize the automotive industry. With optimized energy storage, these batteries can cover longer distances, reducing the need for frequent charging.
Additionally, advancements in battery technology have made electric cars affordable and accessible to more consumers, promoting a cleaner and more sustainable future. The life cycle of an electric car battery has also been enhanced, providing longer durability and reduced maintenance costs. As technology continues to evolve, the future of electric car batteries will undoubtedly continue to improve, offering even greater performance, durability and reliability.
In conclusion, the potential of electric car batteries is immense, and these innovative technologies will continue to provide an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
Conclusion
In the history of the electric automobile, the battery-only powered cars have had their ups and downs. Despite facing obstacles like limited range and high costs in the past, they have continued to evolve with advancements in technology and infrastructure. Today, battery-only powered cars are a viable and practical option for eco-conscious individuals and a promising solution for reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change.
So let’s charge on towards a brighter, greener future with the electric vehicle battery at the forefront of our automotive revolution!”
FAQs
What is the history of the electric automobile?
The first electric cars were built in the 1800s, but they did not become popular until the development of the rechargeable battery in the 1900s.
What is a battery-only powered car?
A battery-only powered car, also known as a BEV (battery electric vehicle), is a type of electric car that uses only a rechargeable battery to power its motor.
What are the advantages of battery-only powered cars?
Battery-only powered cars have zero emissions, are quiet, and have lower operating costs than traditional gasoline-powered cars.
Where can I find a PDF on the history of the electric automobile battery?
A quick internet search will provide numerous options for PDFs on the history of the electric automobile battery, including academic papers and industry reports.